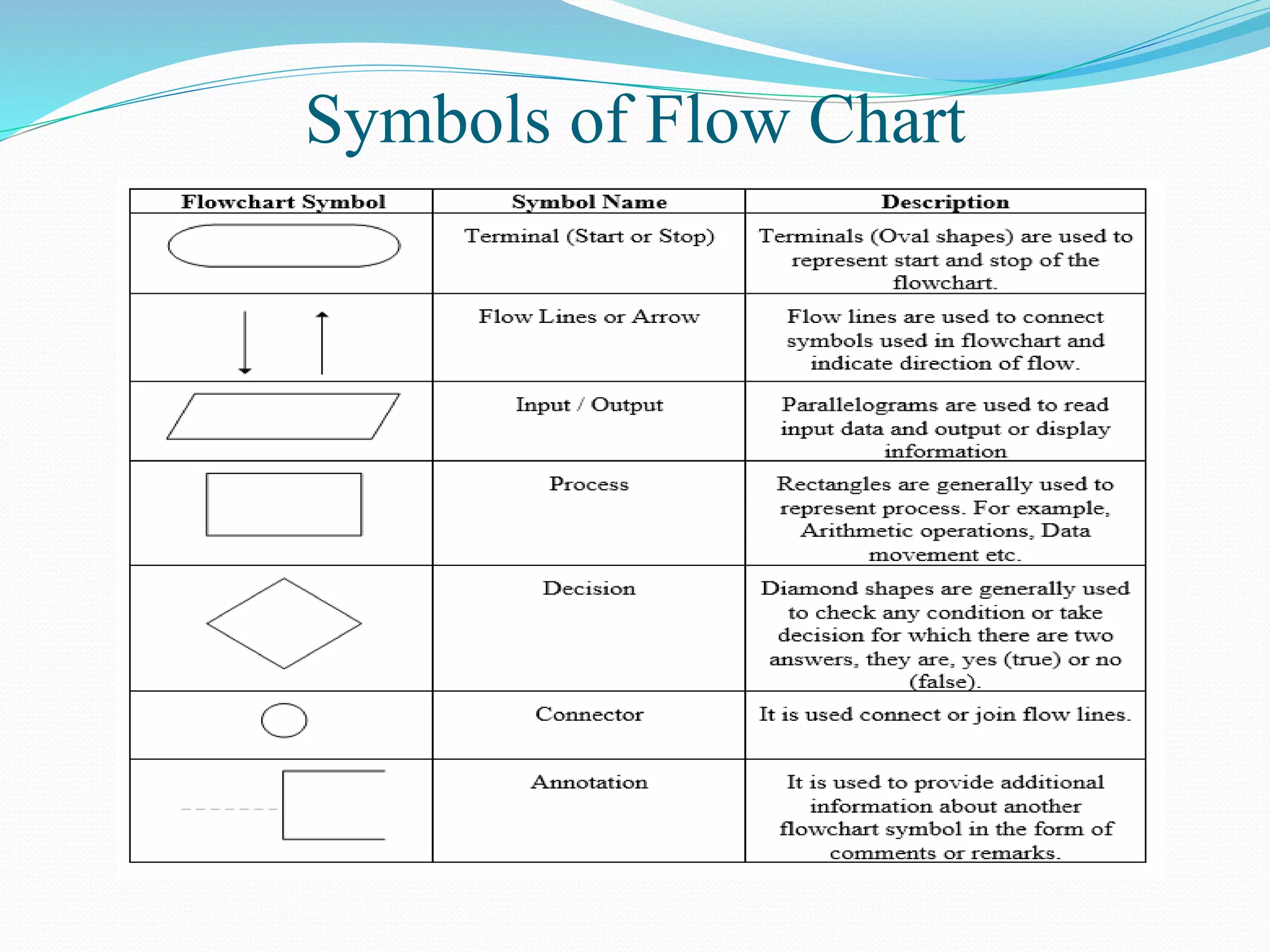
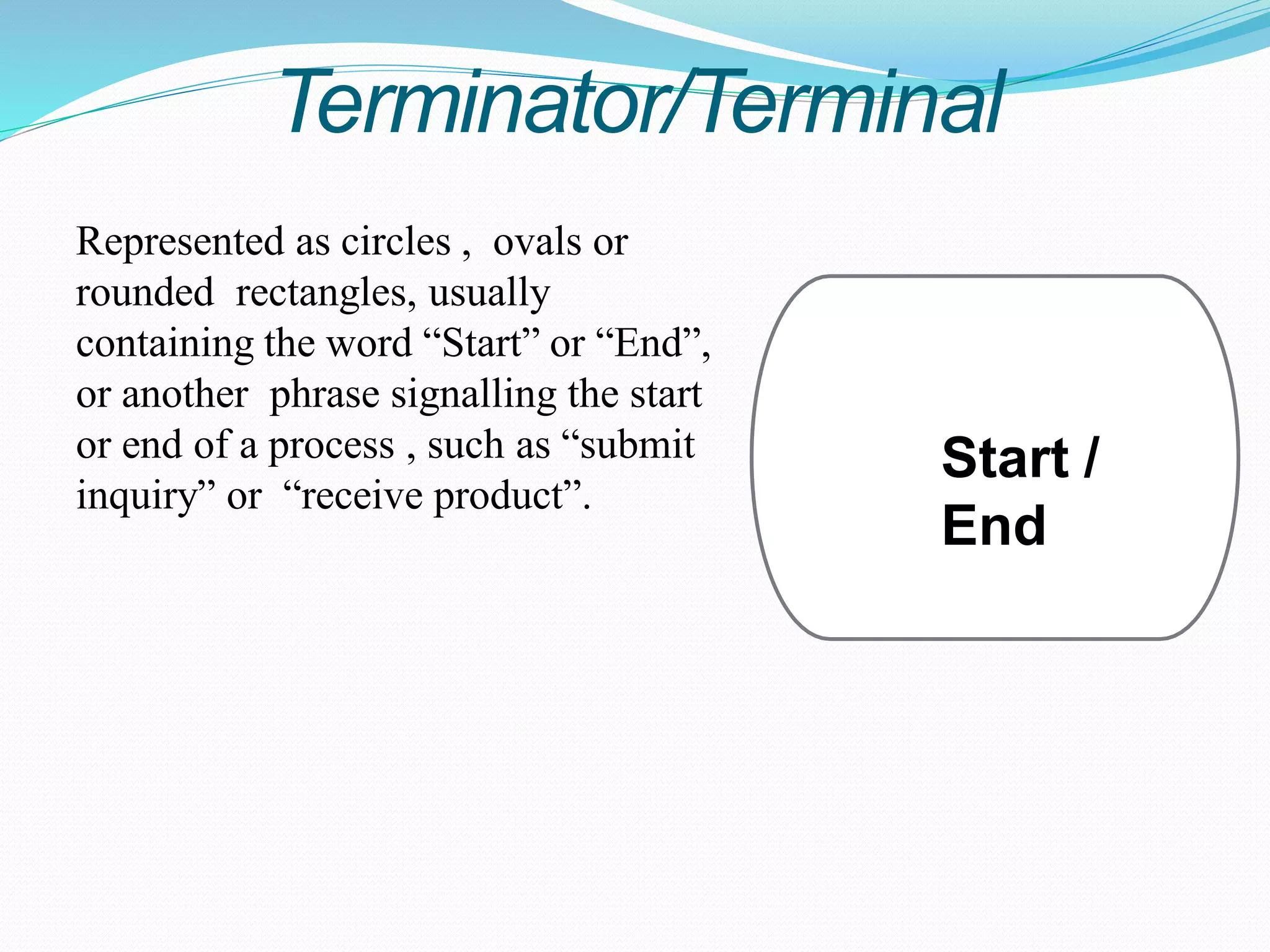
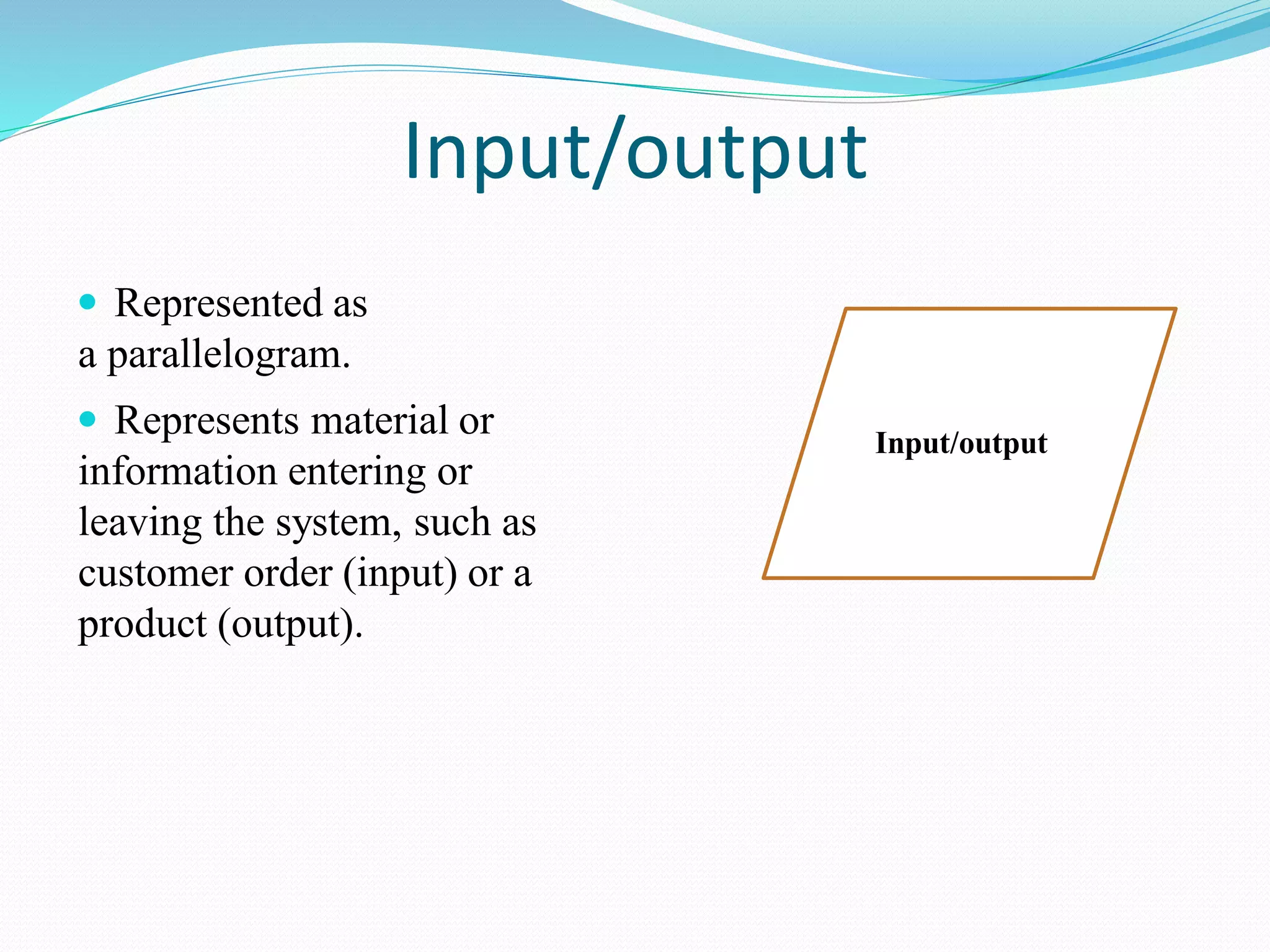
