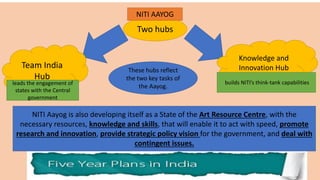
The document outlines the objectives and history of India's five-year plans, initiated by the Planning Commission, which was established in 1950. Key goals include reducing income inequality, enhancing economic growth, and improving infrastructure and education. The National Institution for Transforming India (NITI Aayog) serves as a think tank to guide national policy and promote cooperative federalism among states.