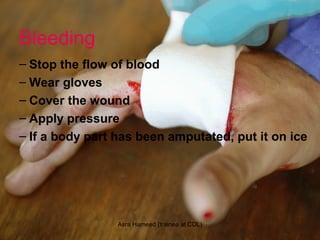
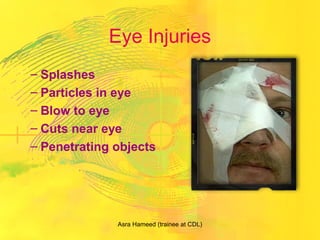
The document outlines the critical role of pharmacists in providing first aid and emergency care, highlighting their responsibilities in community health. It discusses essential first aid techniques, the importance of readiness with well-stocked kits, and the types of medical emergencies pharmacists may encounter. Overall, it emphasizes the significance of first aid in saving lives and enhancing community health awareness.