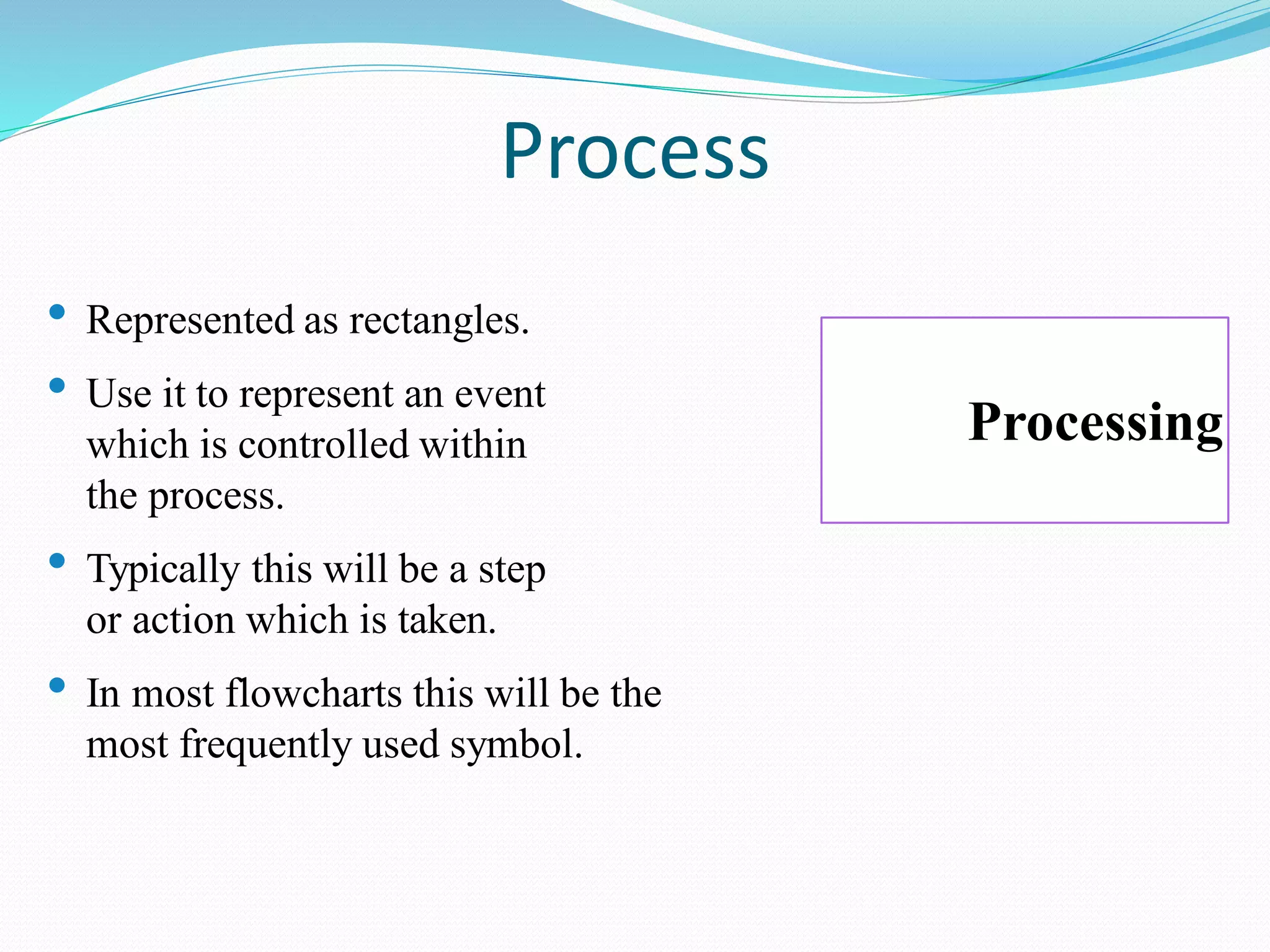
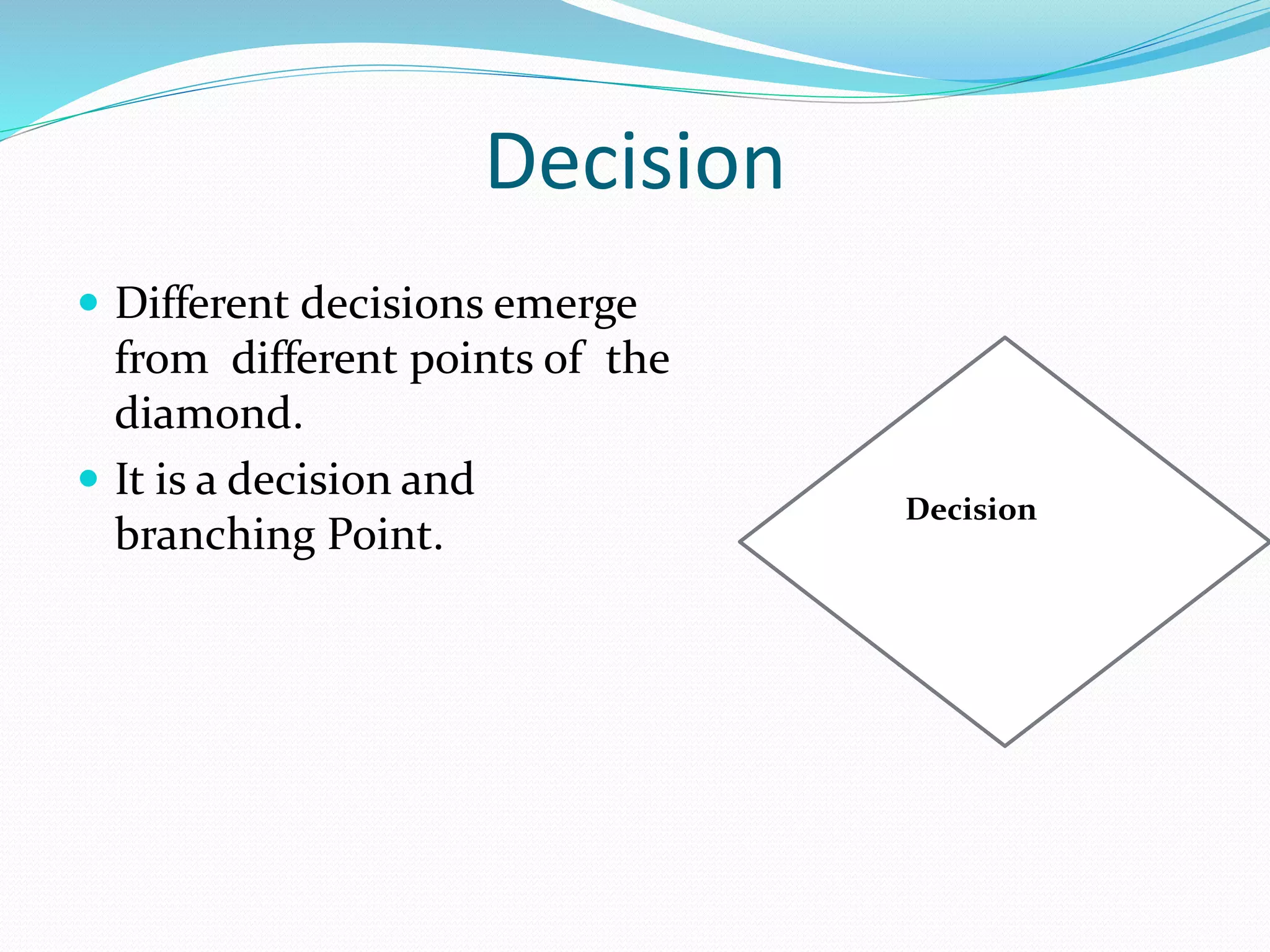
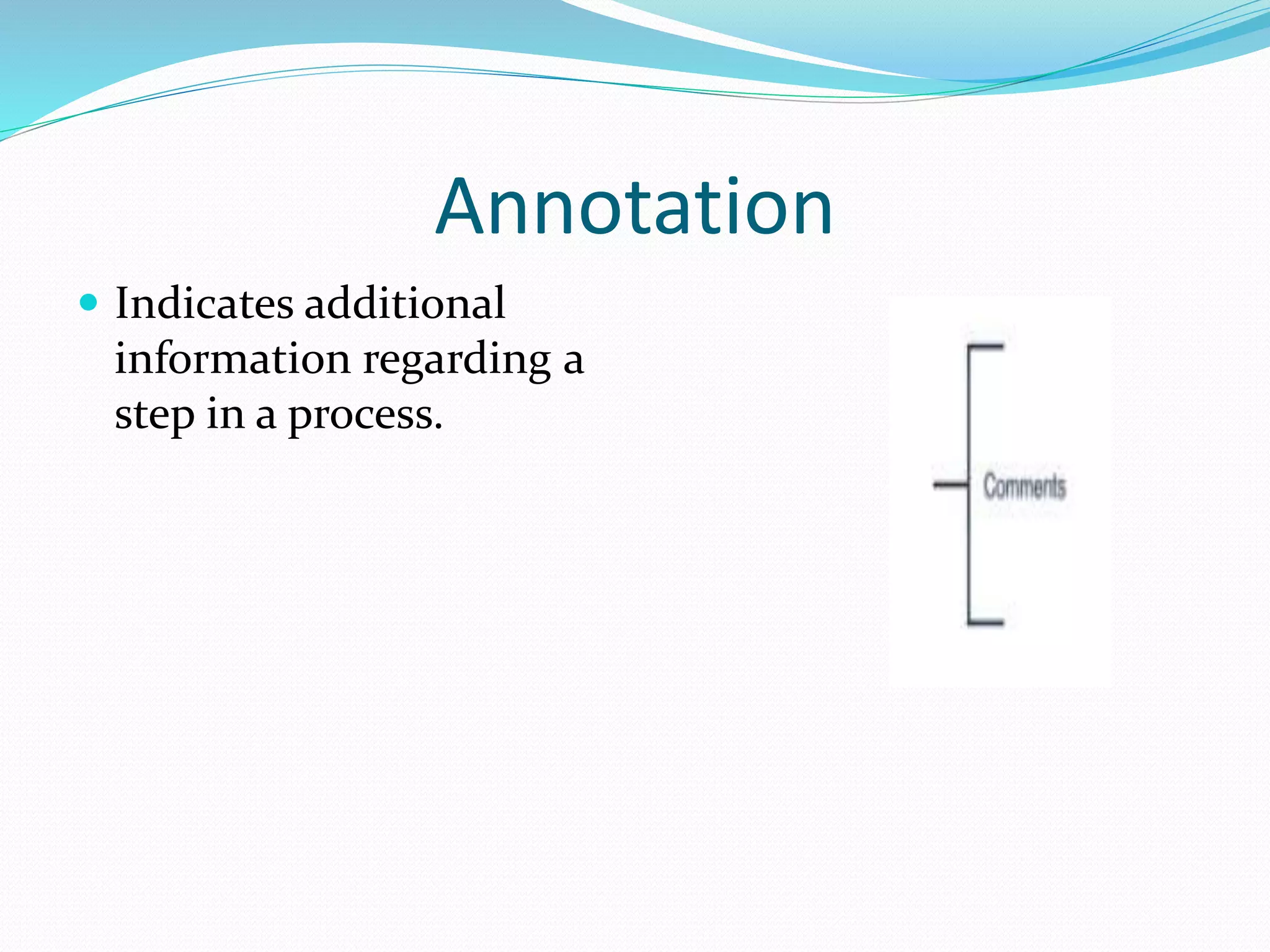
