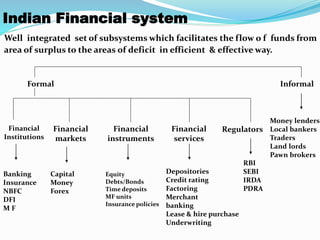
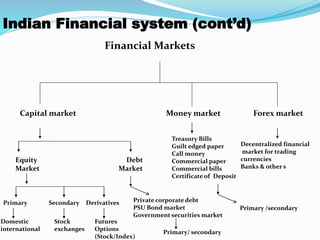
The document describes the evolution and components of the Indian financial system. It discusses how the system evolved from underdeveloped economies with low incomes and no financial intermediaries, to higher incomes with the birth of intermediaries like banks and mutual funds. The current system includes formal institutions regulated by entities like RBI and SEBI, as well as informal local markets. Key components of the system described include banking, insurance, capital markets, money markets, and various financial instruments and their roles in facilitating funds flow. Regulators like SEBI and their roles in developing, regulating and protecting the securities market are also summarized.