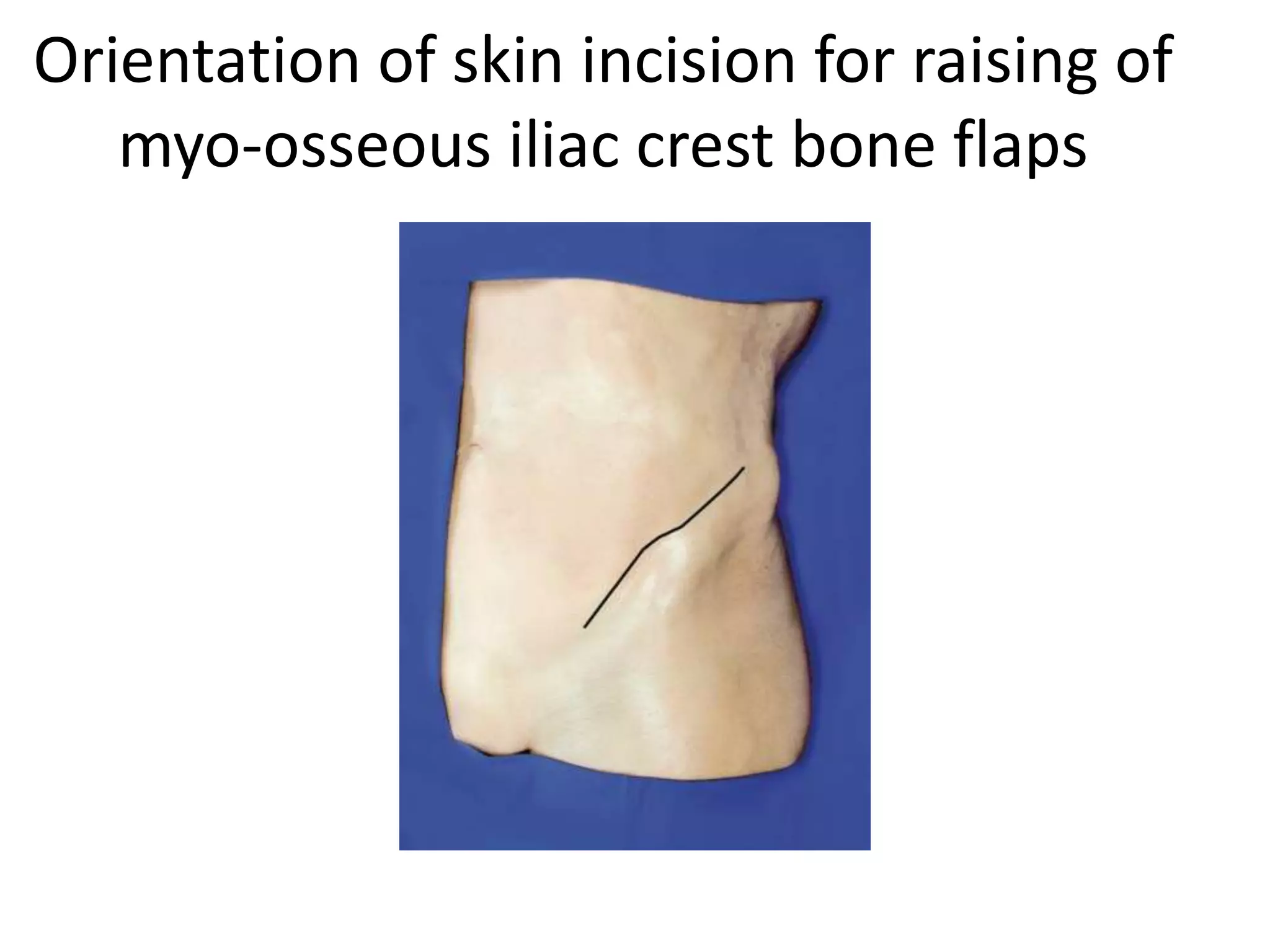
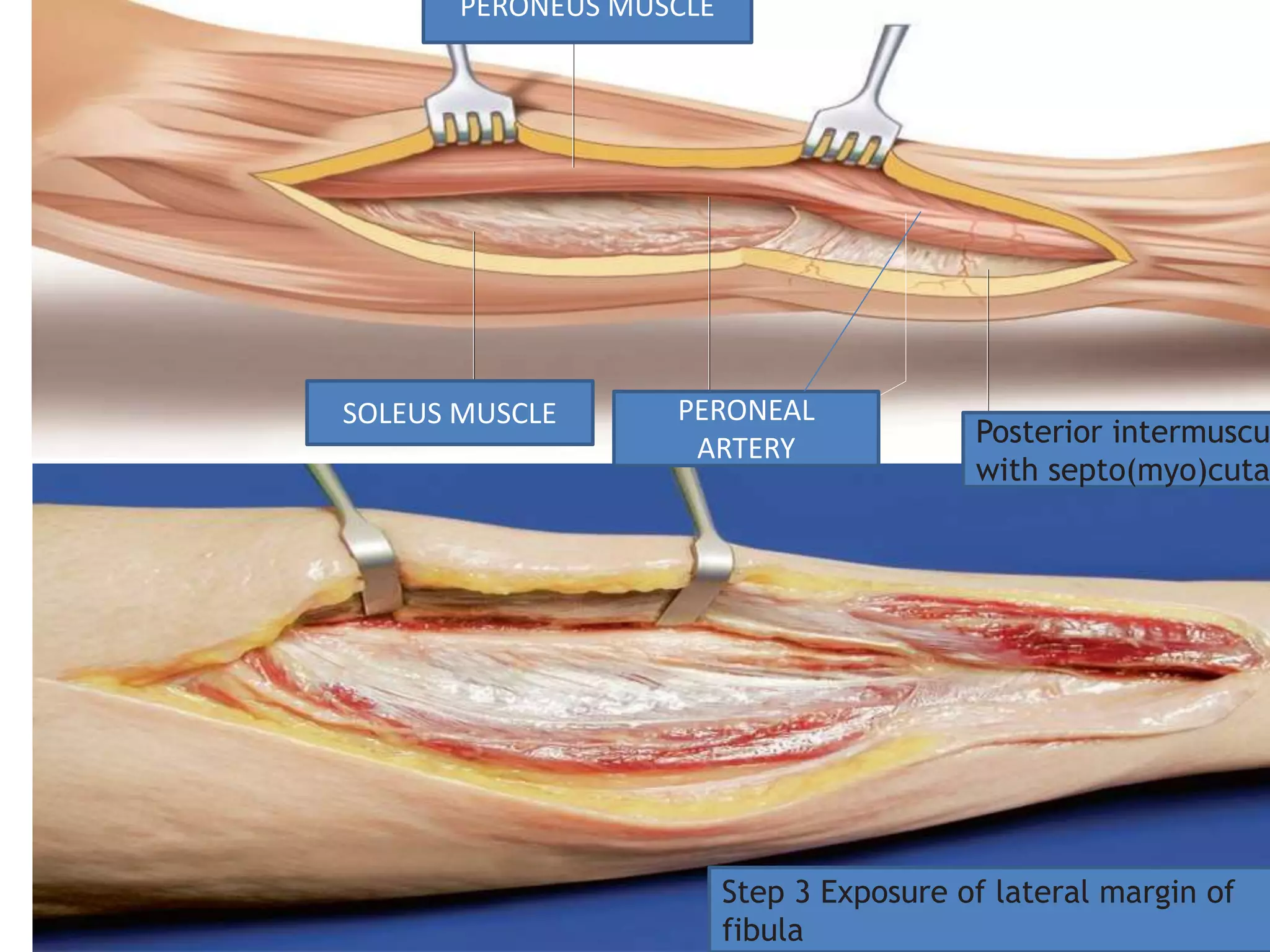
The document describes the step-by-step techniques for raising three types of flaps in microvascular reconstruction: the iliac crest flap, fibular flap, and radial forearm flap. For each flap, the key steps are outlined, including skin and fascial incisions, identification and dissection of vascular pedicles, osteotomies if applicable, and completion of flap elevation. Diagrams accompany the text to illustrate the relevant anatomy and surgical steps. The overall aim is to provide an educational guide to raising these flaps for microvascular transplantation.