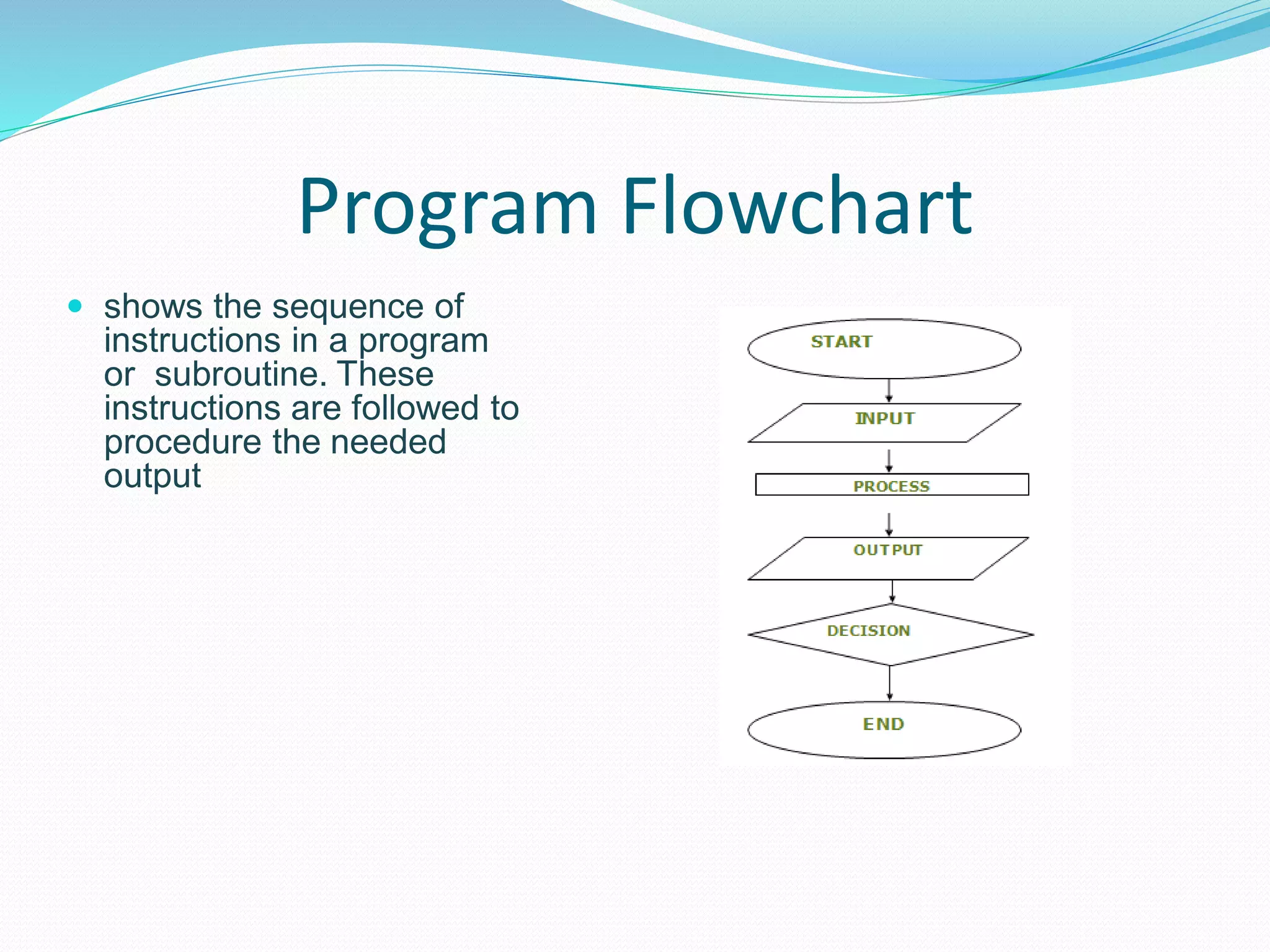
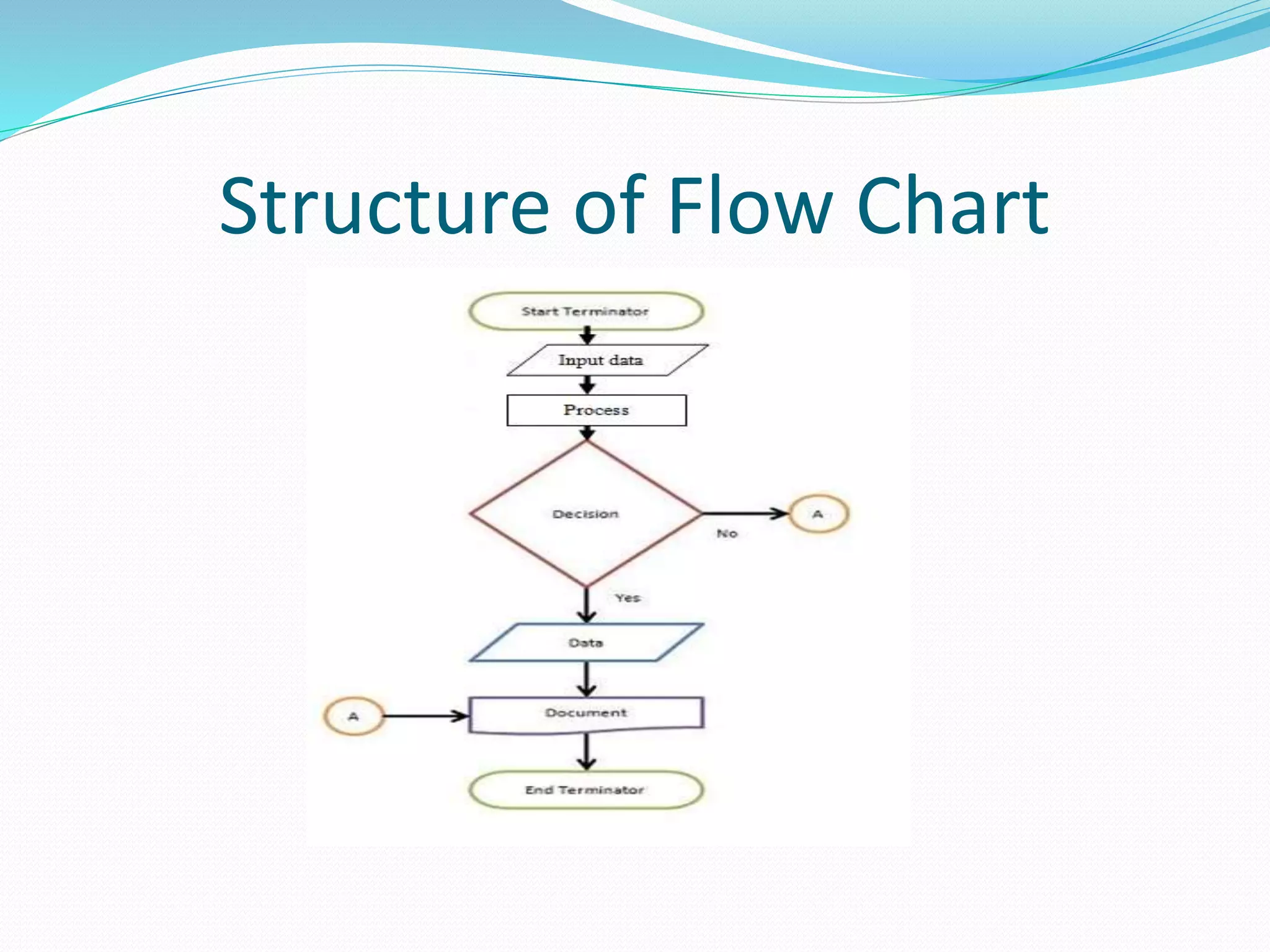
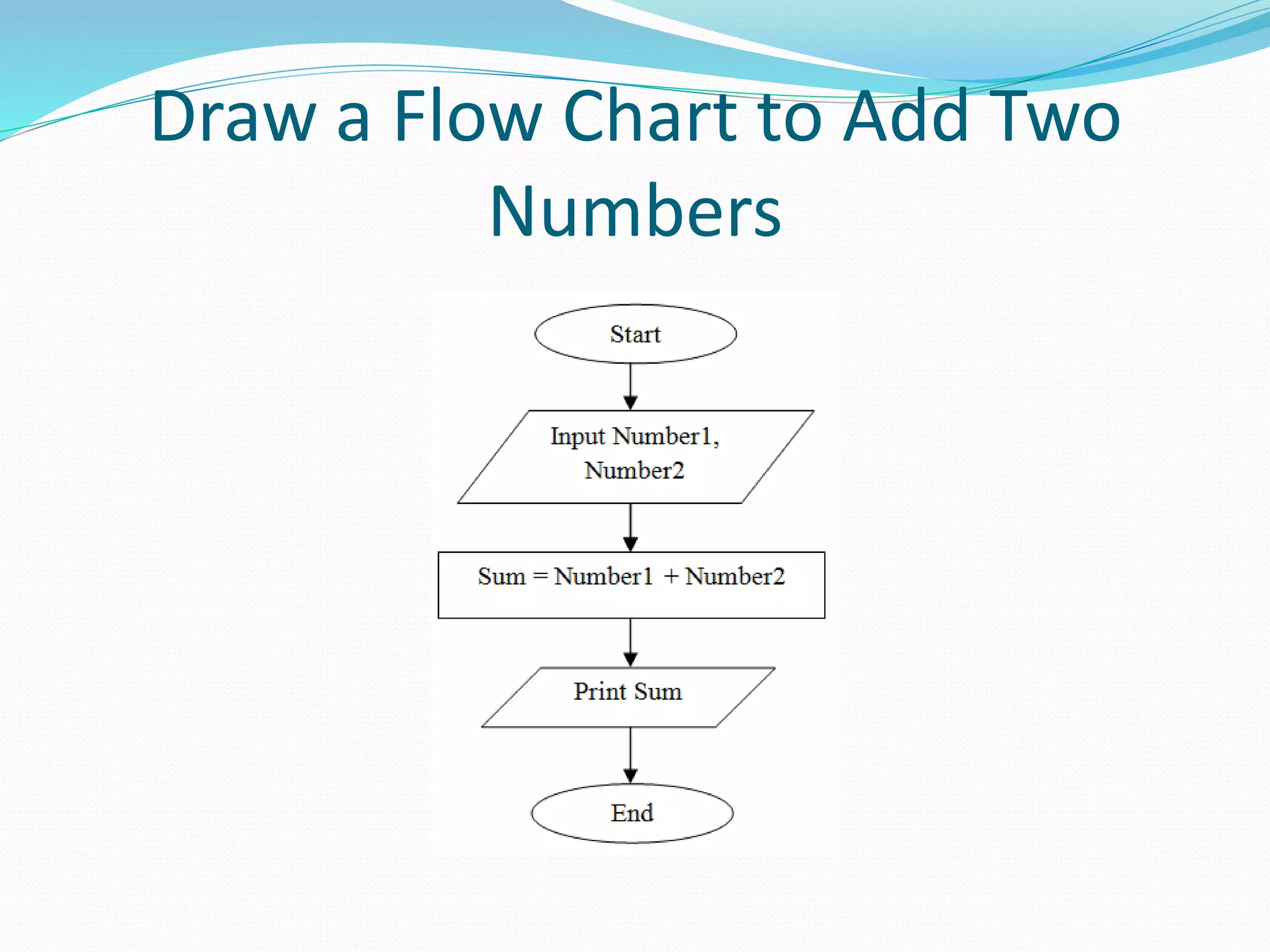
