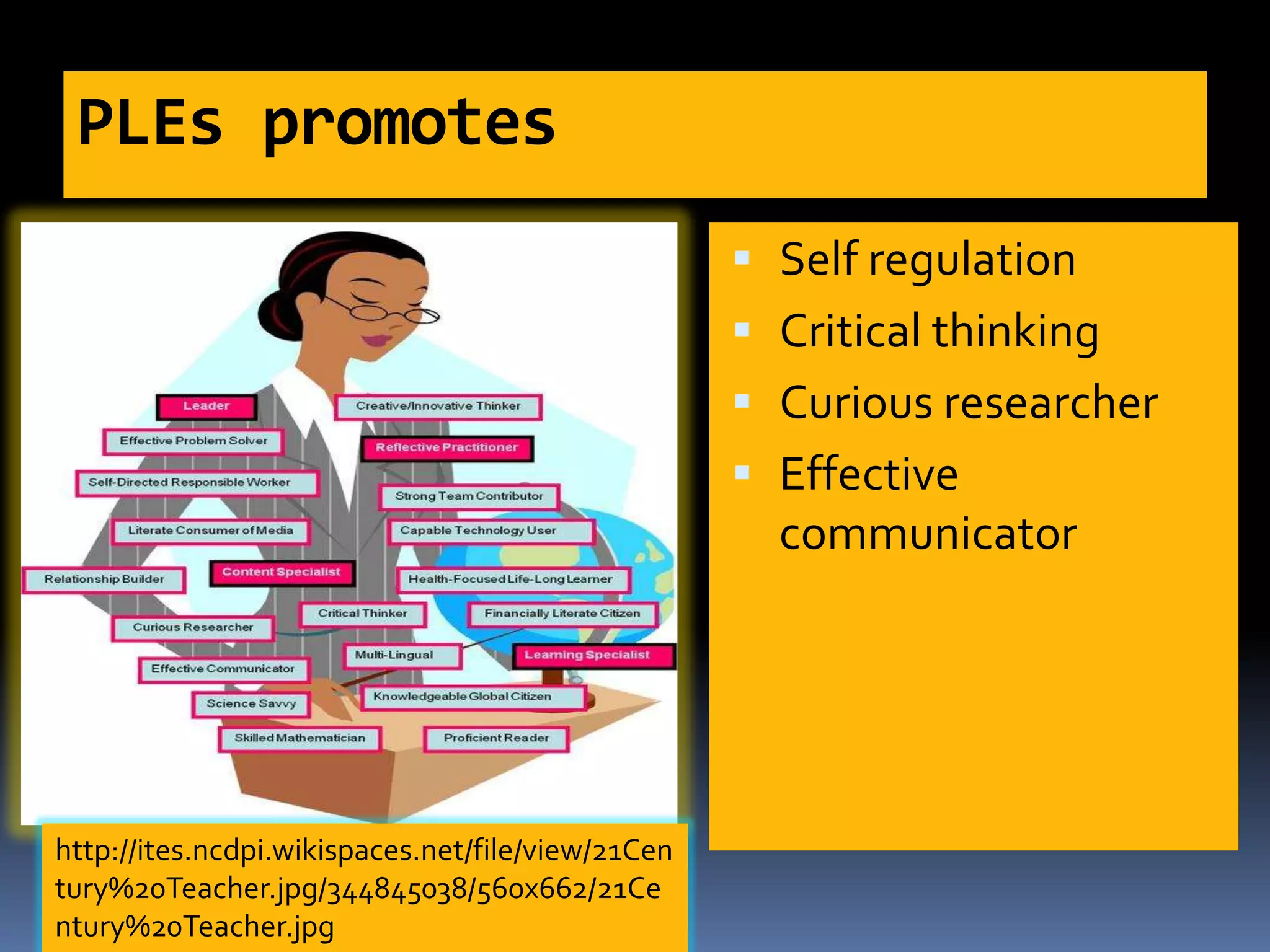
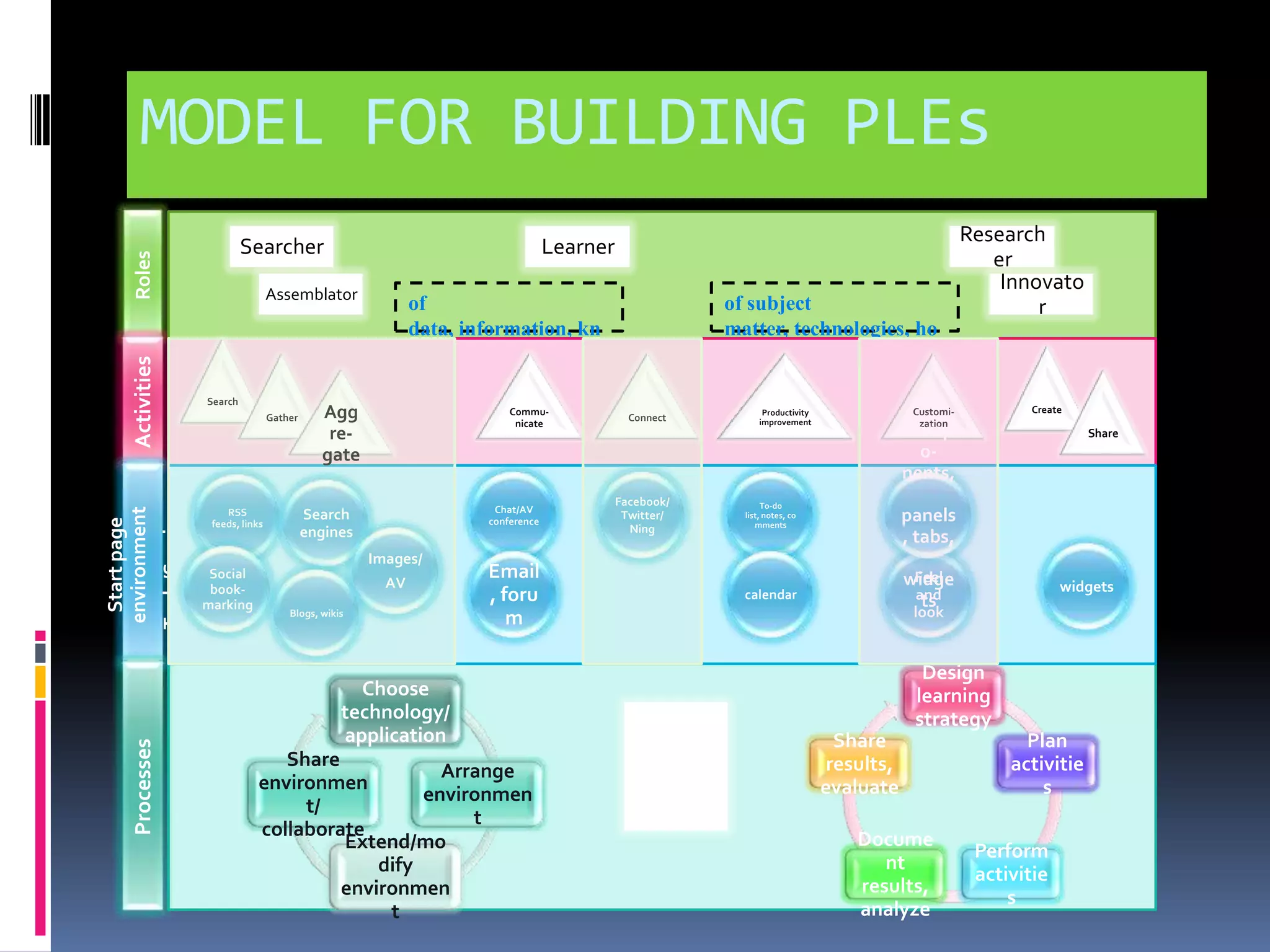
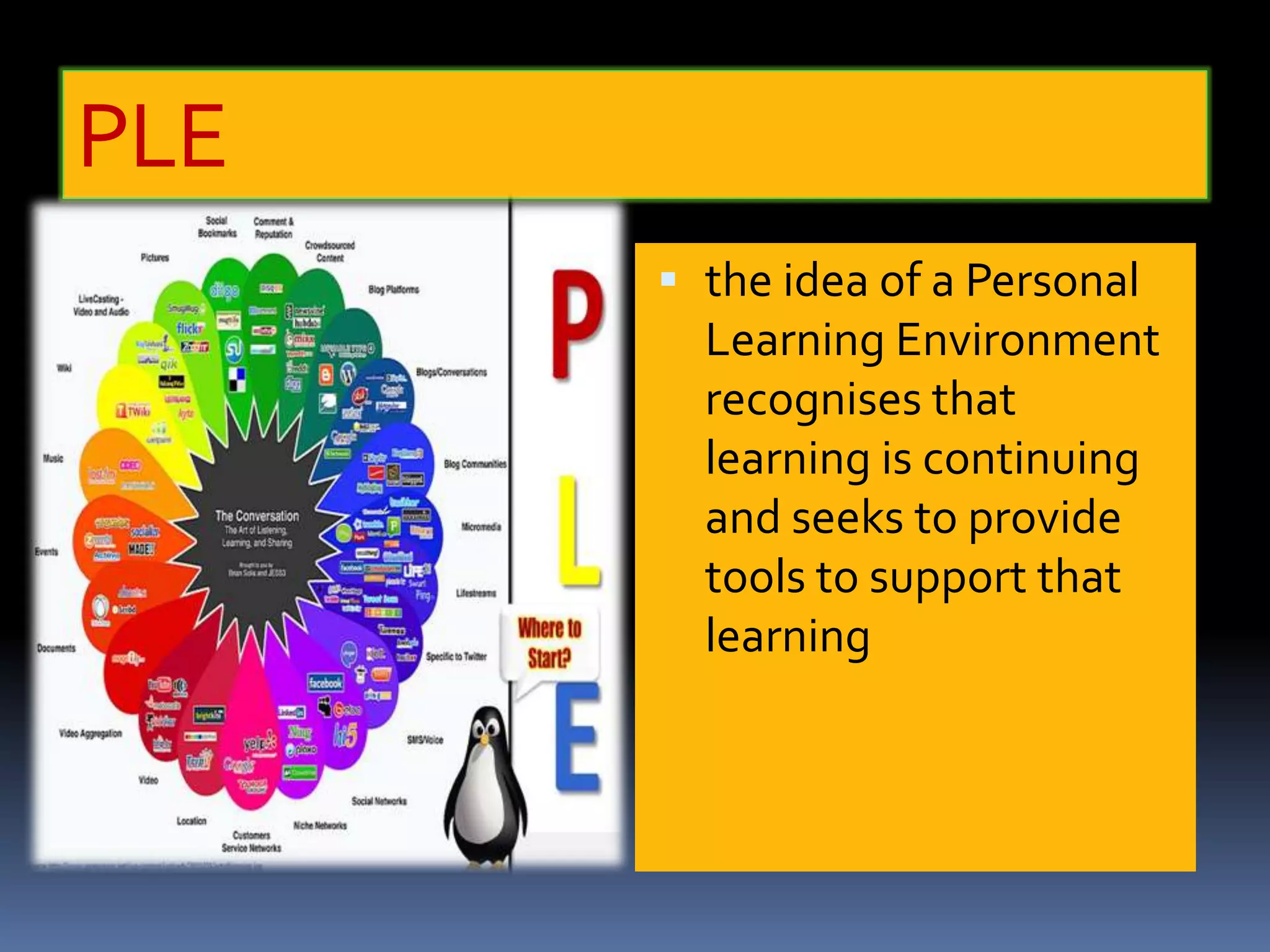
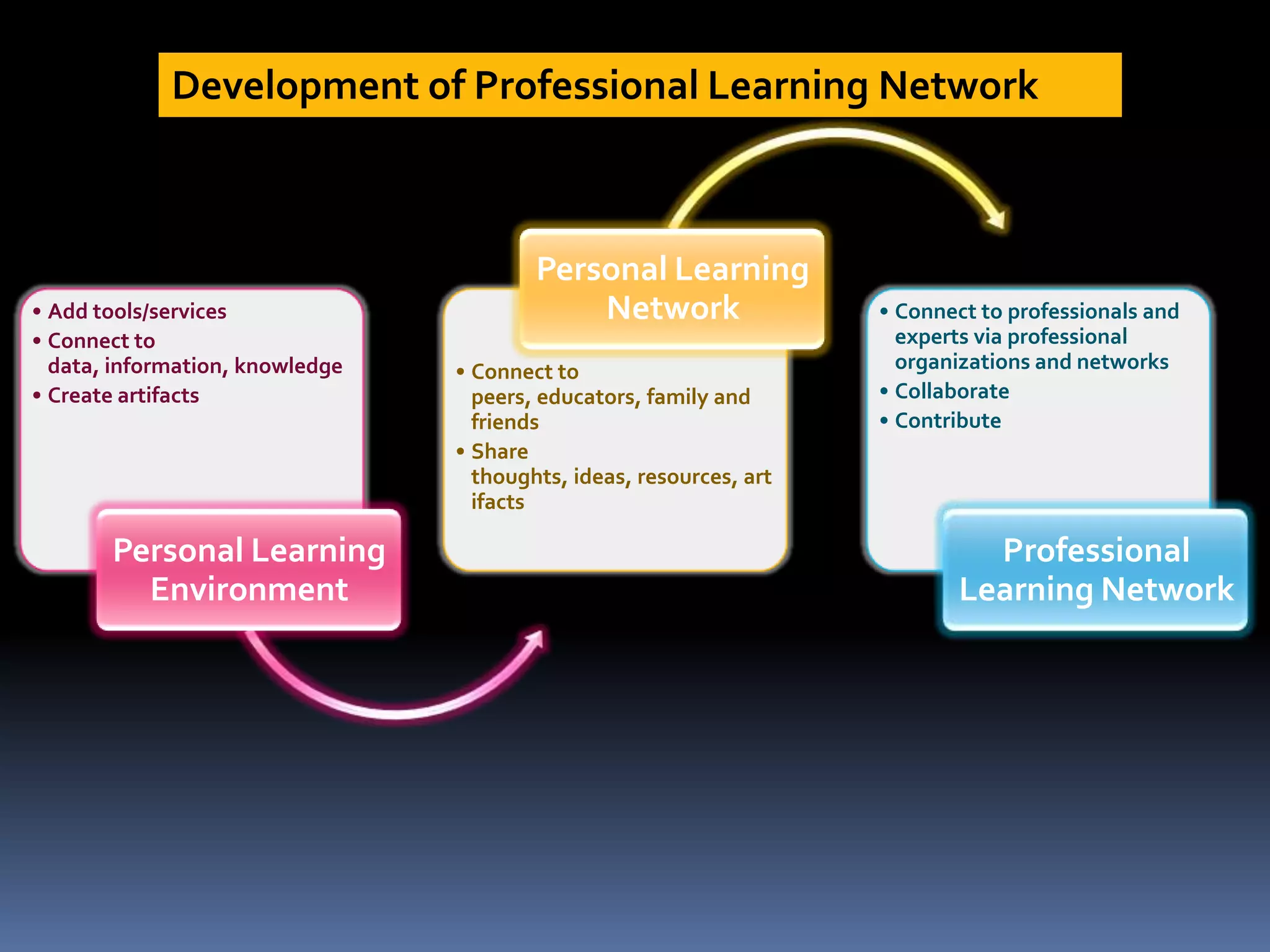
