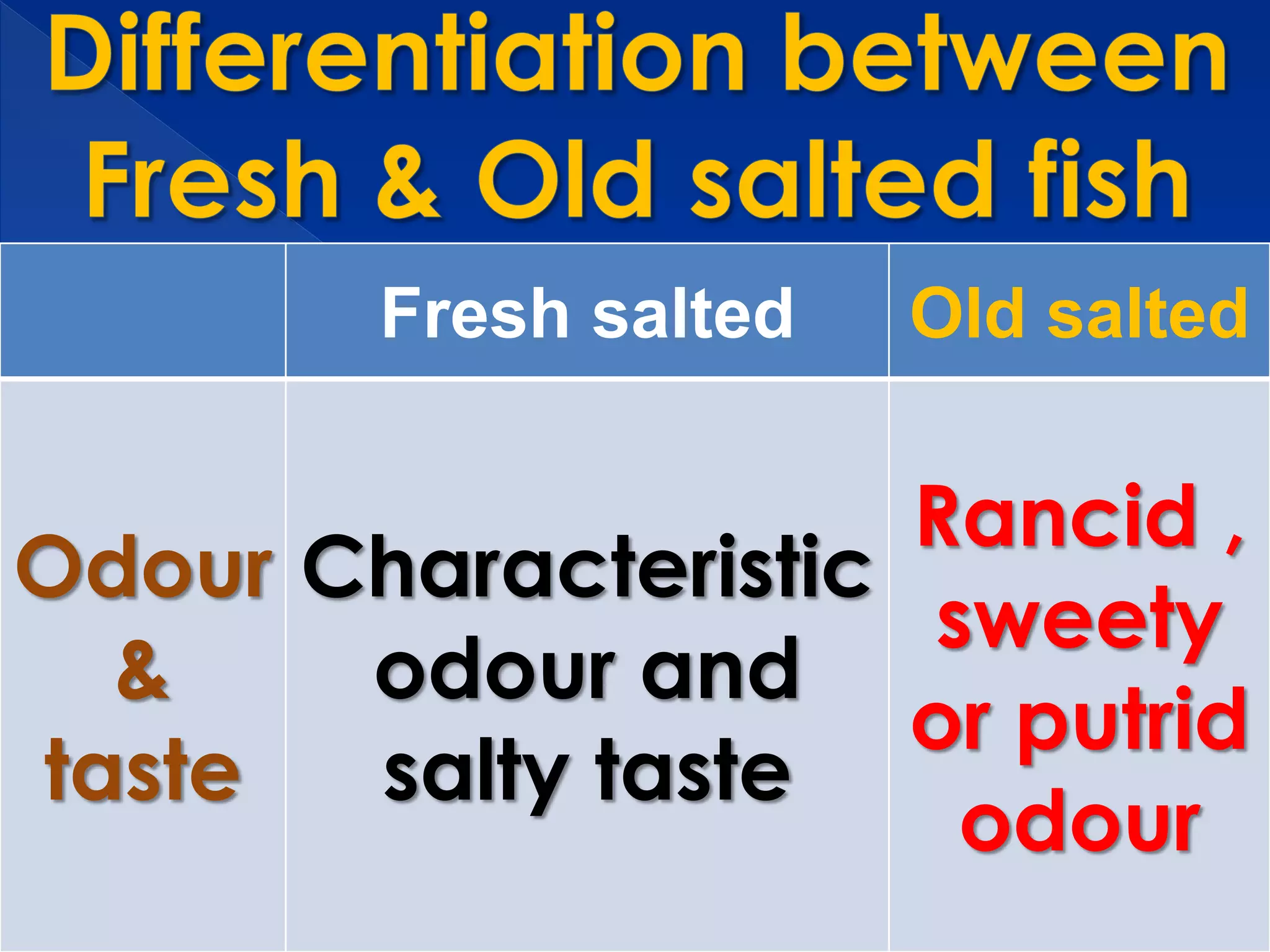
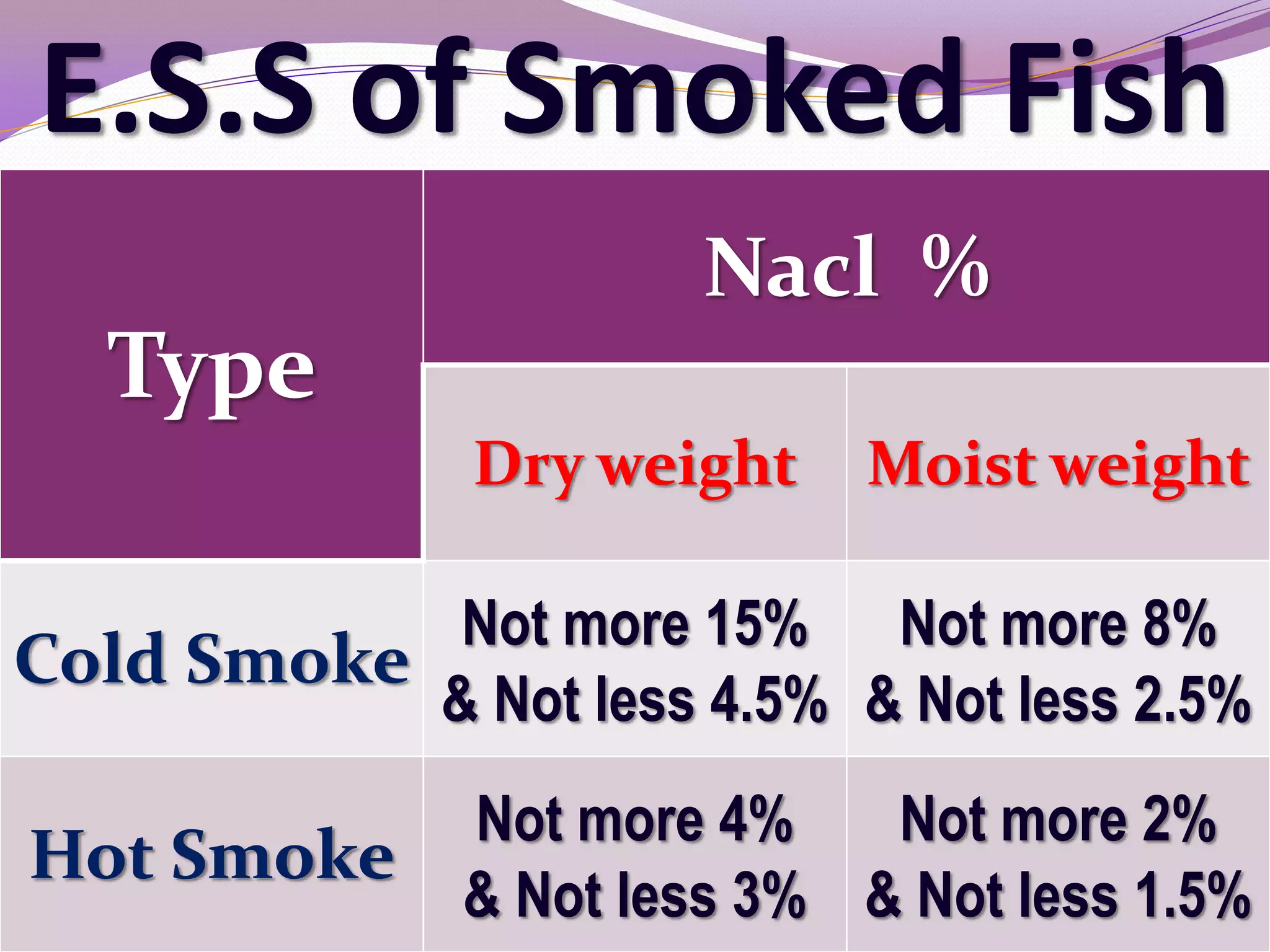
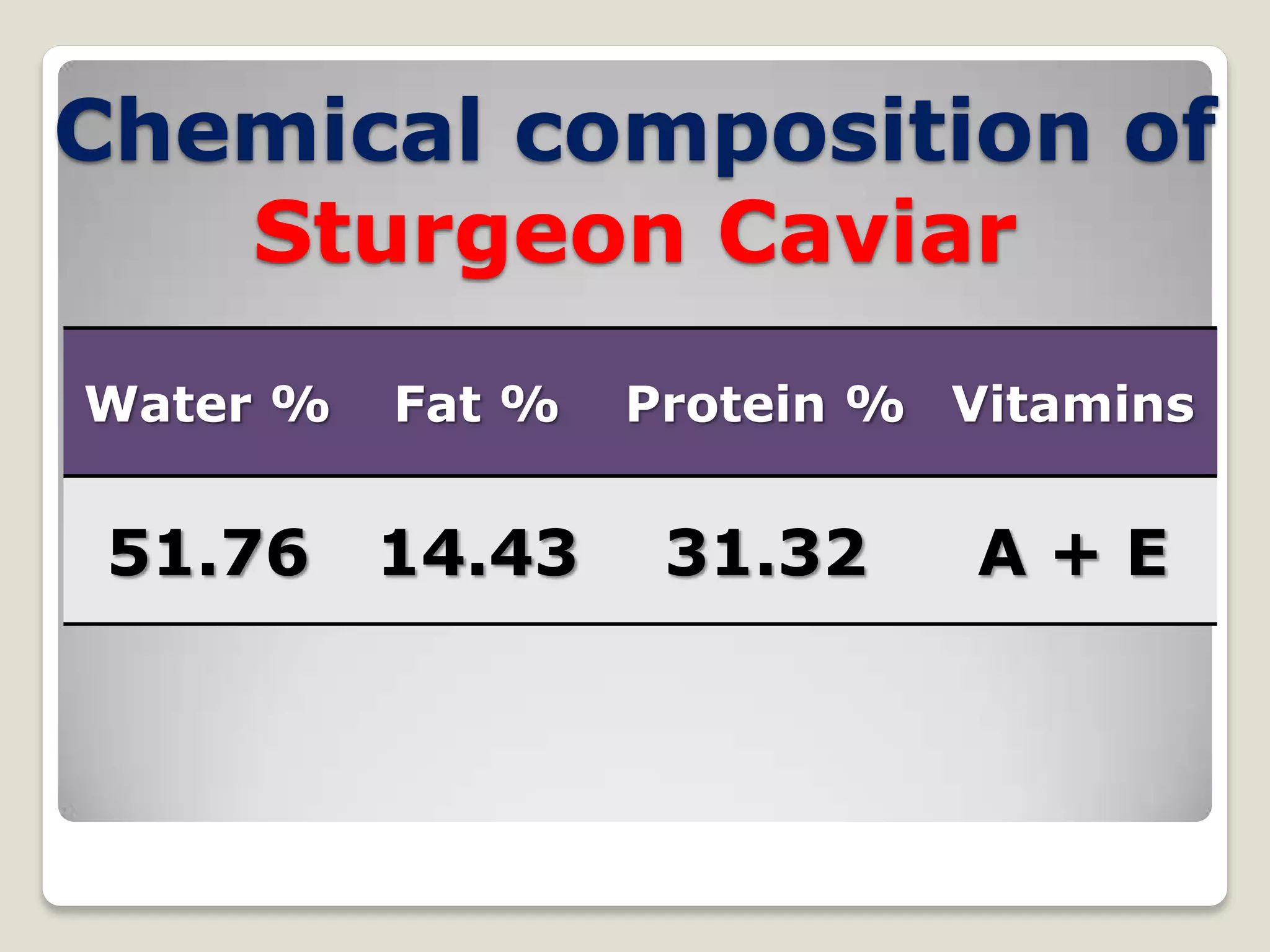
The document discusses the examination of caviar. It describes caviar as consisting of processed, salted sturgeon roe. It provides details on the acceptable color, odor, consistency, taste, dirtiness, size, pH, salt content, and results of bacteriological and chemical examinations of fresh caviar. Any abnormal results would indicate decomposed or contaminated caviar.