The document provides an overview of key financial statements used by companies:
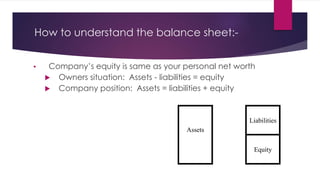
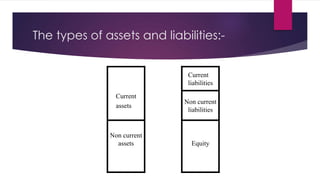
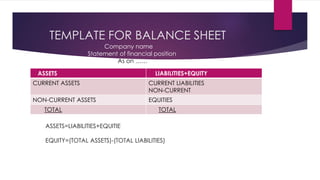
1) The balance sheet describes a company's financial position at a point in time, showing assets, liabilities, and equity. It ensures assets equal liabilities plus equity.
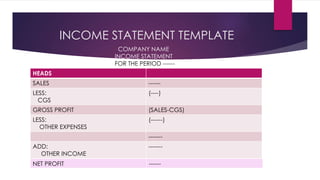
2) The income statement shows revenues, expenses, and profits/losses over a period of time. It calculates gross profit and operating income.
3) The statement of cash flows indicates changes in a company's cash position over time from operating, investing and financing activities.
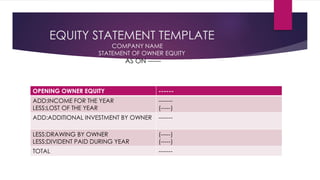
4) The statement of changes in equity outlines changes in shareholders' equity from profits, dividends, and additional investments. It connects to the balance sheet and income statement.