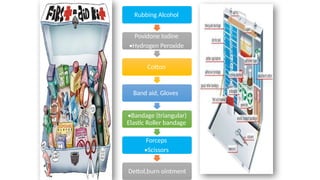
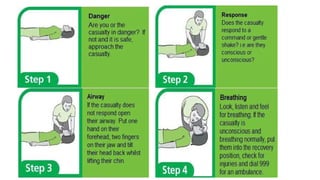
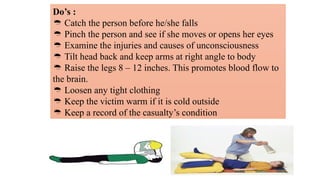
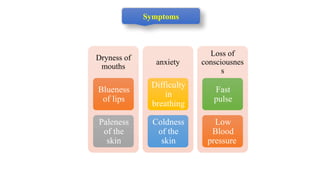
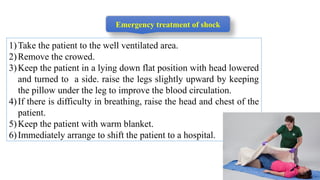
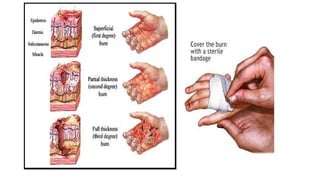
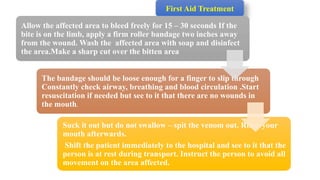
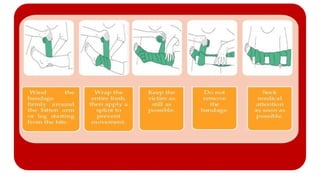
This document outlines the fundamentals of first aid, emphasizing its purpose to provide immediate care to victims before professional medical assistance is available. It covers the characteristics of a good first aider, an action plan for assessing life-threatening conditions, and specific treatments for emergencies such as fainting, burns, and snake bites. Essential do's and don'ts for various situations are highlighted to ensure proper care and safety.