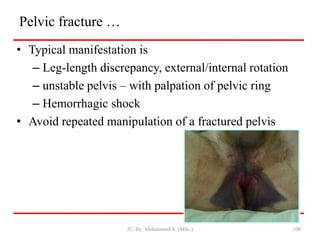
The document provides information on wound classification, types of wounds, bleeding control, and first aid interventions for wounds. It discusses the following:
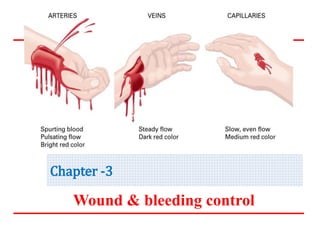
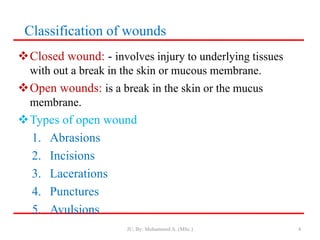
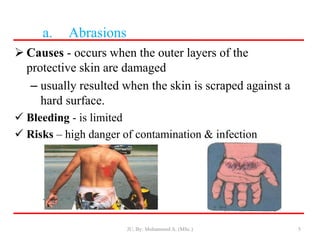
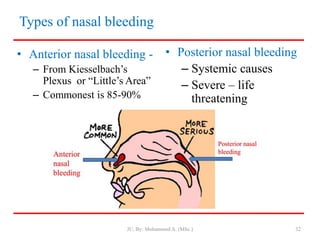
- Classification of wounds as closed or open, with open wounds further divided into abrasions, incisions, lacerations, punctures, and avulsions.
- Approaches to control bleeding include direct pressure, elevation, pressure points, and tourniquets as a last resort.
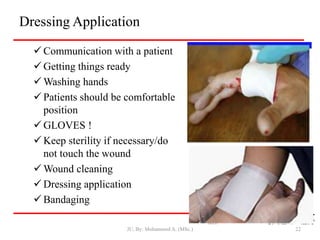
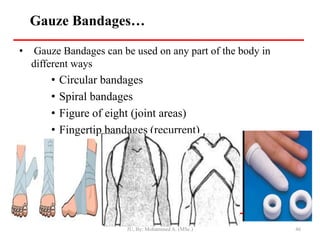
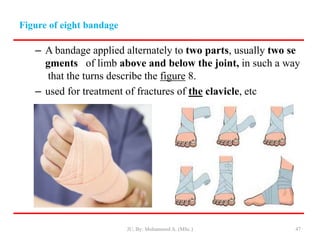
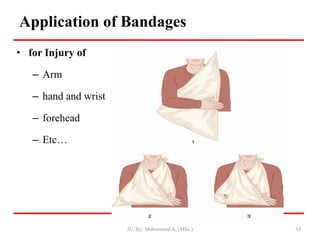
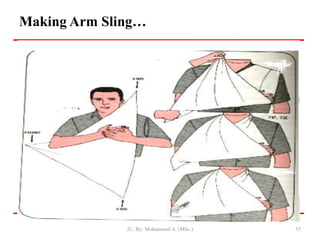
- First aid for wounds involves stopping bleeding, cleaning the wound, and covering it with a sterile dressing and bandage to protect it and prevent infection.
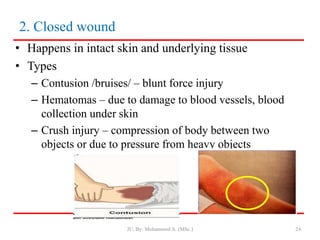
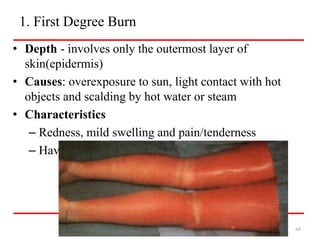
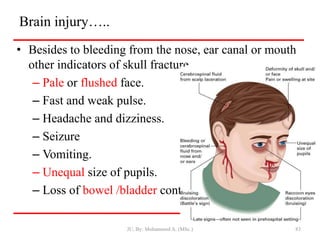
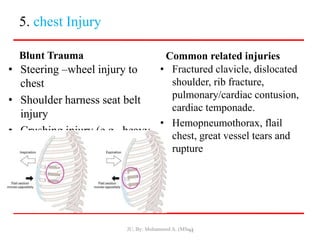
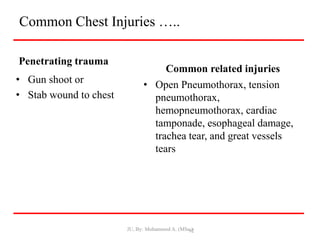
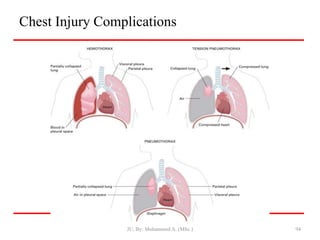
- Closed wounds like bruises, hematomas and crush injuries are also addressed. Signs of internal bleeding and