This document provides a summary of the course ME 2353 – Finite Element Analysis including 20 two-mark questions and answers related to various topics in finite element analysis. The questions cover topics such as variational methods, weighted residual methods, finite element formulation, element types, boundary conditions, discretization, shape functions, element stiffness matrices, and applications to heat transfer and fluid mechanics.



![ME 2353 – FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS
Page 4 of 11
2. Numbering of the nodes.
6. What are the classifications of the co-ordinates?
The co-ordinates are generally classified as ,
1. Global co-coordinates
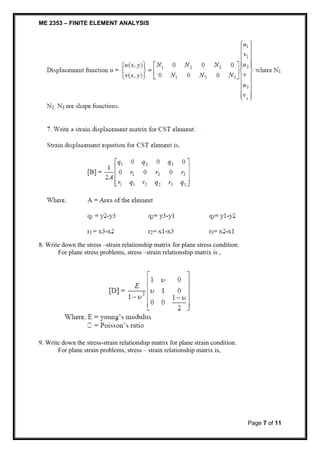
2. Local Co-ordinates
3. Natural co-ordinates
7. What is natural co-ordinates?
A natural co-ordinate system is used to define any point inside the element by a set of
dimensionless numbers, whose magnitude never exceeds unity. This system is useful in
assembling of stiffness matrices.
8. Define shape function.
In finite element method, field variables within an element are generally expressed by
the following approximate relation:
(x,y) = N1(x,y) 1+N2 (x,y) 2+ N3(x,y) 3 where 1 2 3 4 are the values of
the field variable at the nodes and N1 N2 N3 N4 are interpolation function. N1 N2 N3
N4 are called shape functions because they are used to express the geometry or shape of the
element.
9. What are the characteristics of shape function?
The characteristics of the shape functions are follows:
1. The shape function has unit value at one nodal point and zero value at the
other nodes.
2. The sum of the shape function is equal to one.
10. Why polynomials are generally used as shape function?
Polynomials are generally used as shape functions due to the following reasons:
1. Differentiation and integration of polynomials are quite easy.
2. The accuracy of the results can be improved by increasing the order of the
polynomial.
3. It is easy to formulate and computerize the finite element equations.
11. Give the expression for element stiffness matrix.
Stiffness matrix [K] = [ B]T [D ][ D] dv
Where, [B] matrix is a strain displacement matrix
[D] matrix is stress, strain relationship matrix
12. Write down the expression of stiffness matrix for one dimensional element bar element.
AE 1 1
Stiffness matrix [K] =
l 1 1
Where,
A is the area of the bar element
E is the young’s modulus of the bar element
L is the length of the bar element](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fea2mark-141118025455-conversion-gate01/85/Fea-2-mark-4-320.jpg)
![ME 2353 – FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS
Page 5 of 11
13. State the properties of a stiffness matrix.
The properties of the stiffness matrix [K] are,
1. It is a symmetric matrix
2. The sum of the elements in any column must be equal to zero.
3. It i s an unstable element, so the determinant is equal to zero.
14. Write down the general finite element equation.
General finite element equation is,
{F}=[K]{u}
Where, {F} is a force vector
[K] is the stiffness matrix {u} is the
degrees of freedom
15. state the assumptions made in the case of truss element.
The following assumptions are made in the case of truss element,
1. All the members are pin jointed.
2. The truss is loaded only at the joints
3. The self weight of the members are neglected unless stated.
16. Write down the expression of stiffness matrix for a truss element
Where, A is the area
E is the young’s modulus
Le is the length of the elment
L,m are direction cosines
17. Write down the expression of shape function N and displacement u for one
dimensional bar element.
For on dimensional bar element,
Displacement function, u = N1 u1 + N2 u 2
Where, Shape function N1=l-x/l
N2=x/l
18. State the principle of minimum potential energy.
The total potential energy of an elastic body is defined as the sum of total strain
energy
U and the potential energy of the external forces, (W)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fea2mark-141118025455-conversion-gate01/85/Fea-2-mark-5-320.jpg)