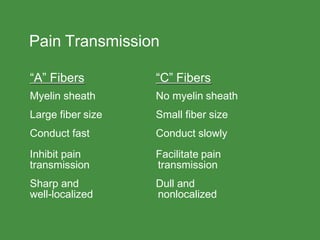
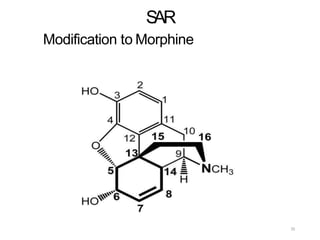
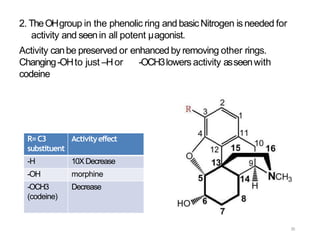
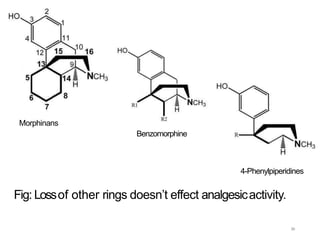
This document discusses opioid analgesic agents and pain transmission. It begins by classifying types of pain and describing pain transmission through A and C nerve fibers and the pain gate theory. Opioid analgesics like morphine work by binding to mu, kappa, and delta opioid receptors in the dorsal horn and brain to close the pain gate and inhibit pain transmission. Side effects include euphoria, nausea, respiratory depression, and constipation. Tolerance can develop with long term use but physical dependence and tolerance do not necessarily indicate addiction. The structure of morphine is also described and how various modifications can increase or decrease its potency.