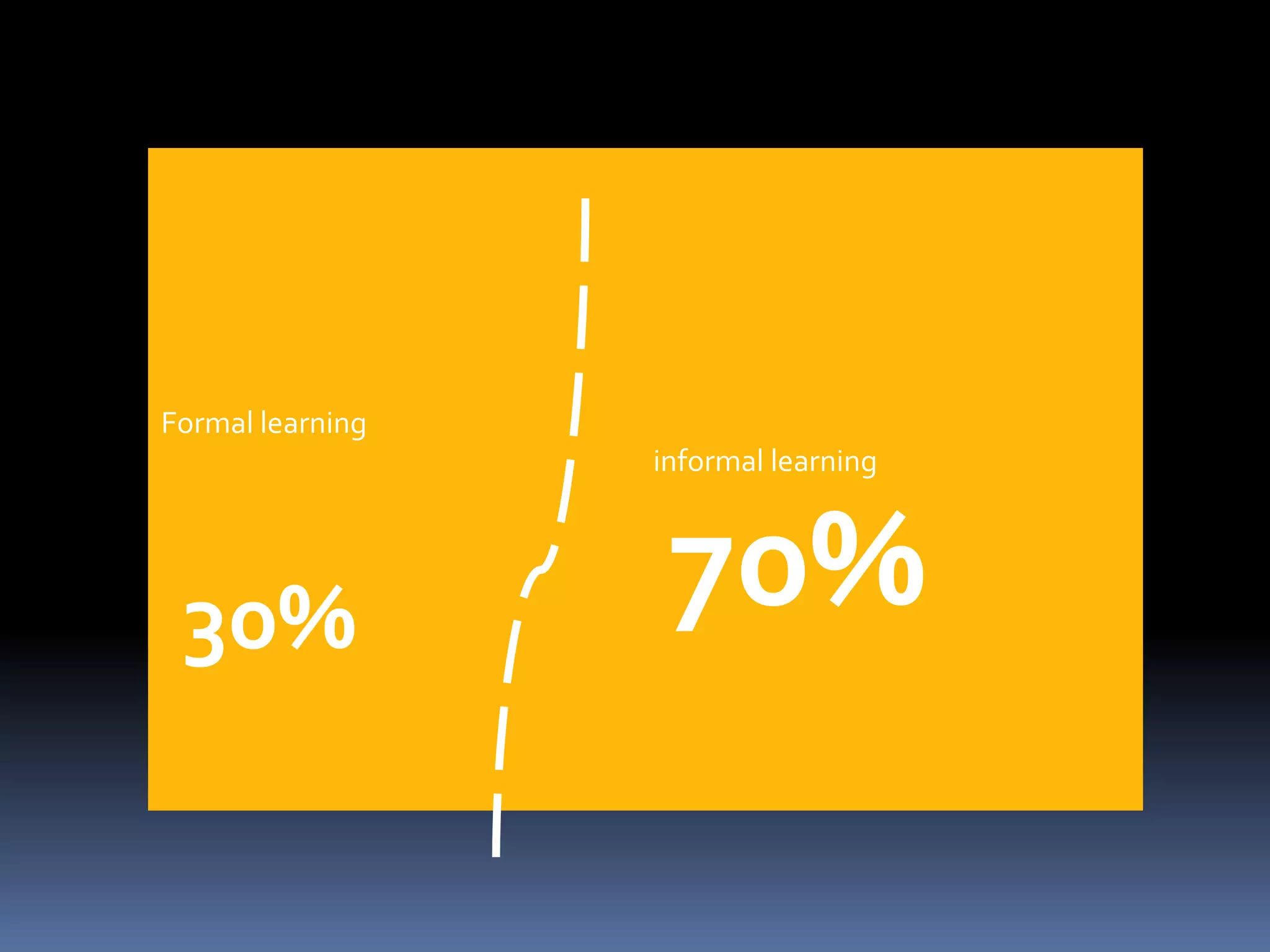
This document discusses personal learning environments (PLEs). PLEs promote self-regulation, critical thinking, being a curious researcher, and being an effective communicator. PLEs aim to analyze experience gained using Web 2.0 tools for competence development and professional networking. PLEs are based on the ideas that learning is ongoing, individuals self-organize their own learning across different contexts, and a single provider cannot provide all learning. PLEs use social web tools and recognize formal and informal learning.