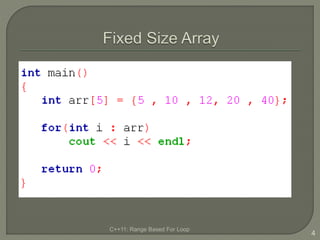
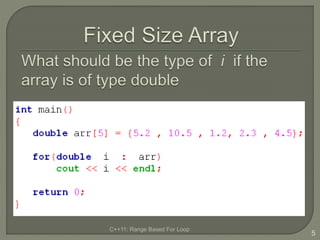
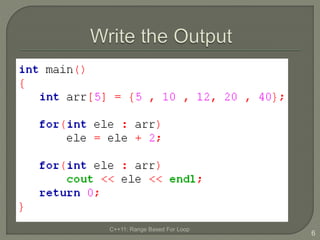
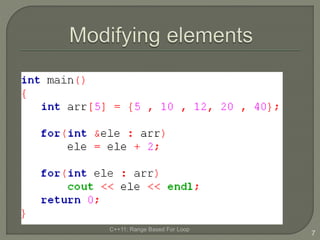
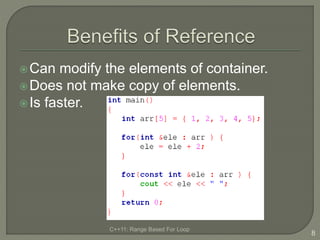
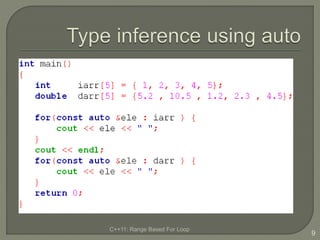
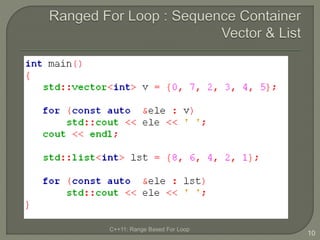
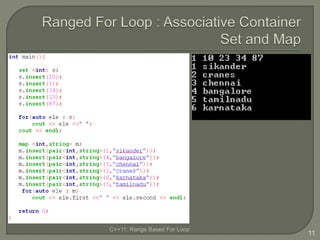
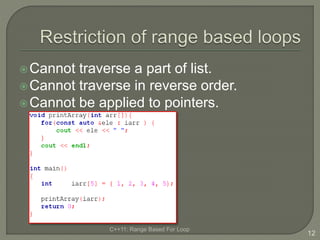
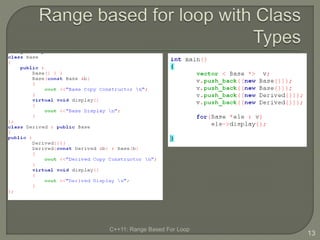
The document discusses the range-based for loop introduced in C++11, highlighting its syntax and advantages over traditional for loops, such as readability and performance. It notes that this loop can operate on fixed-size arrays, vectors, and lists but has limitations, including the inability to traverse parts of lists or pointers. Overall, it emphasizes the benefits of using range-based for loops to simplify program structure when working with containers.