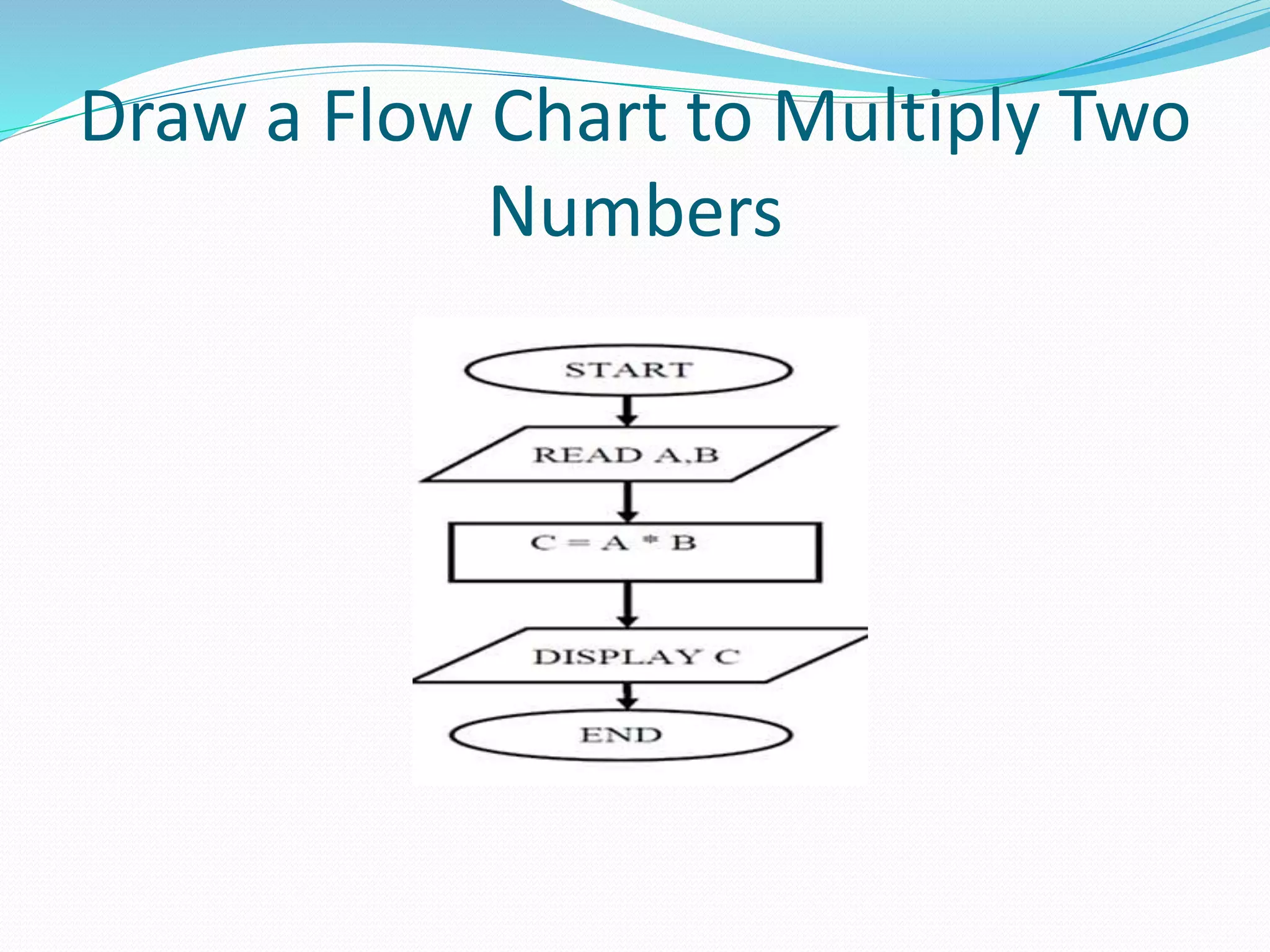
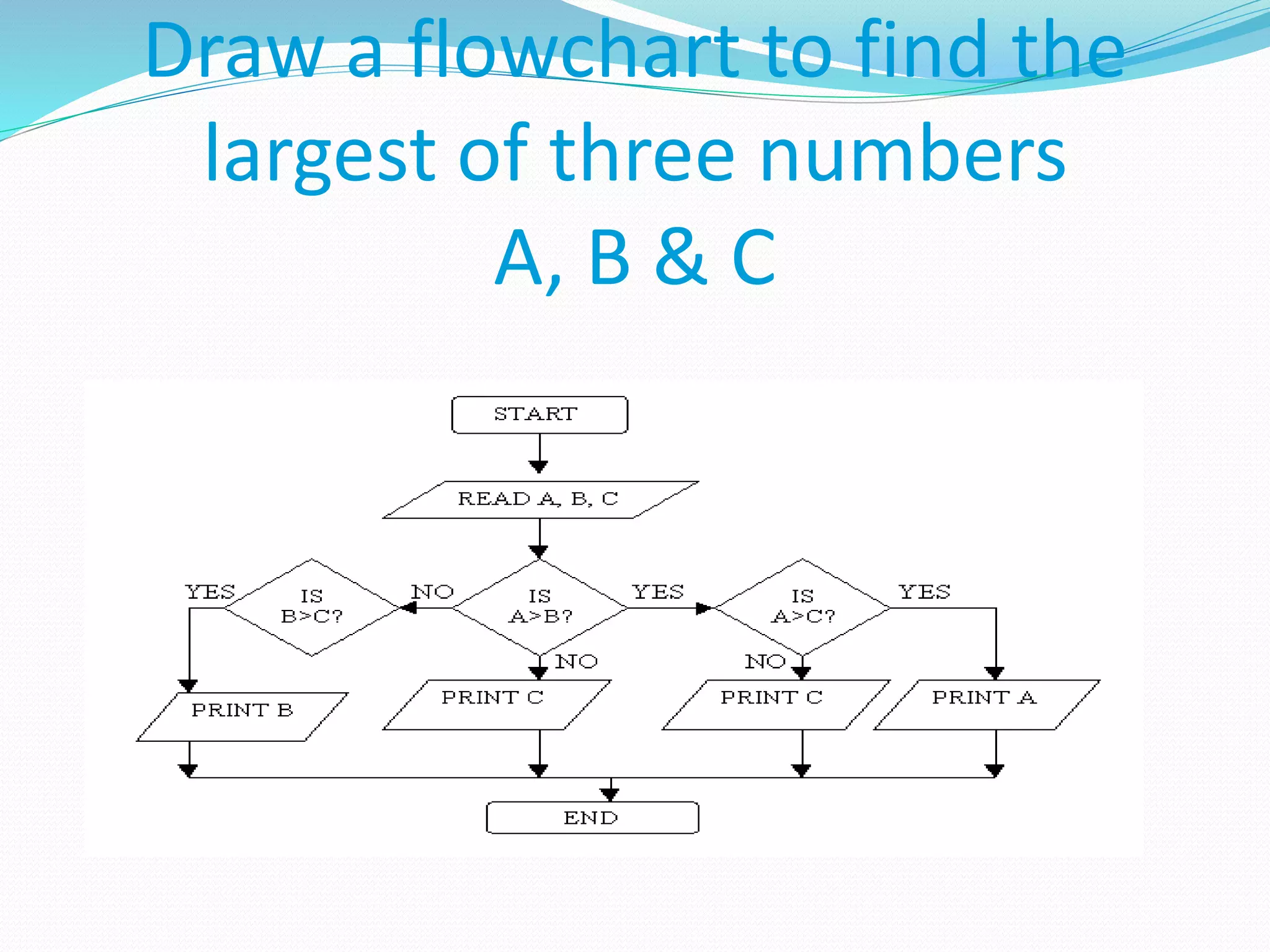
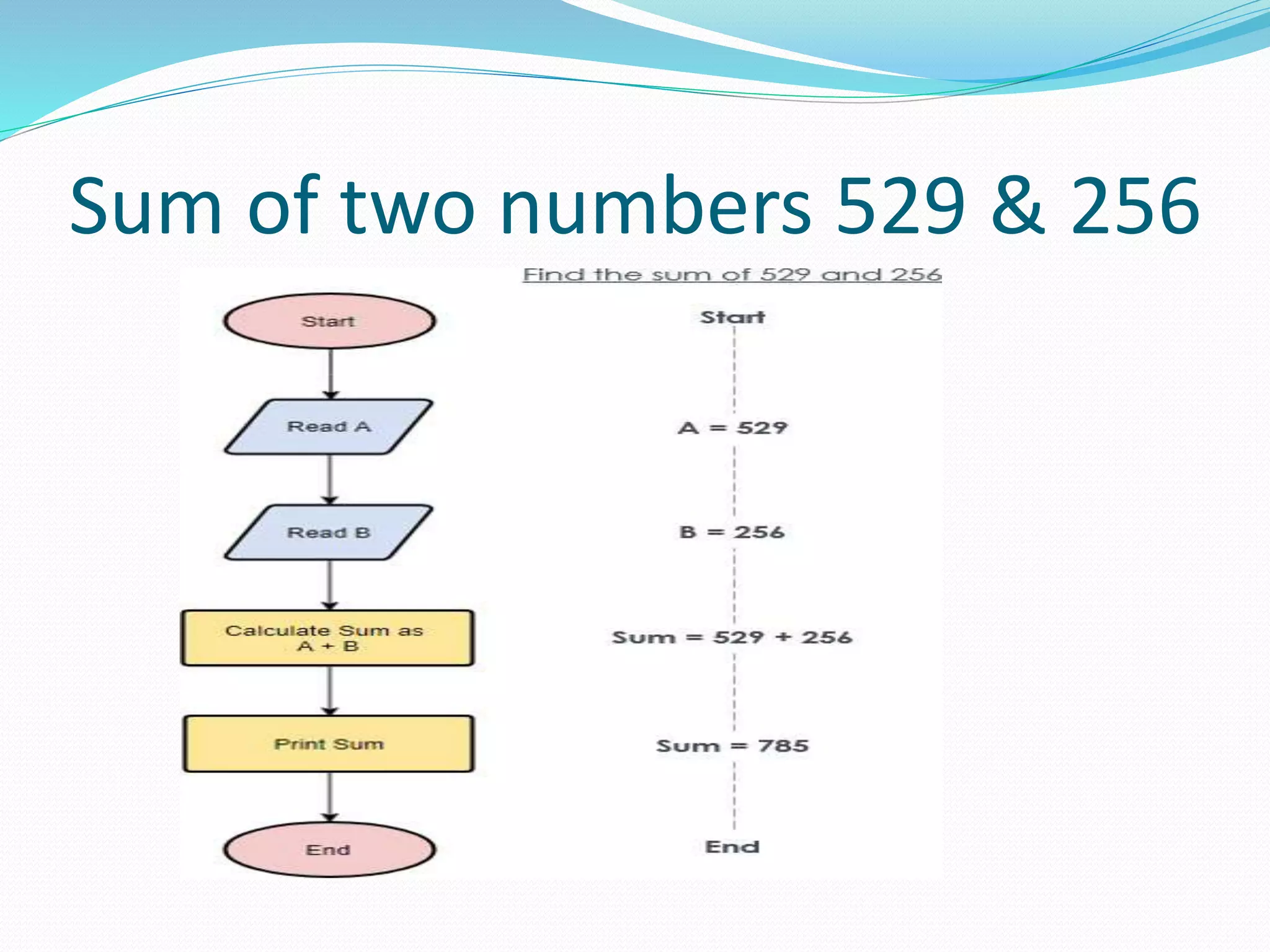
