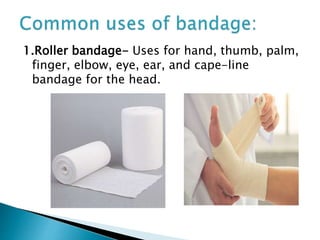
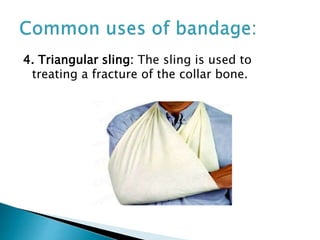
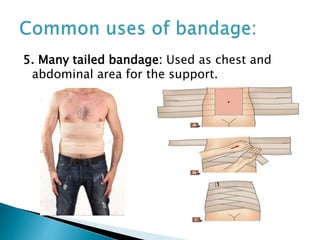
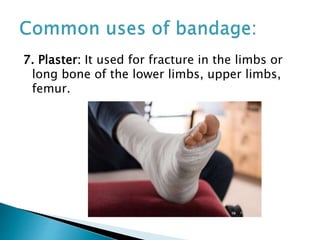
A bandage is a piece of material used to support or restrict movement of an injured body part. Common bandages include roller bandages, triangular bandages, and special bandages for different body areas. The process of bandaging involves wrapping the injured area with bandage material to immobilize it and help with issues like bleeding, swelling, and pain. Proper bandaging technique is important and involves steps like supporting the injured area, applying even pressure from bottom to top, and securing the bandage ends.