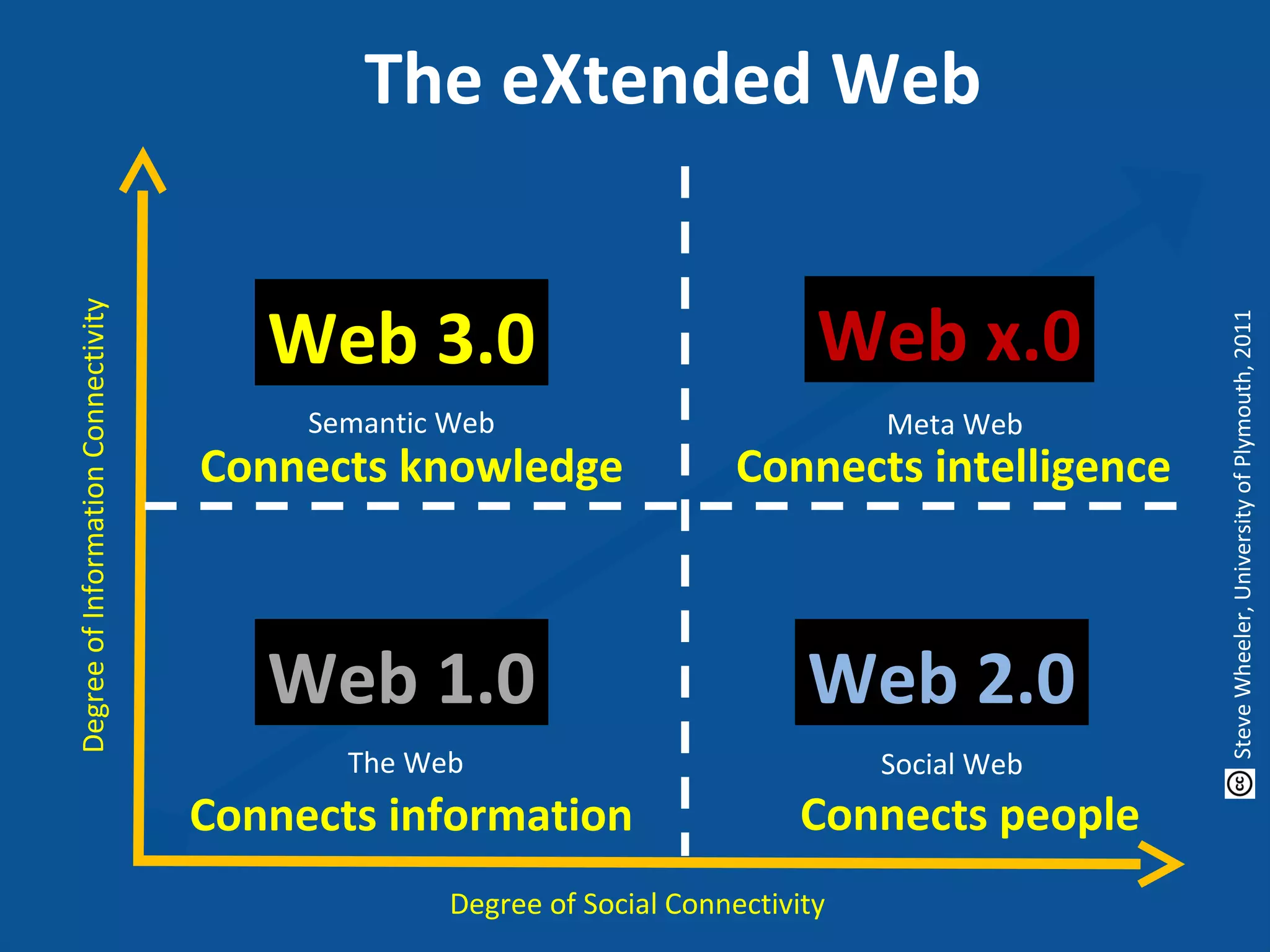
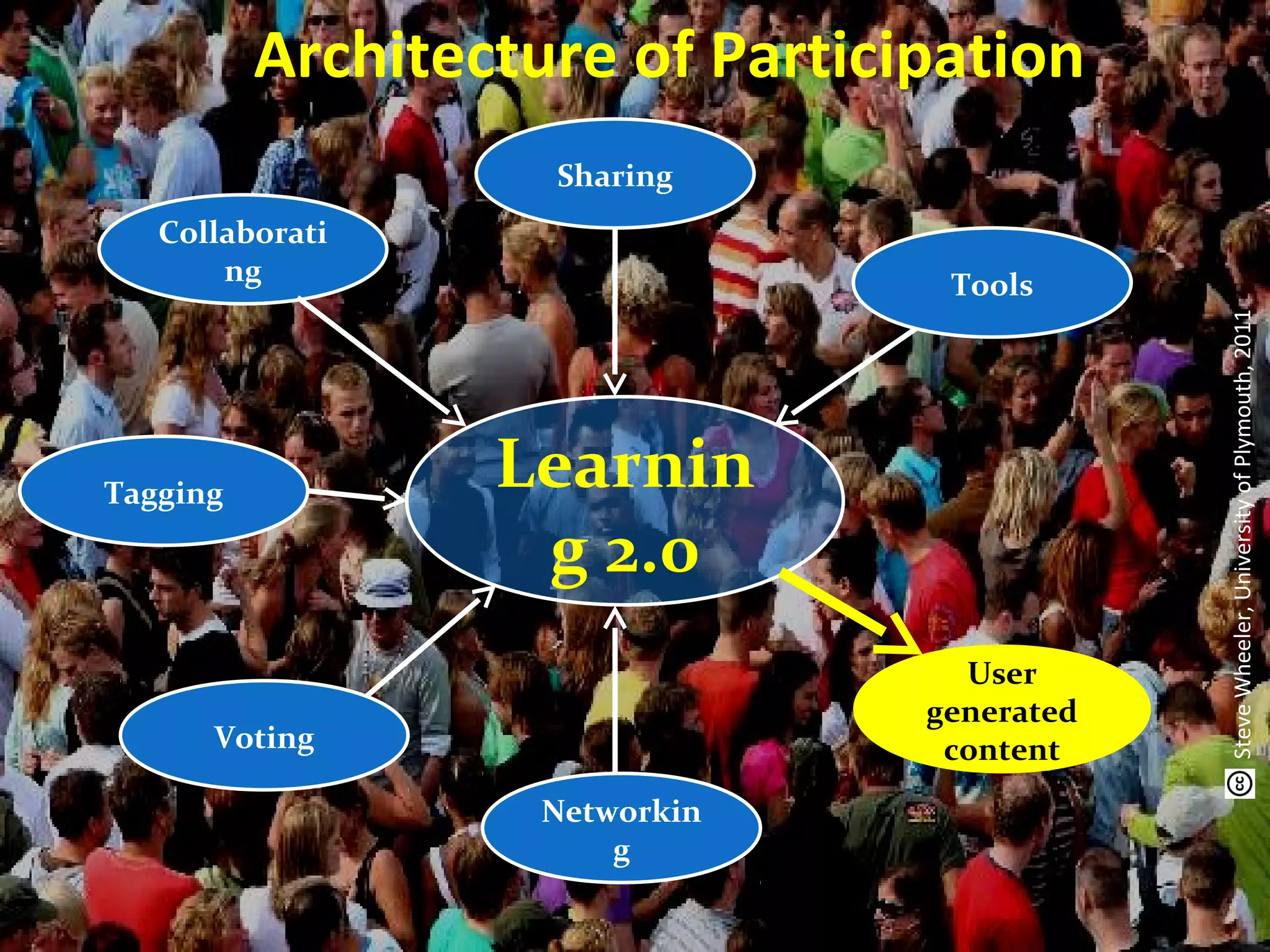
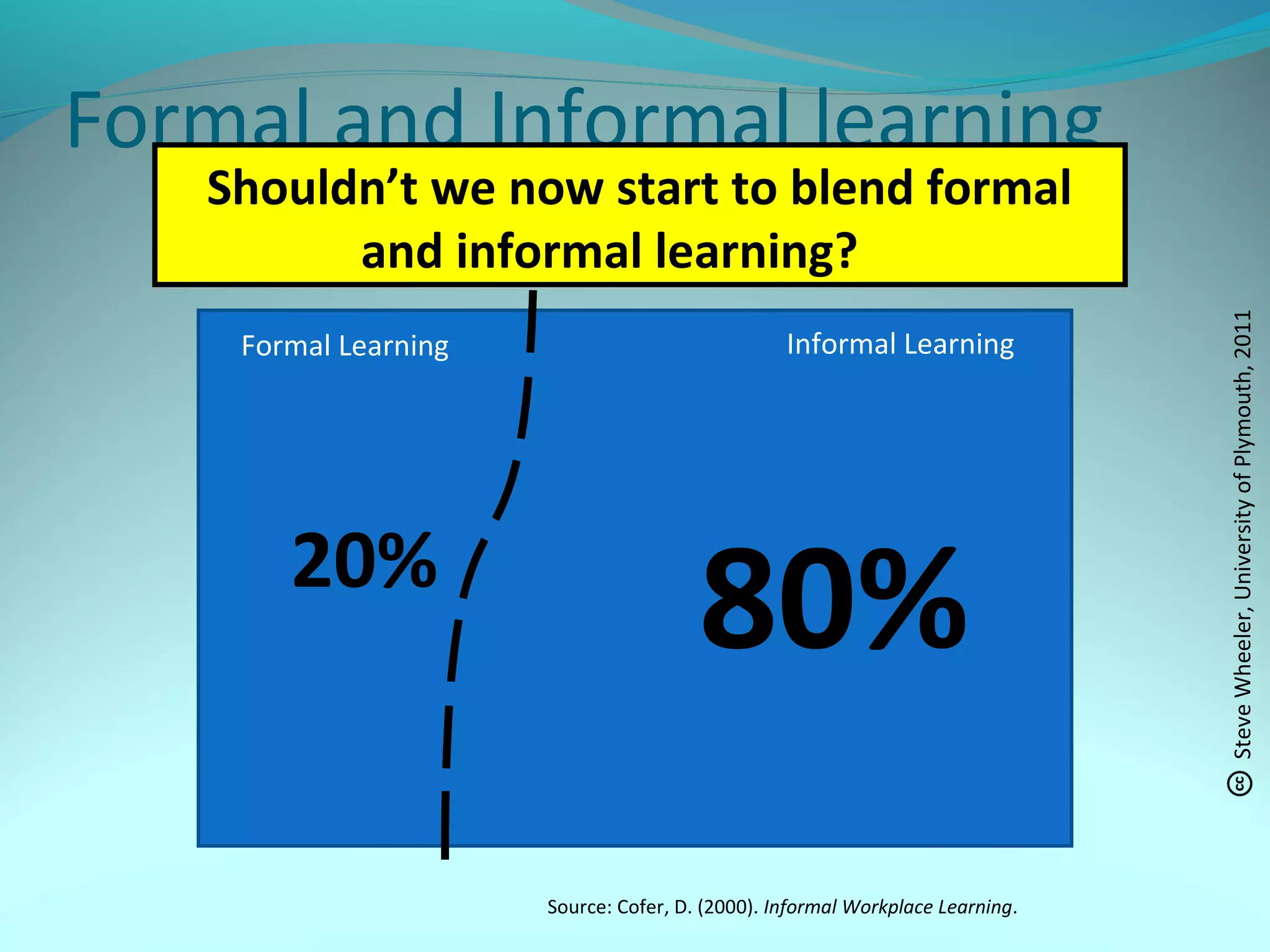
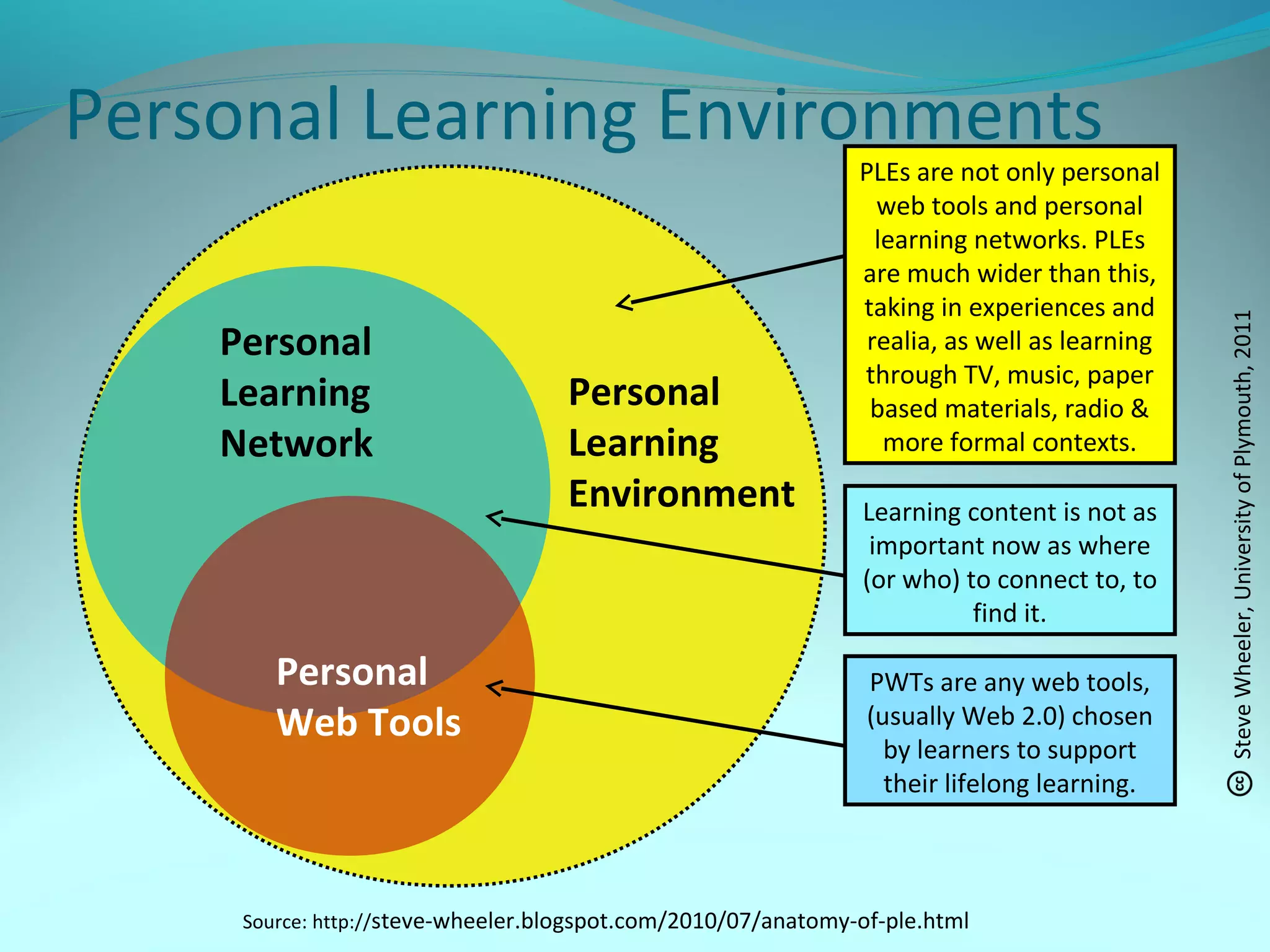
This document discusses personal learning networks (PLNs) and their potential to transform learning. It defines a PLN as involving an individual's goal, practices for organizing relevant content sources to accomplish goals. PLNs are based on Web 2.0 and allow learning through connections with people, services and resources. The document outlines challenges of PLNs in challenging existing education systems and institutions, and argues that PLNs can develop dispersed, networked learning by utilizing various Web 2.0 tools and transforming how one acquires knowledge.