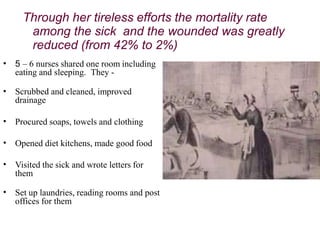
Florence Nightingale was born in 1820 in Italy to wealthy English parents. She received an excellent classical education and felt called to nursing, seeing its potential to alleviate human suffering. During the Crimean War, Nightingale and a team of nurses found the military hospital conditions to be appalling. Through tireless efforts, she reduced the mortality rate from 42% to 2%. Nightingale established the first nursing school in 1860 and wrote seminal textbooks that established nursing as a profession. She is renowned for revolutionizing military and civilian hospital sanitation standards.