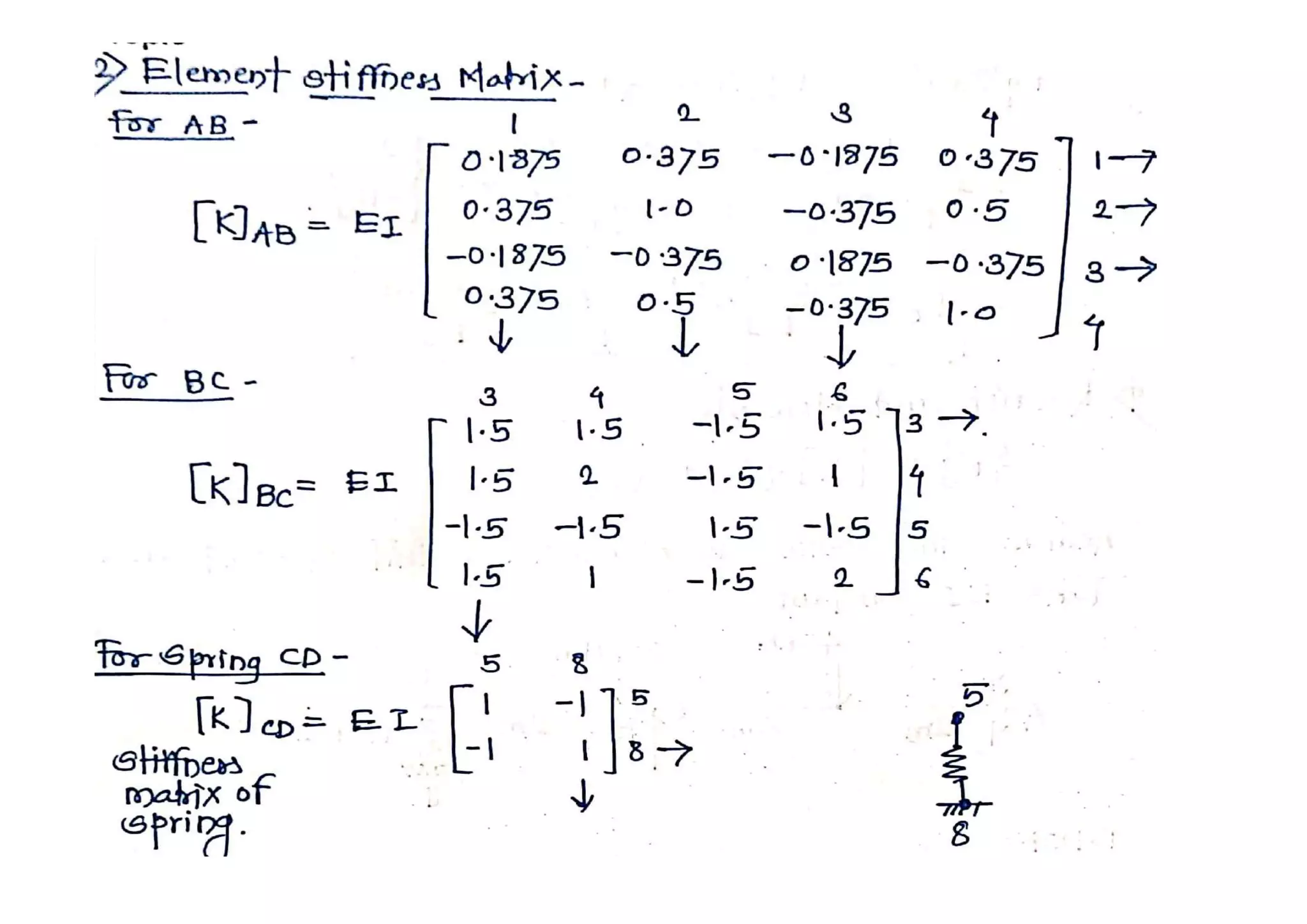Embed presentation
Downloaded 16 times
![FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF CONTINUOUS BEAM
Steps for the solution of continuous (Indeterminate) beams using
finite element method:
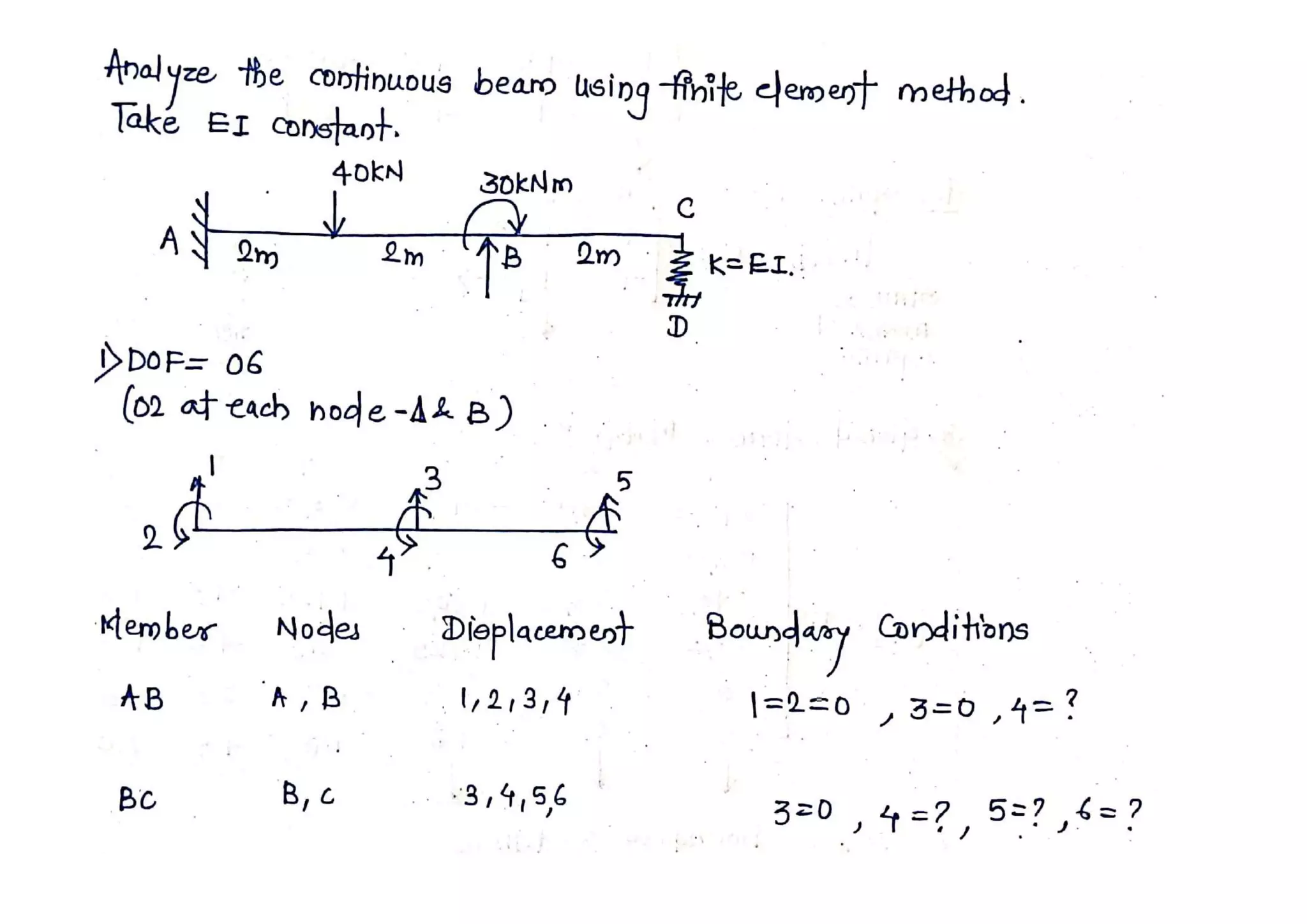
