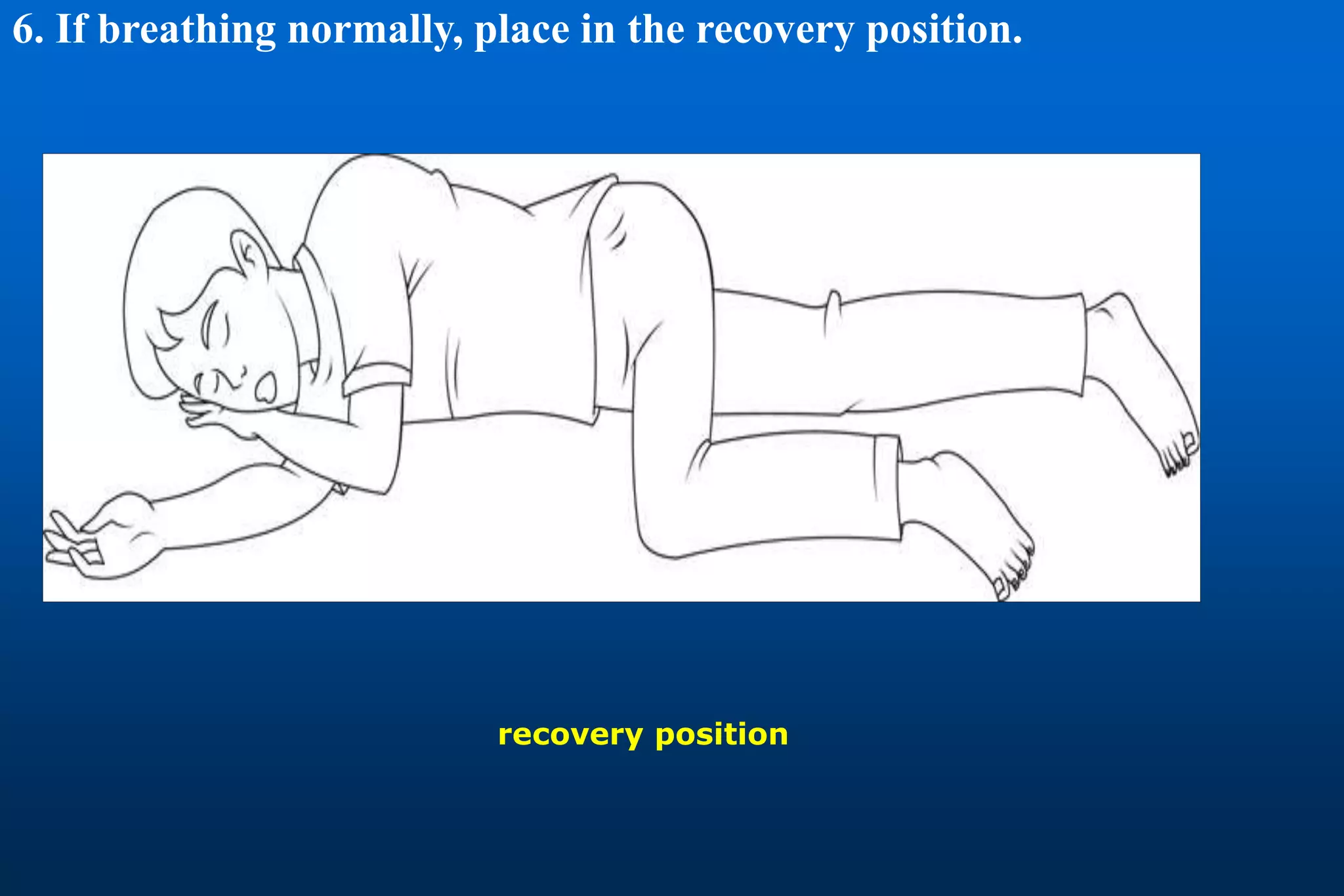
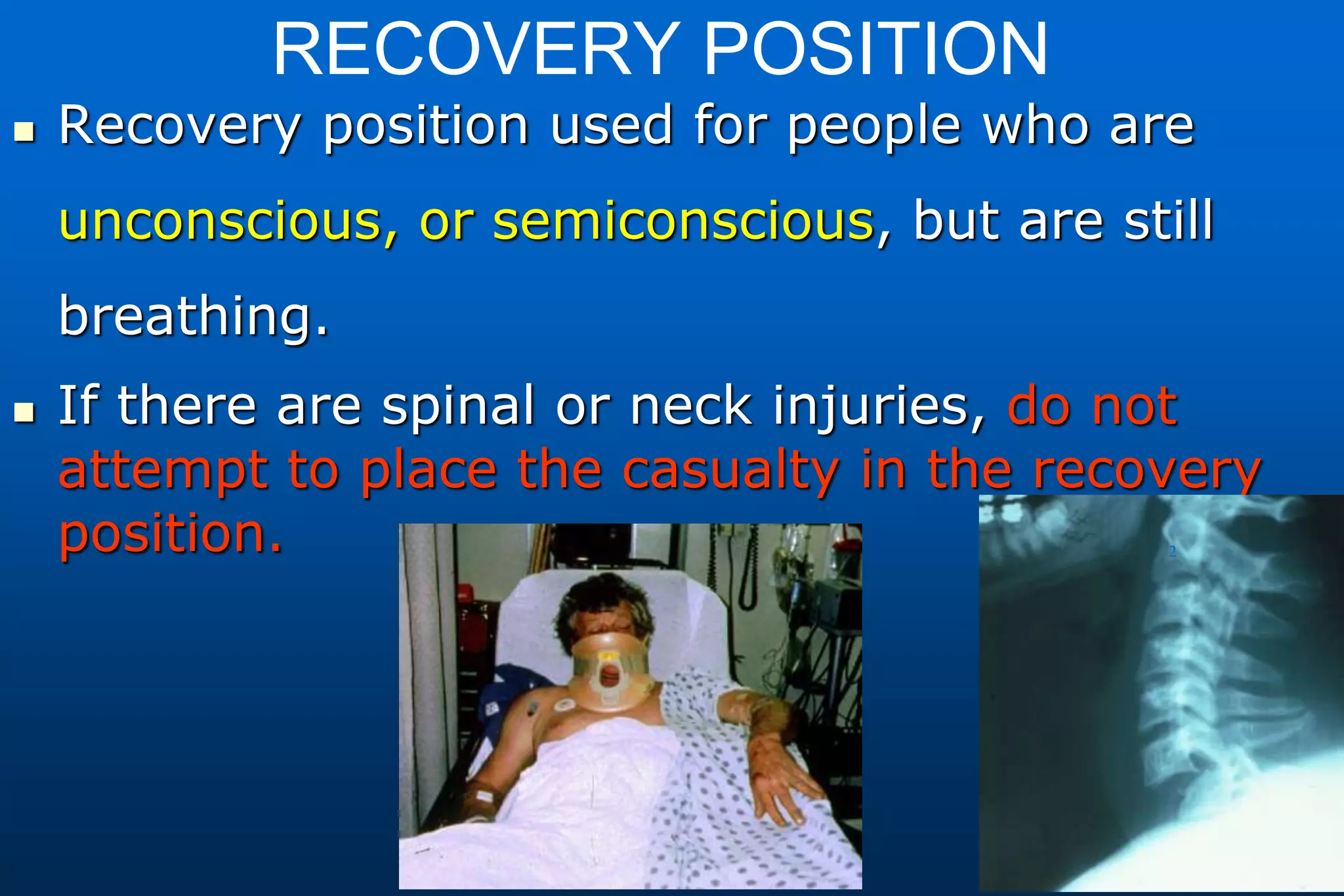
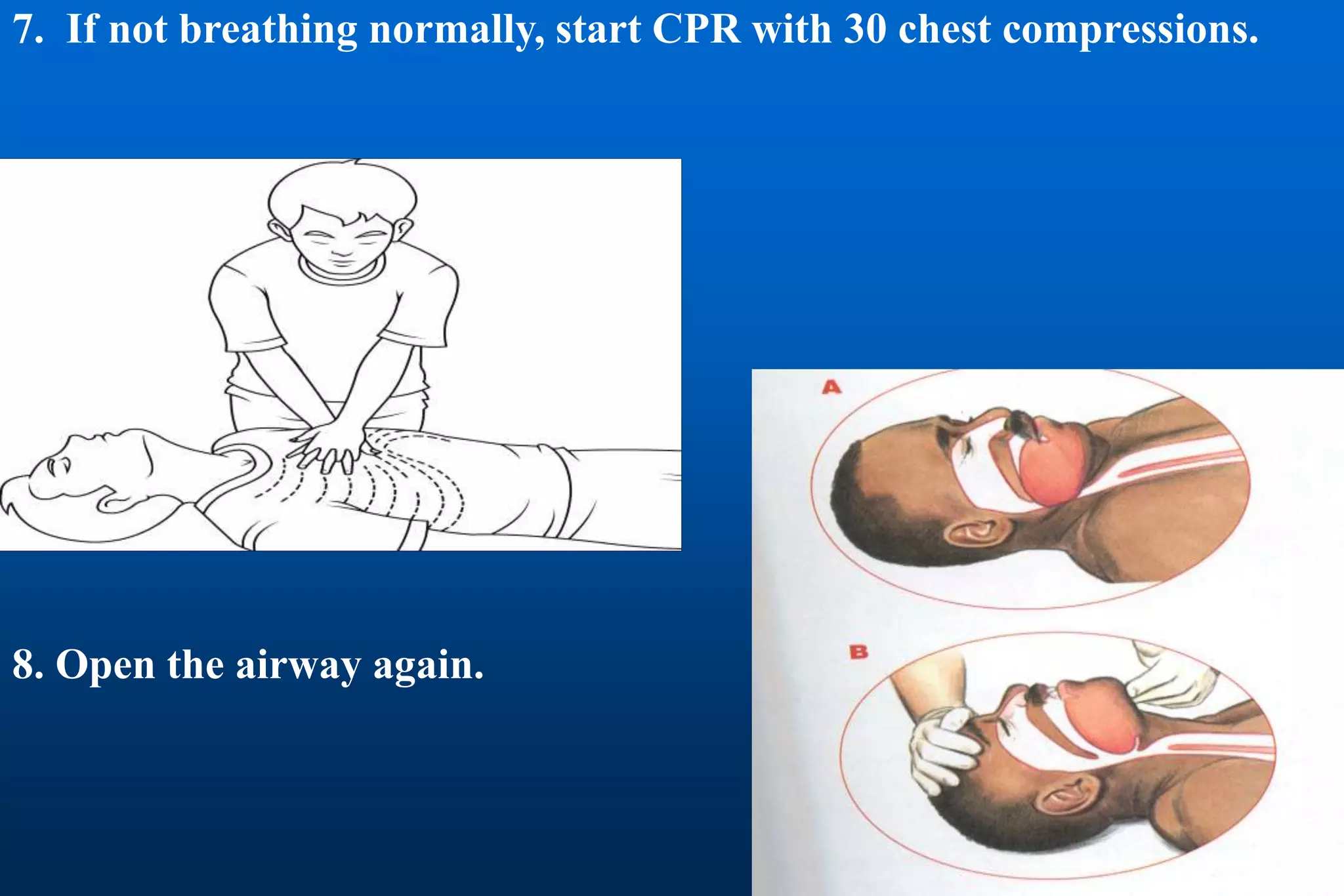
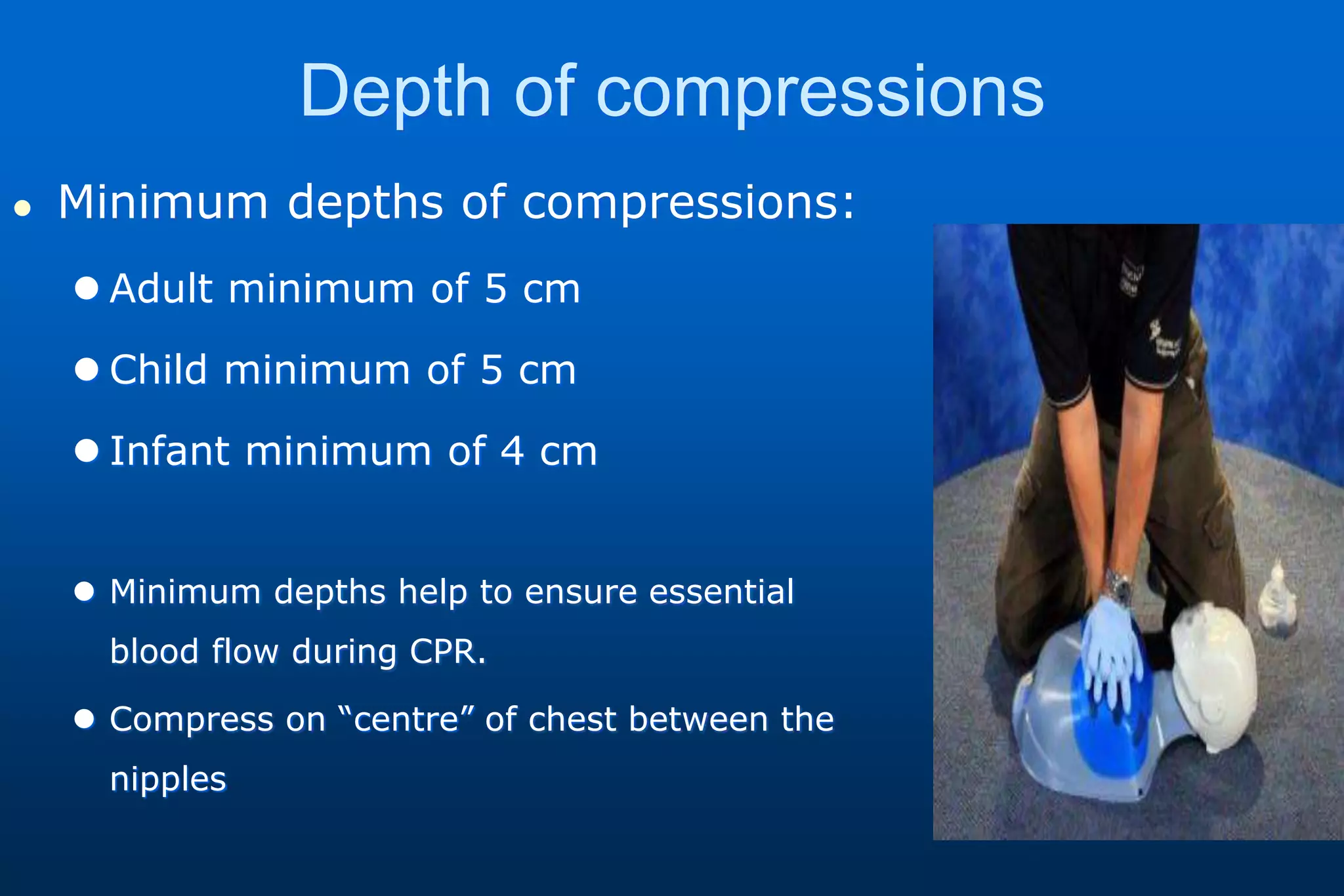
This document provides information on cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and first aid measures. It lists common causes of respiratory or cardiac arrest that may require CPR, including electric shock, drowning, heart attack, drugs overdose, and trauma. It notes that brain damage can begin within 4 minutes if oxygenated blood flow does not reach the brain, and brain death is certain after 10 minutes without flow. The document then outlines the steps for performing CPR, including checking for danger and response, calling for help, opening the airway, checking breathing, giving chest compressions and breaths, and continuing until qualified help arrives. It provides details on proper hand positioning, compression depths for adults and children/infants