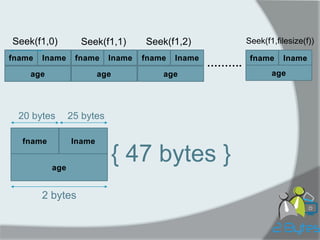
This document provides instructions for a programming assignment on binary files. It defines a record type for books with fields for number, title, author, publication date, and borrowed status. It describes a program that reads book data from a text file into a binary file, allows the user to specify borrowed books by number, updates the borrowed field in the binary file, and outputs a list of borrowed books. It also shows how to access specific records in the binary file using seek and read the publication dates of the 5th and last books.


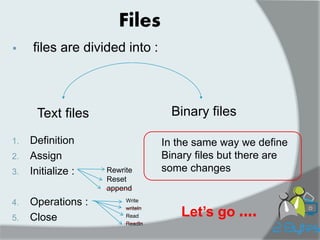
![Ex:
1. Type person=record
fname: string[20];
lname: string[25];
age: integer;
end;
Var f1 : file of person ;
2.Var f2: file of char ;
3.Type arr=array[1..100] of real;
Var f3: file of arr ;
Note : Binary files are similar to arrays but there are
Two different points …
A. Accessible to the element
B. Size ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2bytesprog2course2014c4binaryfiles-141203172904-conversion-gate01/85/2Bytesprog2-course_2014_c4_binaryfiles-5-320.jpg)




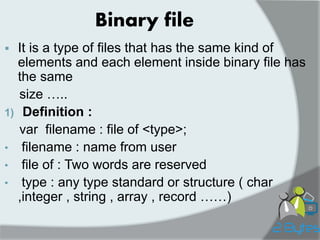
![Program 2_bytesprog
Uses wincrt
Type Date=record
day:1..31;
month:1..12;
year:1900..2013;
end;
Book=record
number : integer;
title,author: string[30];
pub_date : Data;
borrowed : Boolean;
end;
Var : f_text :text;
f_bin,temp :file of Book;
i,j,n : integer;
abook: book;
C: char; found: Boolean;
Borrowed_book : array of integer;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2bytesprog2course2014c4binaryfiles-141203172904-conversion-gate01/85/2Bytesprog2-course_2014_c4_binaryfiles-11-320.jpg)

![writeln('enter the total number of the lend books');
readln(n);
for i:=1 to n do
begin
writeln('enter the number of the book'); readln(Borrowed_book[i]);
end;
Assign(temp,’c:/myfile.bin)
reset(f_bin);
rewrite(temp);
While not eof(f_bin) do begin read(f_bin,abook); found:=false; i:=1; while i<=n and not found do begin if Borrowed_book[i]=abook.number then found:= true; i:=i+1; end; if found then abook.borrowed:=true; write(temp,abook); end;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2bytesprog2course2014c4binaryfiles-141203172904-conversion-gate01/85/2Bytesprog2-course_2014_c4_binaryfiles-13-320.jpg)



