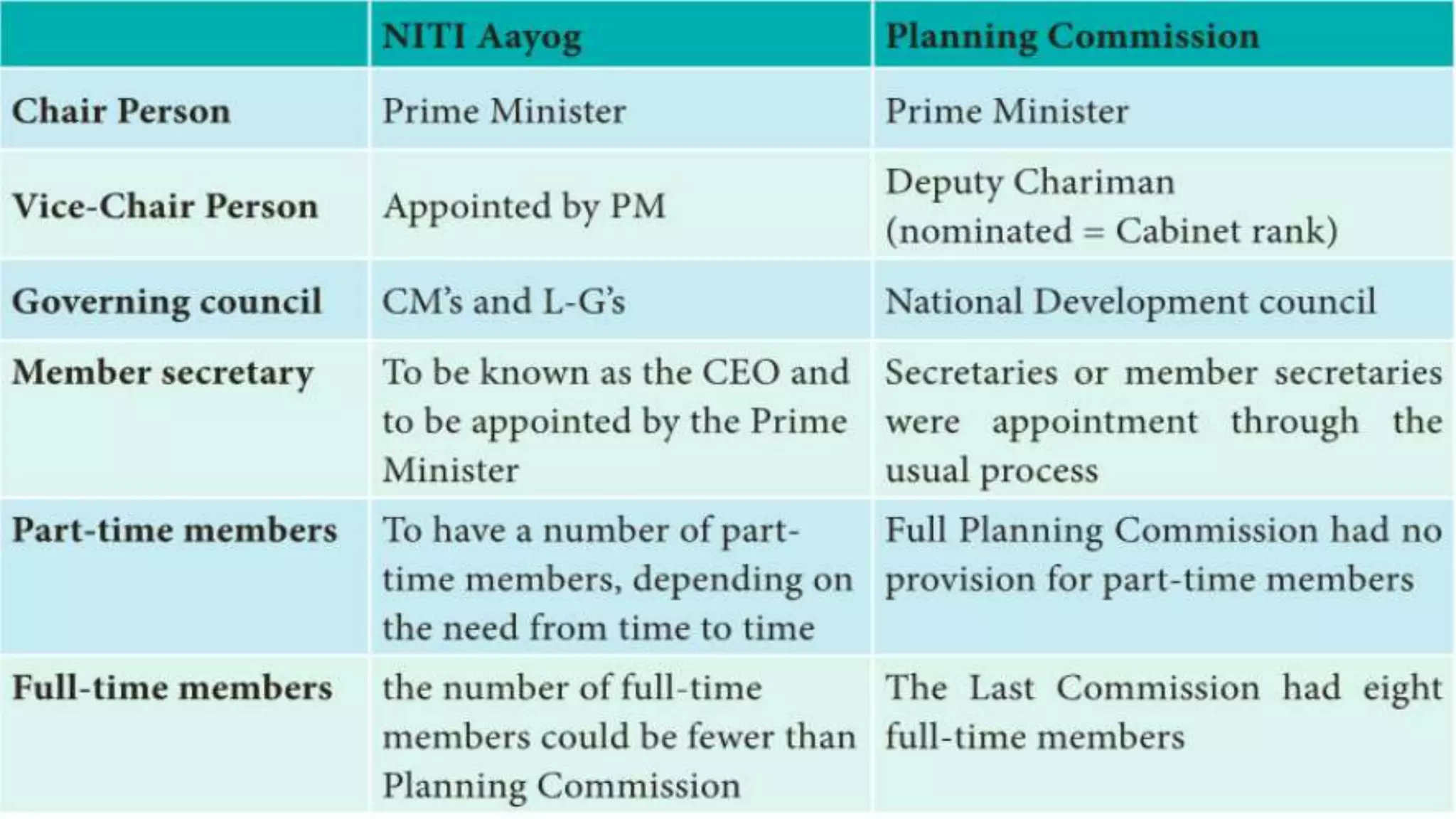
The Planning Commission of India was replaced by NITI Aayog in 2015 to promote cooperative federalism, address the diverse needs of states, and transform India into a global competitive economy. Key differences include NITI Aayog functioning as a think tank rather than allocating funds, encouraging participation from states in policymaking, and focusing on evidence-based strategic policy frameworks. It aims to foster multi-directional policy flows between central and state governments to achieve equitable development through collaborative efforts.




![Functions and Responsibilities of the Planning Commission
•Make assessment of all resources of the country
•Augment deficient resources
•Formulate plans [Five Year Plans (FYP)] for the most effective
and balanced utilization of resources and determining
priorities.
•Determine the stages of plan implementation
•Determine the nature of machinery required.
•Indicate the factors which tend to retard economic
developments.
•Monitor and evaluate.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/planningcommissiontonitiaayog-211226174351/75/Planning-commission-to-niti-aayog-5-2048.jpg)