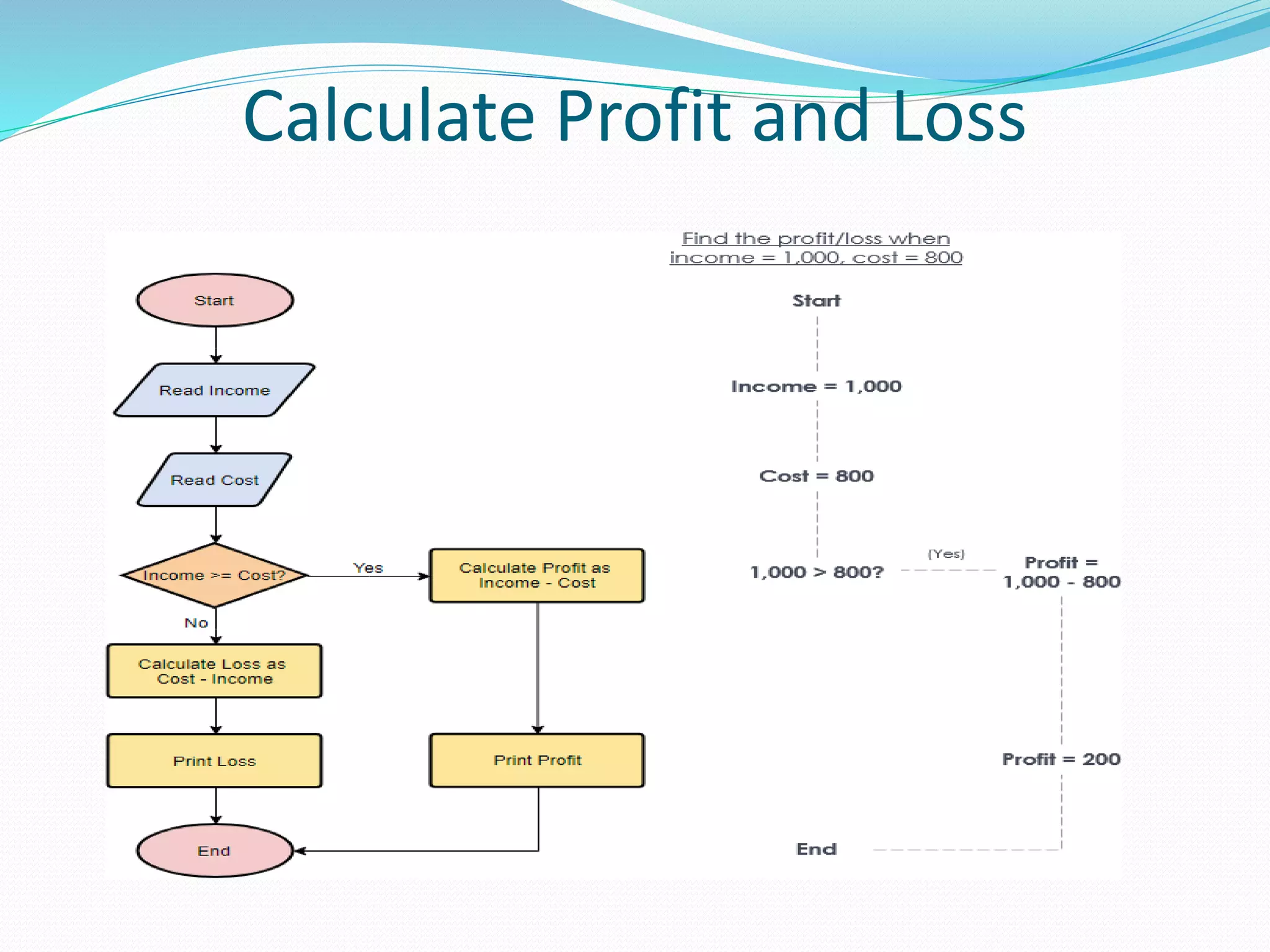
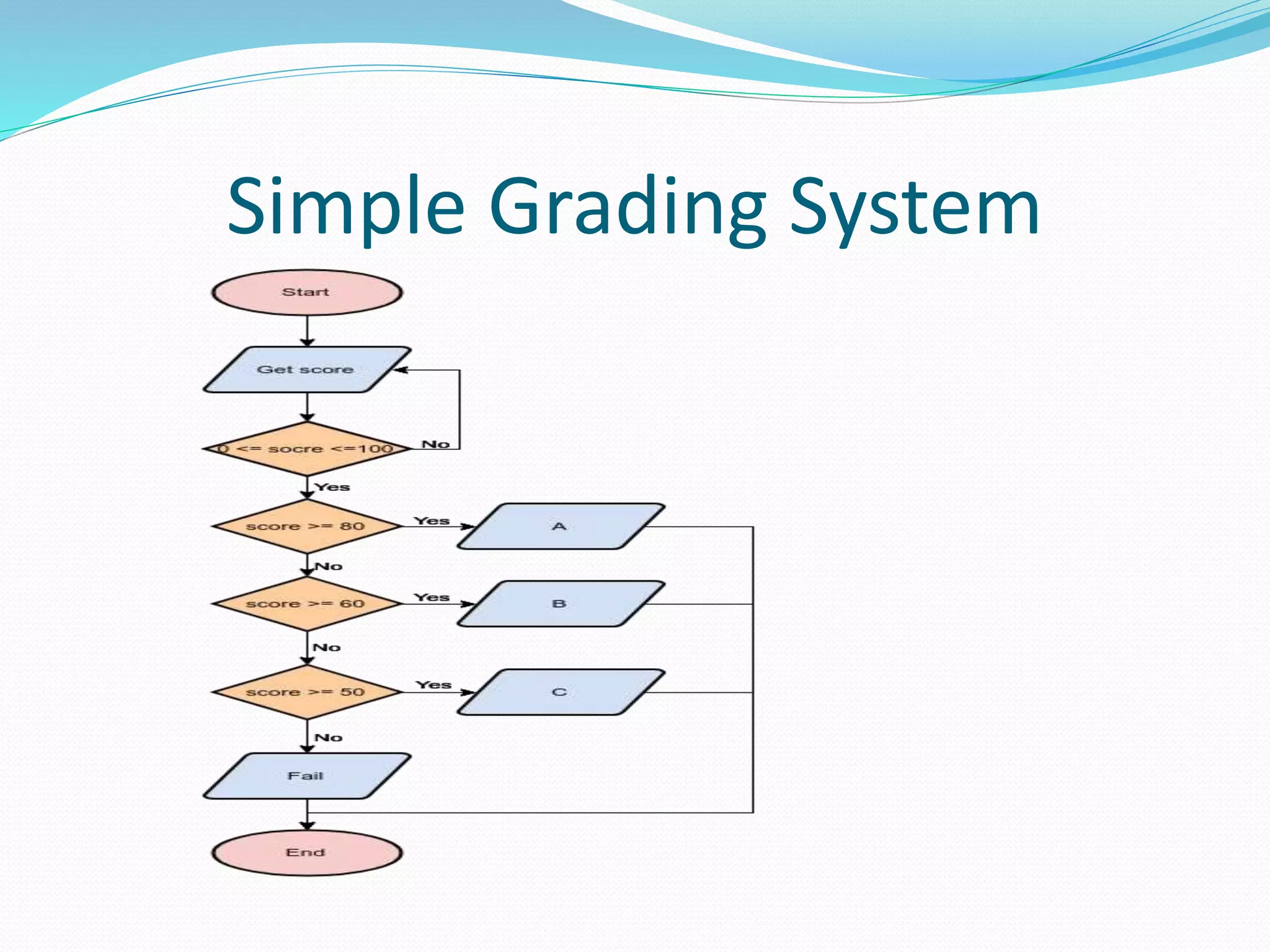
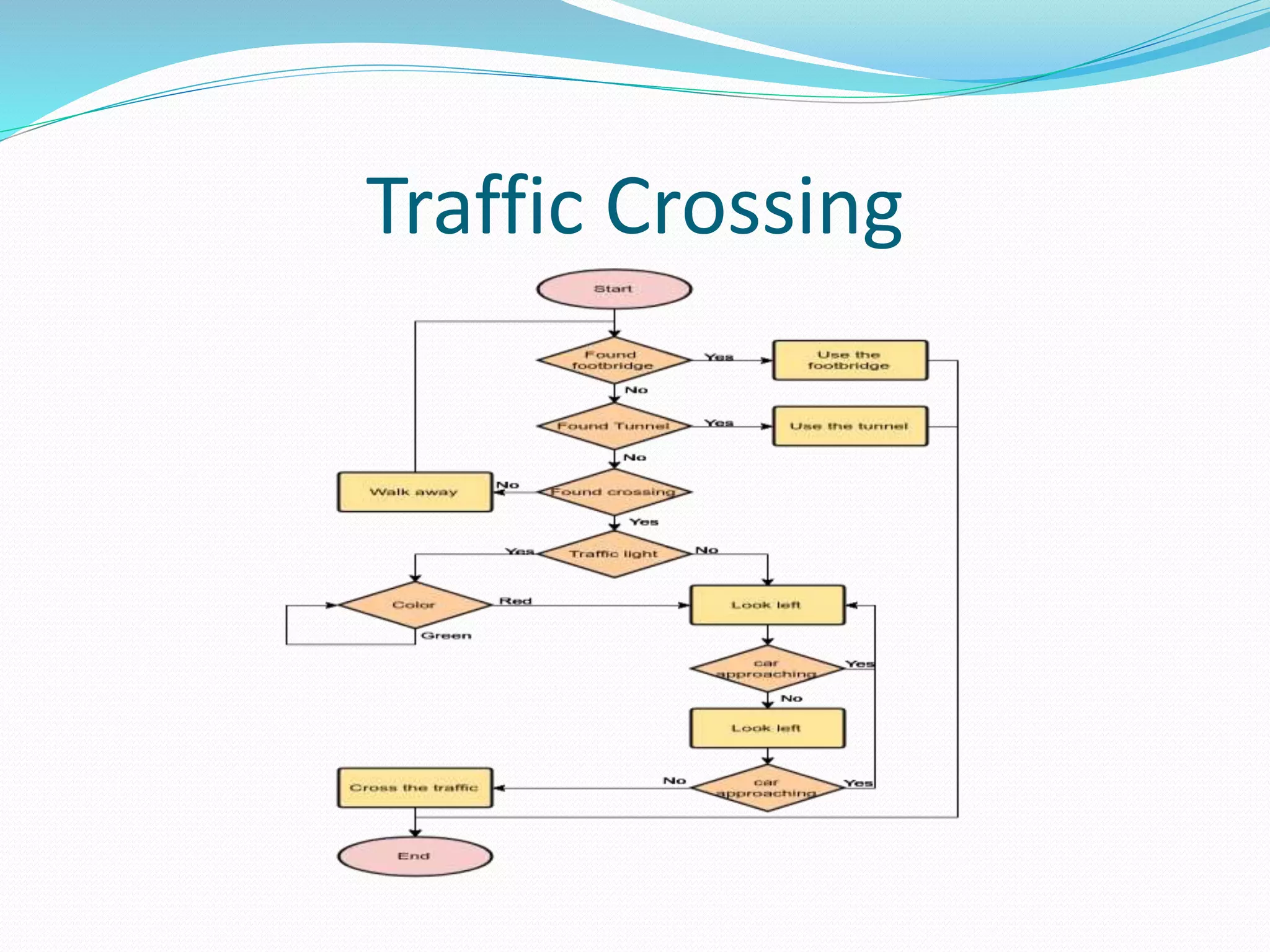
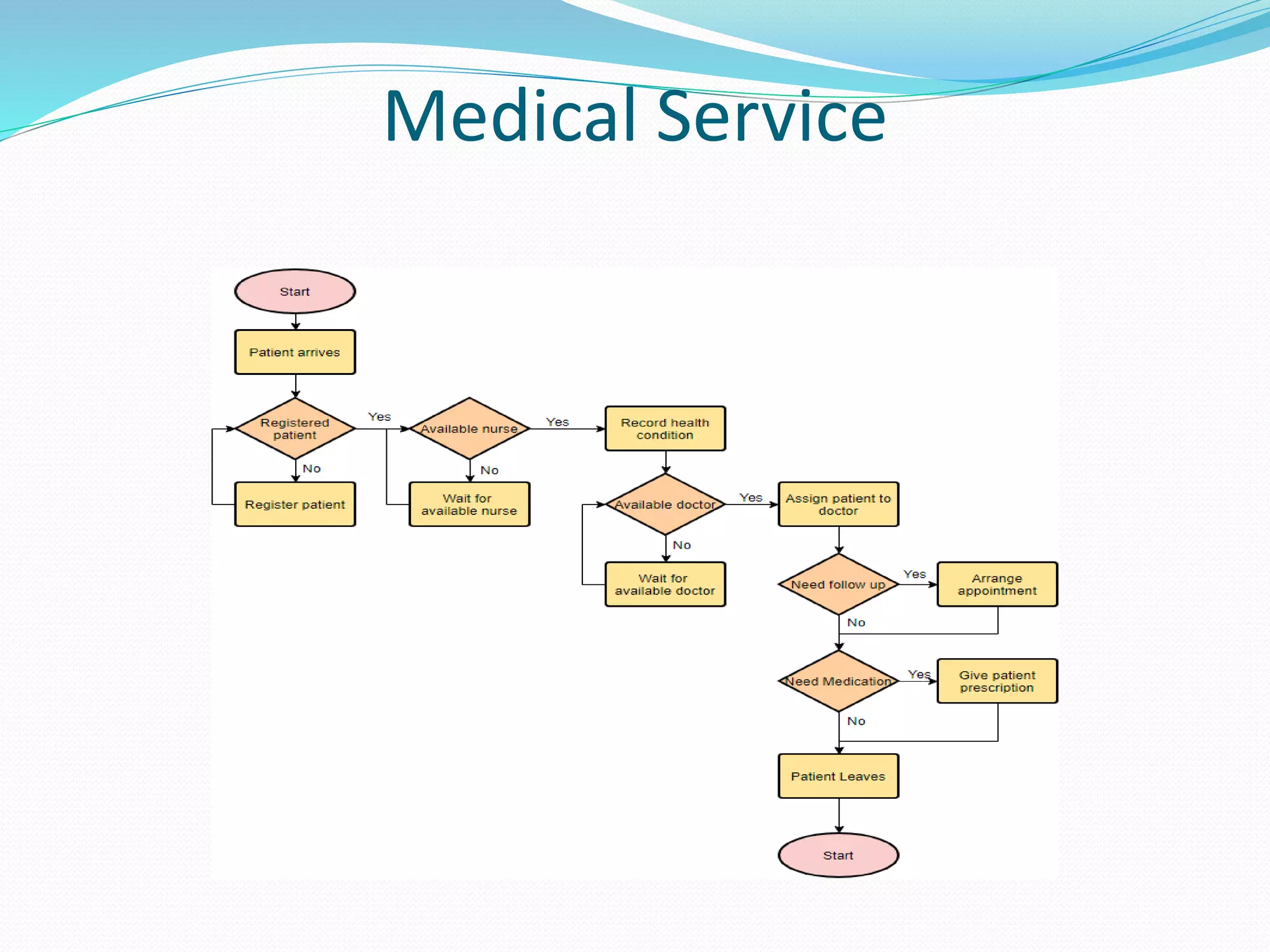
The document presents a flowchart overview by Prof. Amiya Bhusan Bagjadab, covering its definition, advantages, and common symbols. Flowcharts are used to diagrammatically represent workflows or algorithms, leading to better communication and efficient program management. It includes practical examples to illustrate the application of flowcharts in various processes.