1. Divide the beam into number of elements (Take one member as one
element)
2. Identify total degrees of freedom (Two D.O.F. at each node,
translation and rotation)
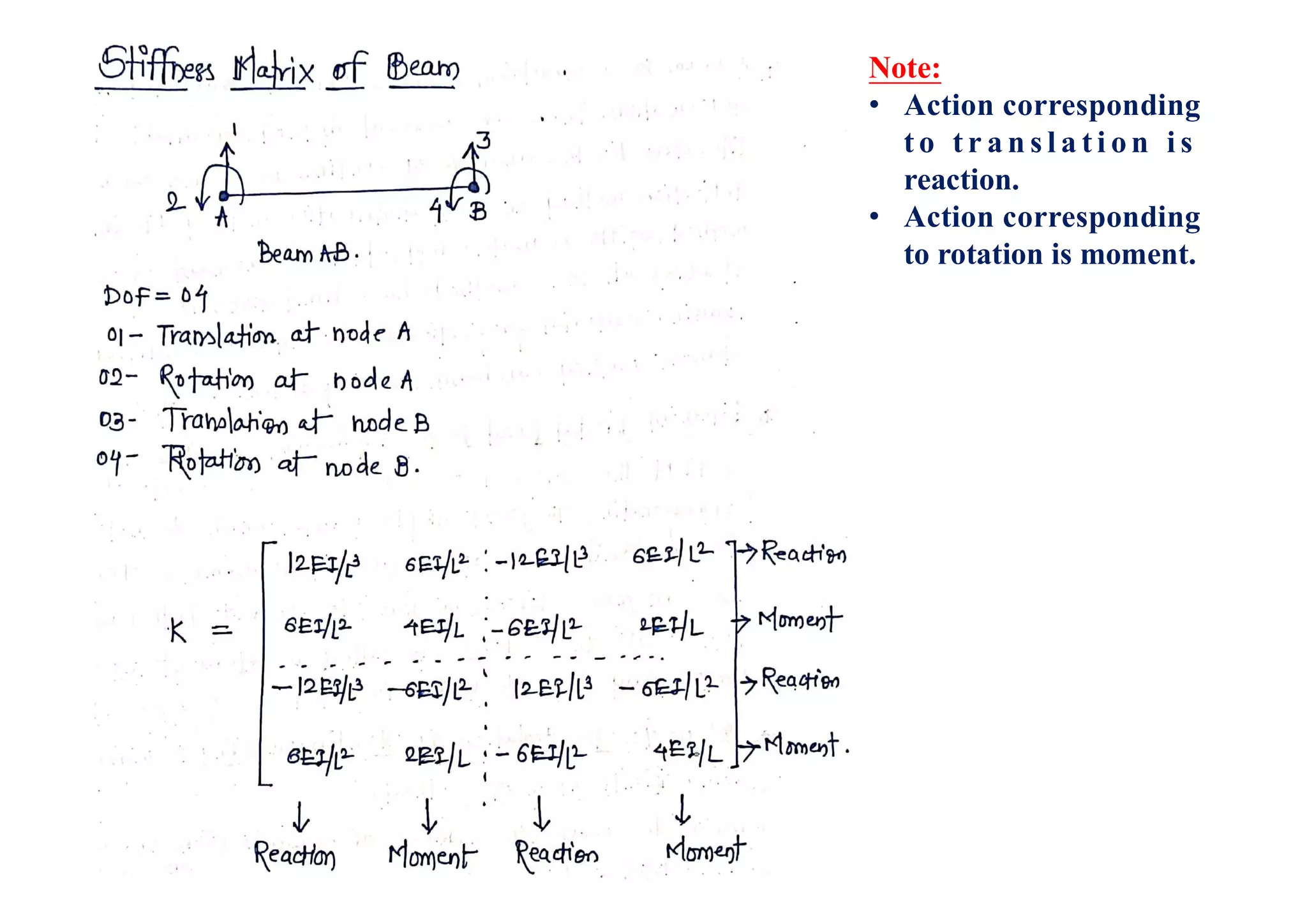
3. Determine stiffness matrices of all elements ([K]1, [K]2………)
4. Assemble the global stiffness matrix [K]
5. Impose the boundary conditions and determine reduced stiffness
matrix
6. Determine element nodal load vector [q] (Restrained structure)
7. Determine equivalent load vector [f]
8. Apply equation of equilibrium [K]{Δ}={f} and determine unknown
joint displacements.
