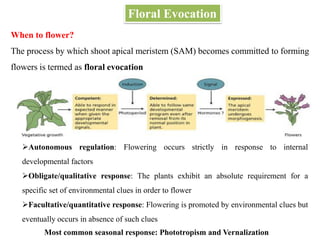
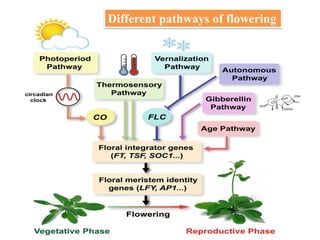
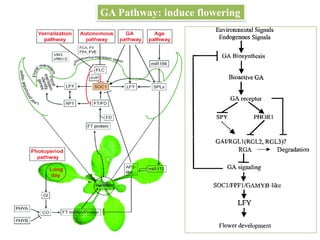
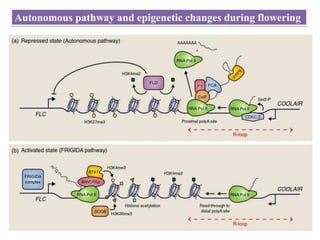
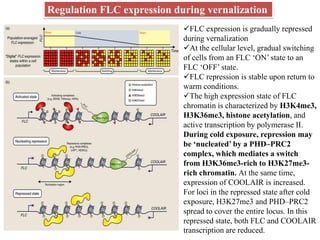
This document summarizes different mechanisms of floral evocation and flowering in plants. It discusses three types of flowering responses: autonomous, obligate, and facultative. Common seasonal cues include photoperiodism and vernalization. Flowering is regulated by microRNAs, circadian rhythms, photoperiod pathways, and genes such as FLC that promote or suppress flowering under different environmental conditions. Vernalization gradually represses FLC expression leading to an epigenetic switch from a flowering-suppressive to flowering-permissive state. COOLAIR non-coding RNA is involved in vernalization by facilitating histone modifications that stabilize FLC repression.