This tutorial discusses the Linux find command, which helps locate files based on attributes like name, permissions, size, and owner. It describes common uses like finding files owned by a user or with suid bits. The key flags and options for find are explained, such as -type to specify file type, -name for filename matching, and -size to filter by file size in bytes, kilobytes, or megabytes. Examples are provided to search the home directory for text files sized 20 bytes and to combine flags to find all 20-byte text files in the /usr directory. More advanced techniques will be covered in a future part 2 focused on penetration testing and privilege escalation.

![This flag is used to specify the file type.
● For example if you are searching for directory then we will write -type d
● If we are searching for the file type the we use -type
-name :
This flag lets us search a file using file name or the words that contain in the file name.
Ex: finding a file having name .txt at the end -name “*.txt”
-size: m,k,c
This flag is used to search the file with the help of the size of that file.
Options:
M for Mibs
K for kibs
C for bytes
Ex: finding a file having size 10 bits -size 20c
Till now we have learned about the flags and options.Now comes the interesting part of
practical execution.
To search a directory we need to use “/” after find command.
Some Examples:
● To search in the home directory : find /home …
● To search in /usr/bin directory : find /usr/bin...
● To search in the root directory then : find /root ..
Now we will combine all our flags to get the desired result.
See you just need to remember this while writing the command:
Where to search[Directory]
What to search[File specifications]
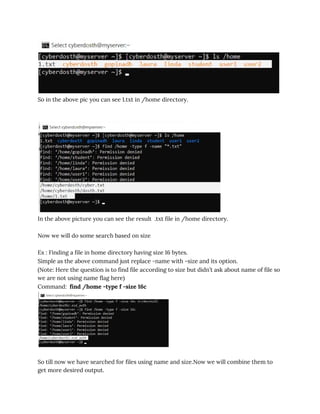
Example 1 : Finding a file in /home directory having last name “*.txt”
Now we need to search in /home dir then search for file type after finding file type then
we are going to find out using file name.
Command: find /home -type f -name “*.txt”
Check the Screenshots for more understanding.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/find-210211032724/85/Find-2-320.jpg)