9. Apply equation [K]{Δ}+[q] ={f} to determine reactions and
moments](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/beam5-201028061412/75/Stiffness-matrix-method-of-indeterminate-Beam5-2-2048.jpg)
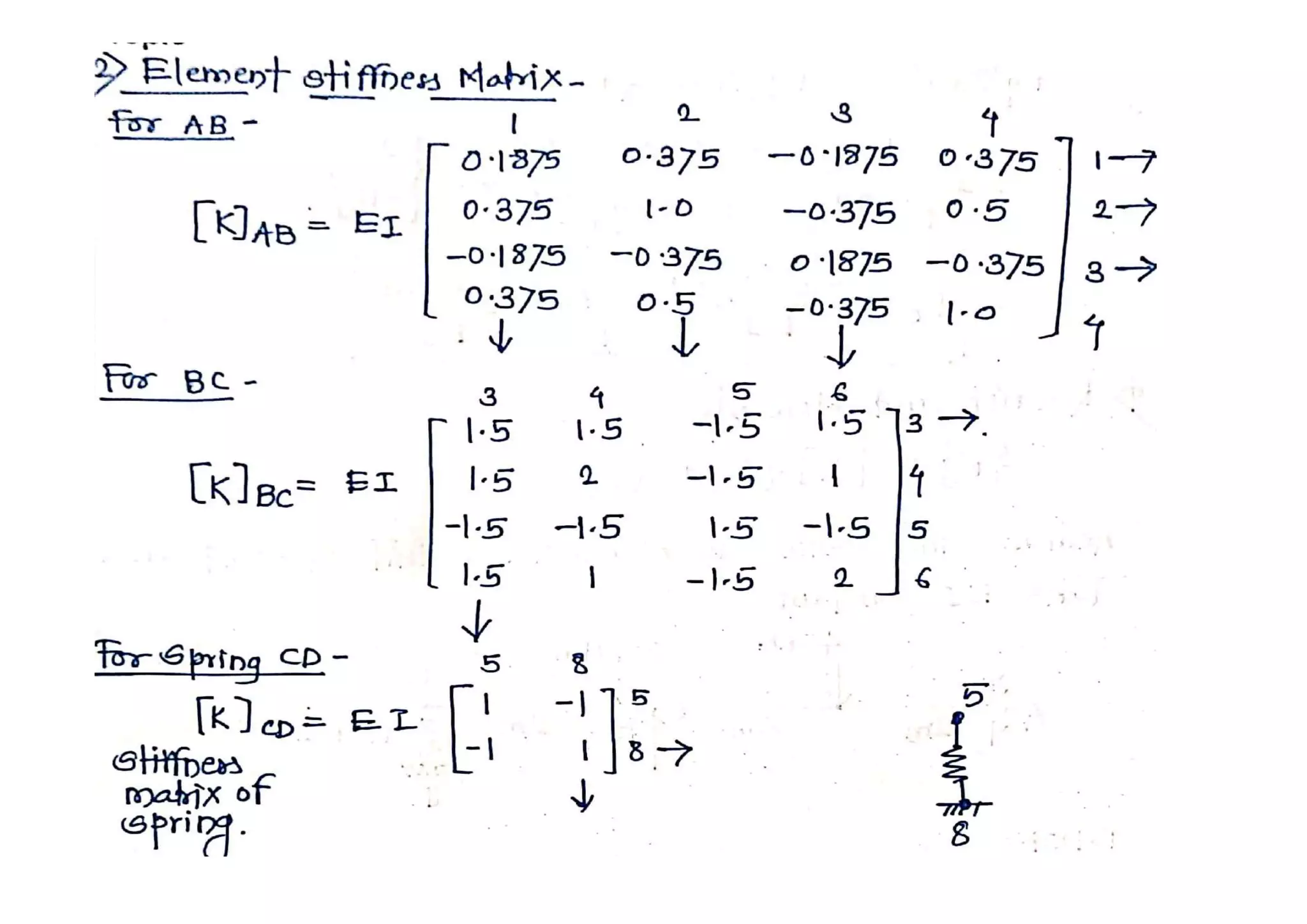

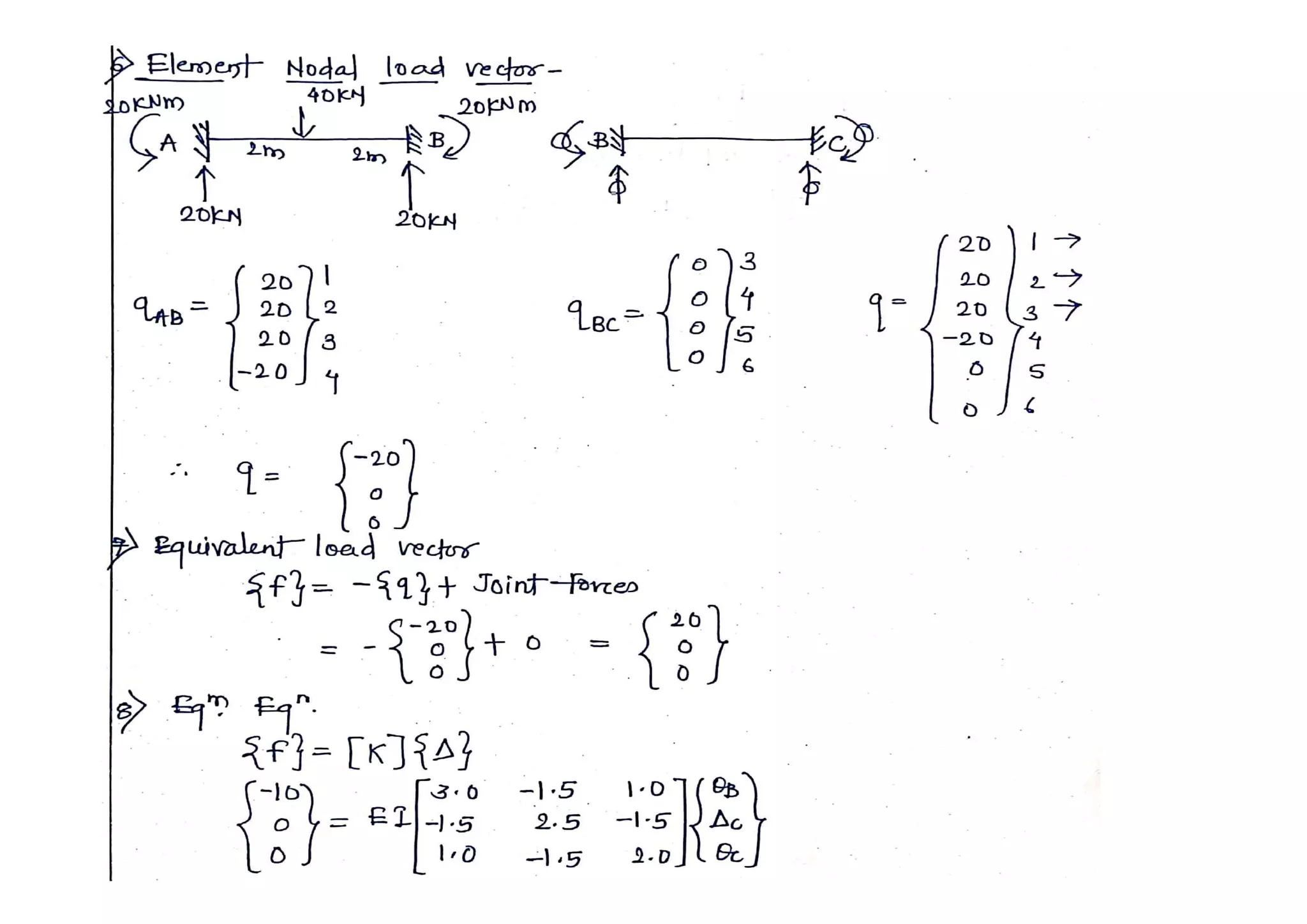
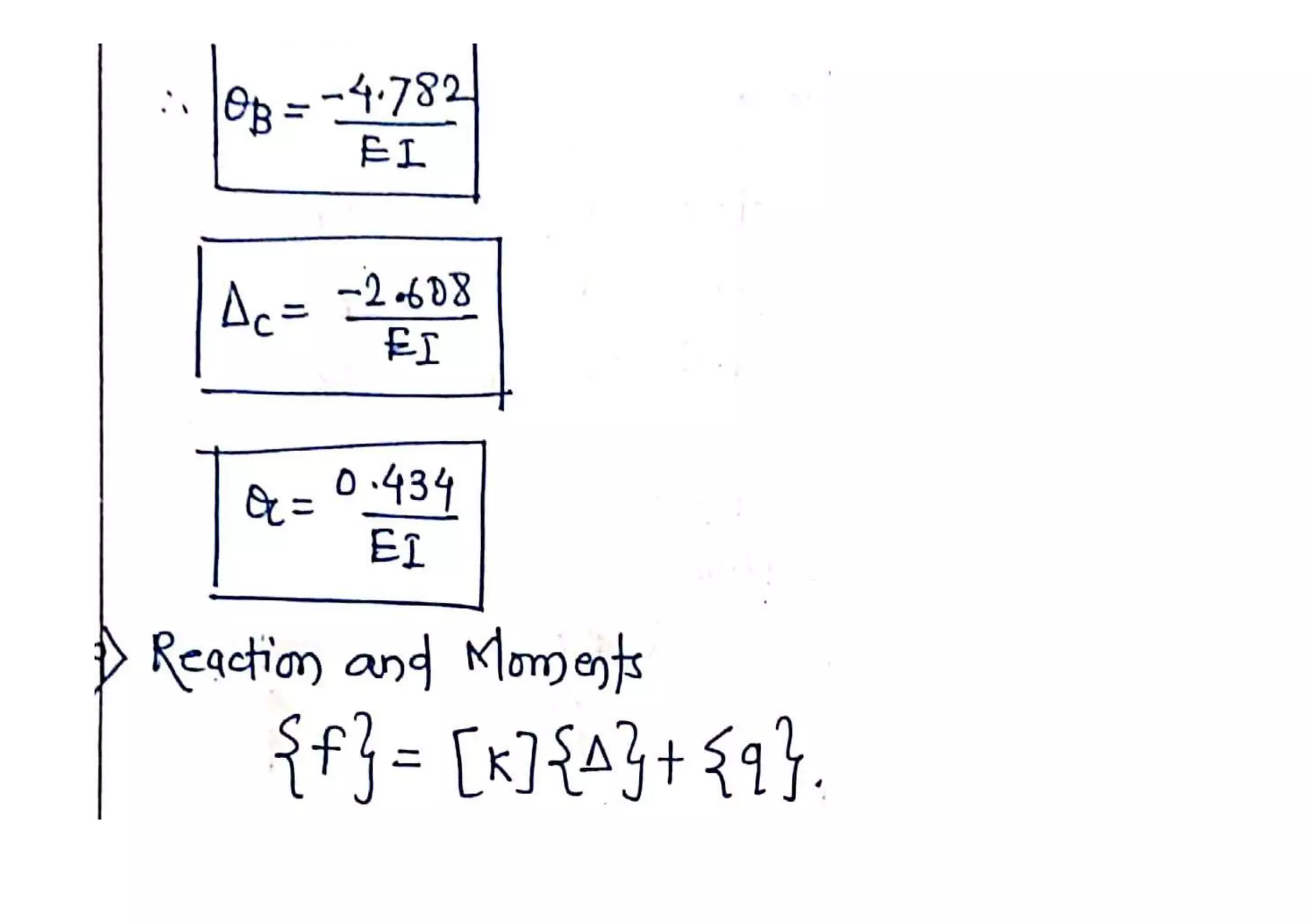

This document discusses the finite element analysis of continuous beams. It provides the steps to solve continuous or indeterminate beams using finite element methods. These steps include: 1) dividing the beam into elements, 2) identifying degrees of freedom, 3) determining element stiffness matrices, 4) assembling the global stiffness matrix, 5) imposing boundary conditions and determining the reduced stiffness matrix, 6) determining element nodal loads, 7) determining equivalent loads, 8) solving for unknown displacements using equilibrium equations, and 9) determining reactions and moments.

![FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF CONTINUOUS BEAM
Steps for the solution of continuous (Indeterminate) beams using
finite element method:
1. Divide the beam into number of elements (Take one member as one
element)
2. Identify total degrees of freedom (Two D.O.F. at each node,
translation and rotation)
3. Determine stiffness matrices of all elements ([K]1, [K]2………)
4. Assemble the global stiffness matrix [K]
5. Impose the boundary conditions and determine reduced stiffness
matrix
6. Determine element nodal load vector [q] (Restrained structure)
7. Determine equivalent load vector [f]
8. Apply equation of equilibrium [K]{Δ}={f} and determine unknown
joint displacements.
9. Apply equation [K]{Δ}+[q] ={f} to determine reactions and
moments](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/beam5-201028061412/75/Stiffness-matrix-method-of-indeterminate-Beam5-2-2048.jpg)