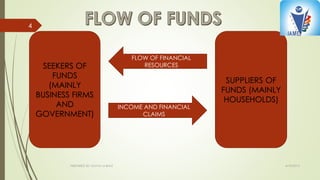
The document discusses India's financial system, which consists of three main parts: financial assets like loans and deposits, financial institutions like banks and mutual funds, and financial markets like the money market and capital market. It describes the evolution of India's financial system over three periods from 1949 to the present, noting the nationalization of banks in 1969, the financial repression of 1969-1991, and the major reforms beginning in 1991 in response to committee recommendations. The current system is largely deregulated and liberalized compared to the earlier regulated periods.