This document presents a finite element analysis of a spring assembly. It contains the following key points:
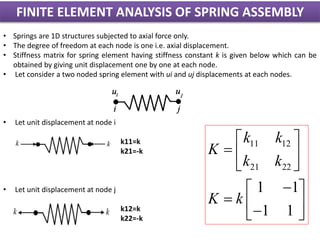
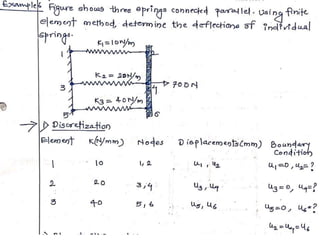
1) It describes a finite element model of a two-spring assembly, where each spring is modeled as a 1D element with one degree of freedom (axial displacement) at each node.
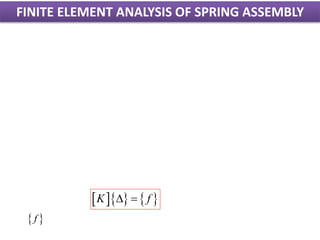
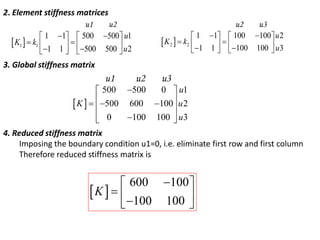
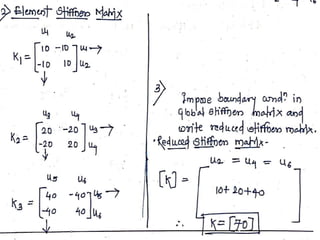
2) It presents the stiffness matrix formulation for a two-node spring element and shows how the element stiffness matrices are assembled into a global stiffness matrix.
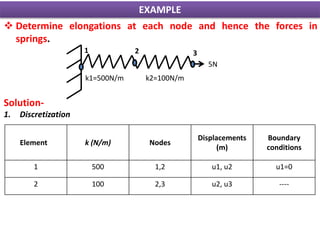
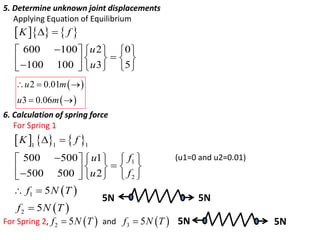
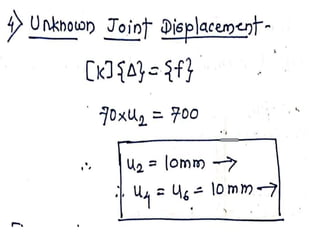
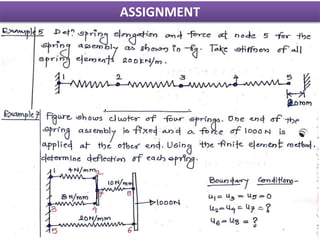
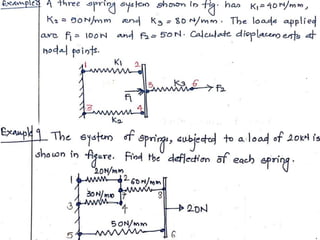
3) It shows an example problem where the displacements and forces in each spring are determined when a 5N force is applied to the free end of the assembly. The analysis involves forming the stiffness matrix, applying boundary conditions, solving the equilibrium equations, and calculating the