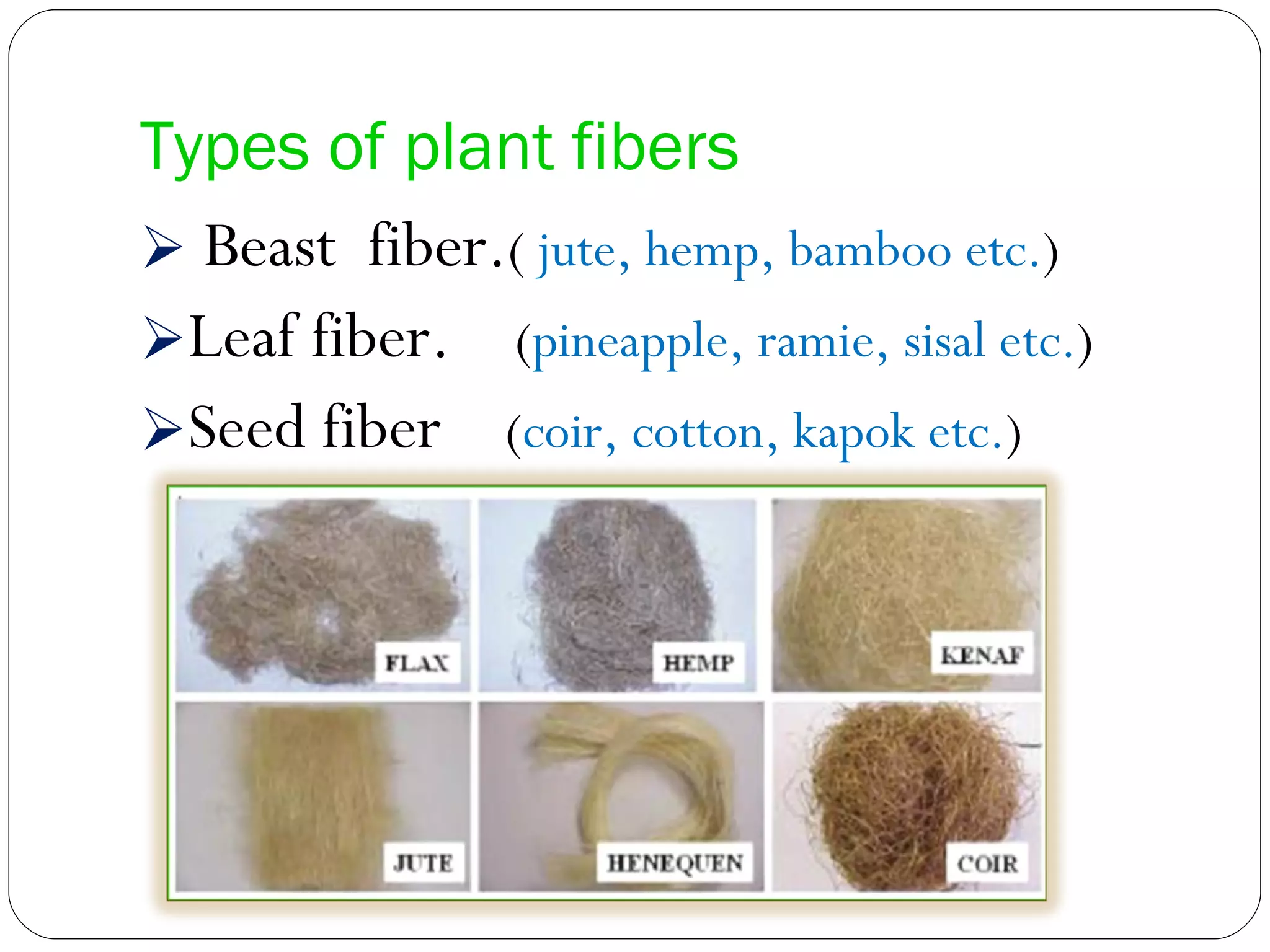
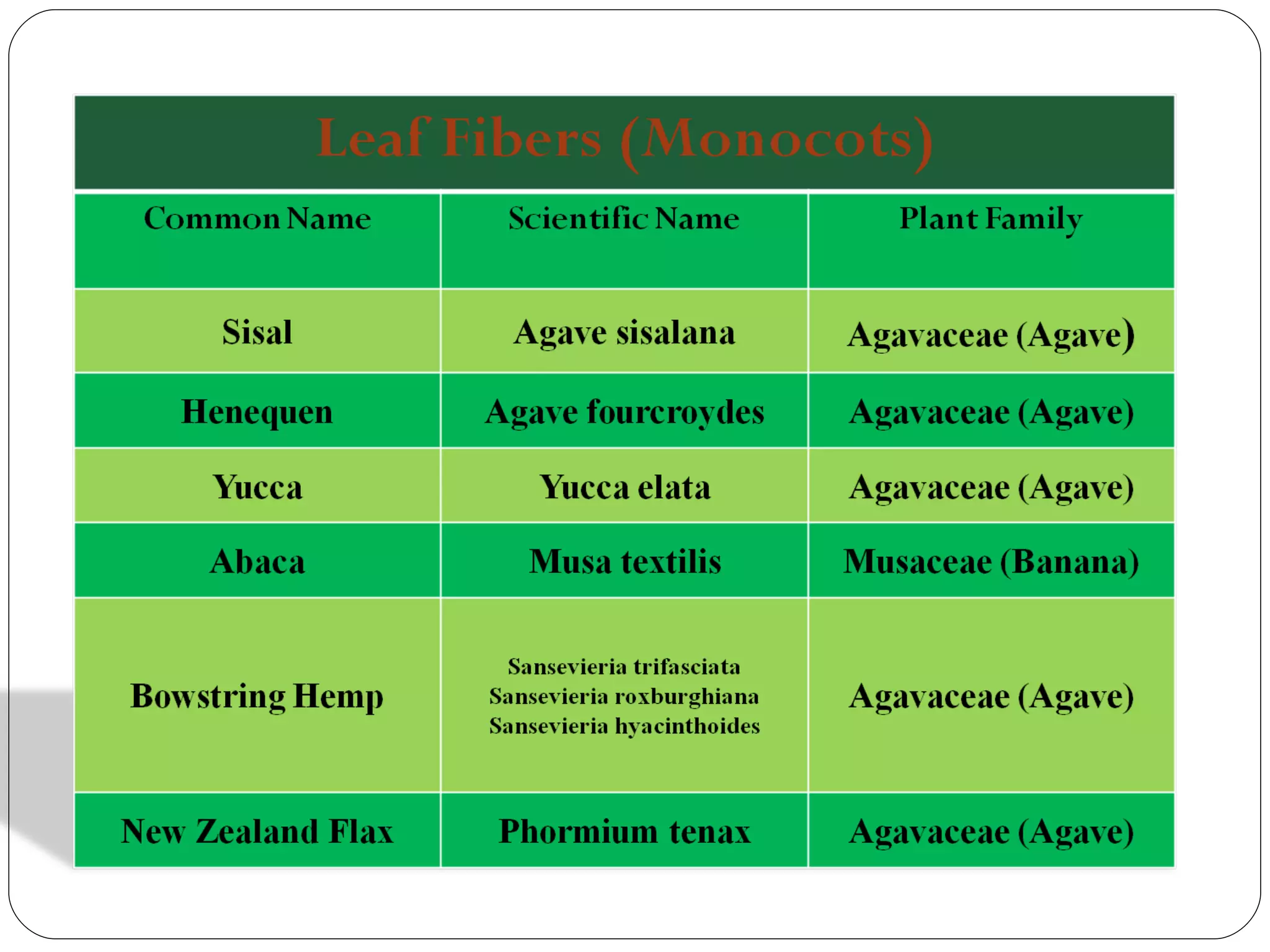
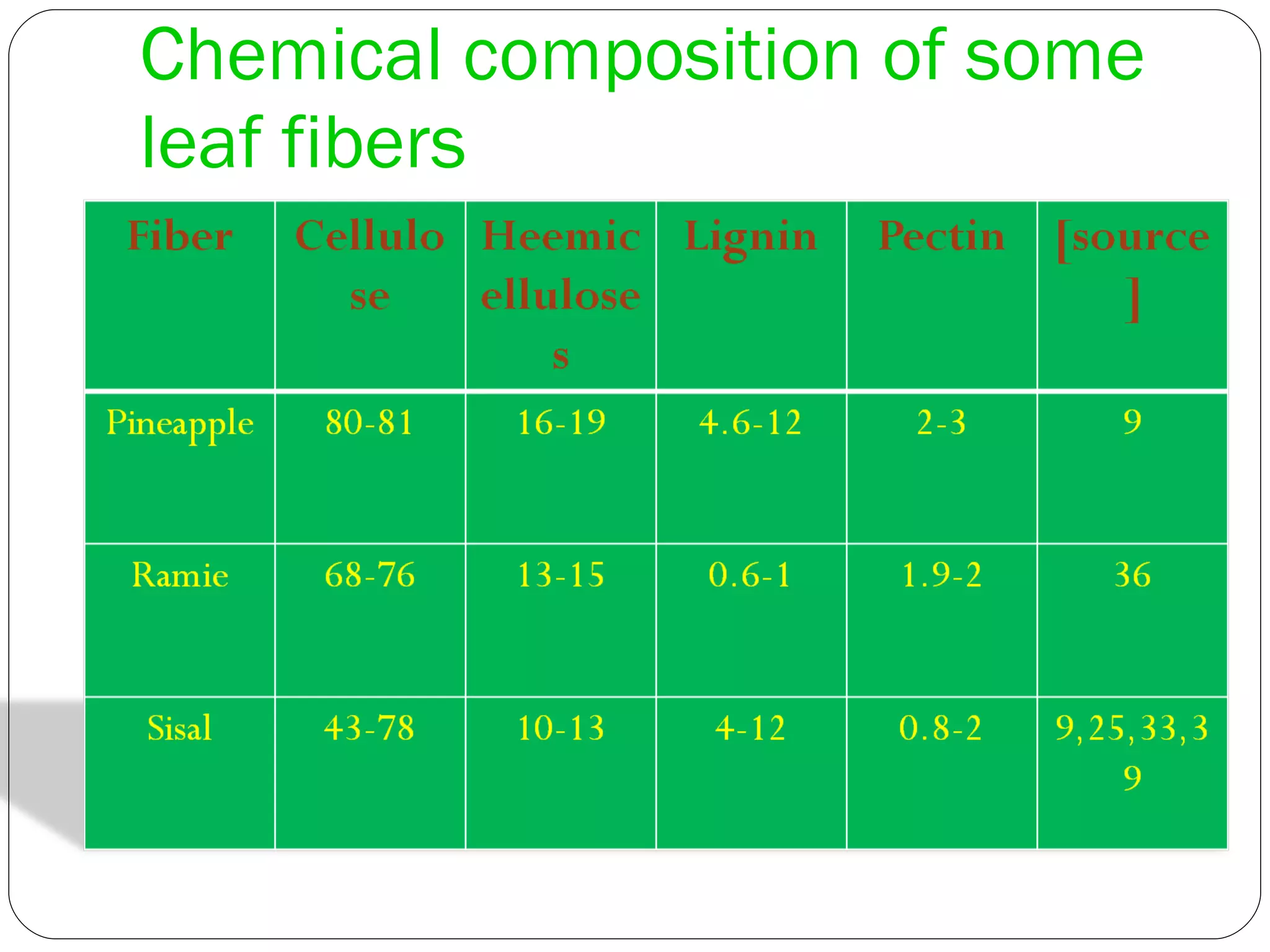
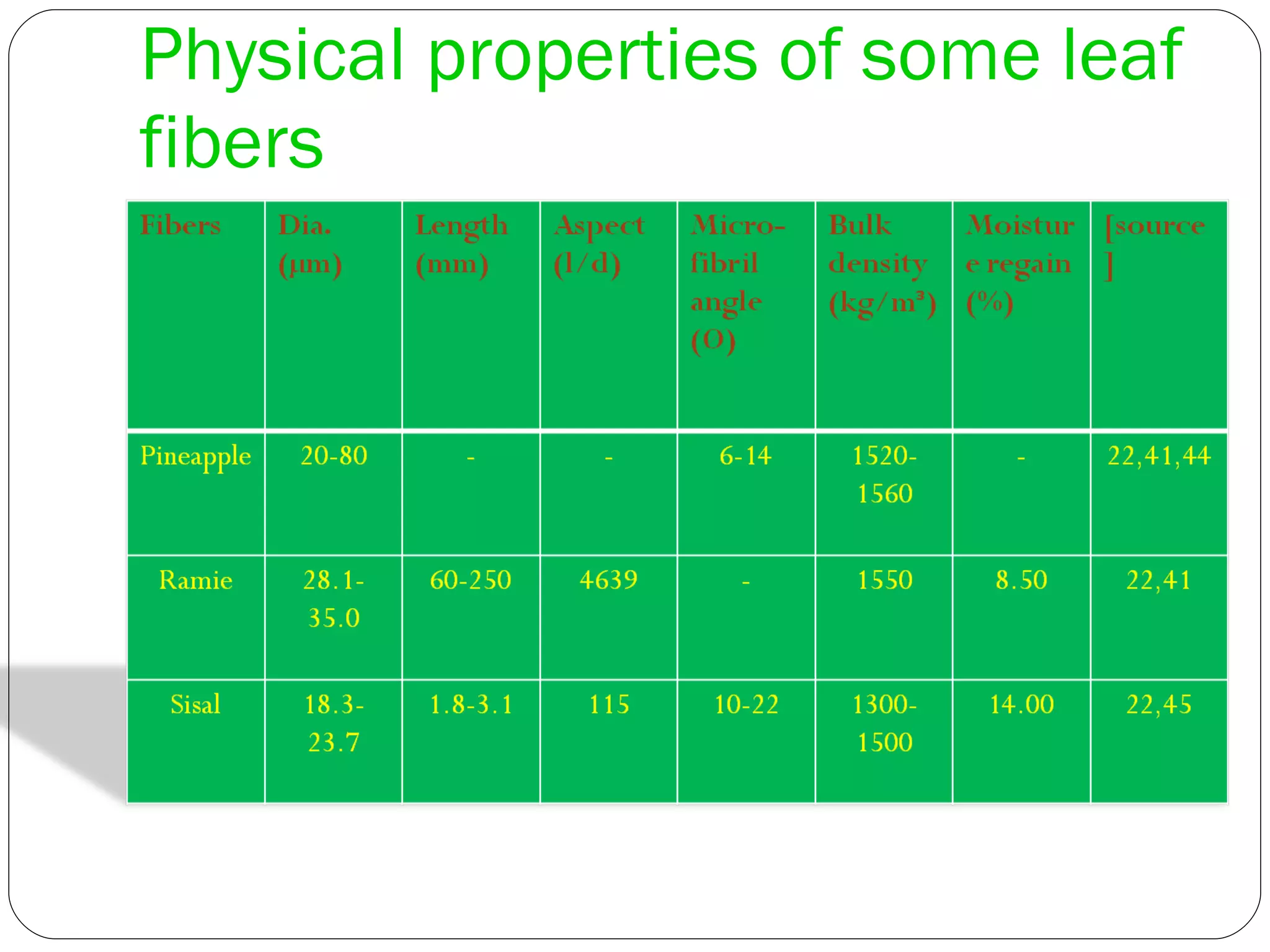
This document discusses various leaf fibers, including their sources, properties, and applications. It provides details on sisal, pineapple, banana, agave, and other leaf fibers. Sisal fibers are extracted through retting and used to make ropes, twine, and composites. Pineapple fibers come from pineapple leaves and are used for textiles. Banana fibers have various applications including textiles, paper, and purification. Agave fibers are extracted through decortication and used for ropes, mats, and non-woven fabrics. Overall, the document examines the sources, extraction processes, properties, and end uses of different leaf fibers.



























![References: Zarapkar, K.P. (2004), Zarapkar System of Cutting, Navaneet Publication (I) Ltd., Dantali, Gujarat, Pp. 172-174. Indian Textile Journal-2003, Non-Woven Fabric Application. Non–Wovens By BTRA [Monograph Series] www.altavista.com www.pfaf.org www.ibiblio.org www.google.com www.nnfcc.co.uk www.fibre2fashion.com http://www.adventurenetwork.com/ http://www.resil.com/ www.indiantextilejournal.com/articles/ www.techexchange.com/thelibrary.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalleafprocessingpresantation2010-100622073617-phpapp01/75/Final-leaf-processing-presantation-2010-36-2048.jpg)
