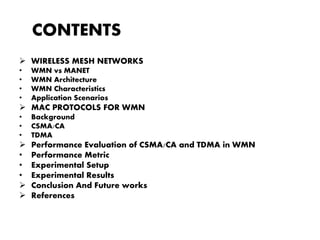
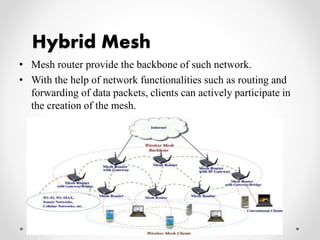
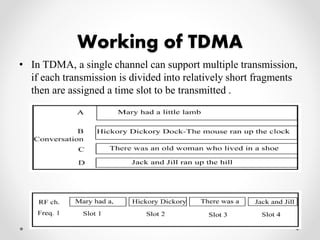
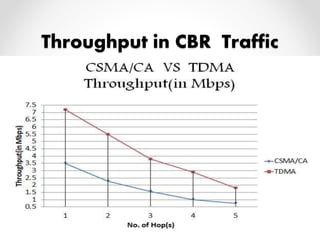
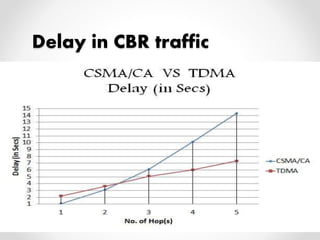
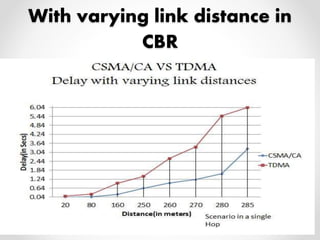
This document summarizes a project presentation on analyzing the performance of CSMA/CA and TDMA MAC protocols in wireless mesh networks. It first provides background on wireless mesh networks and describes their architecture and characteristics. It then discusses CSMA/CA and TDMA protocols and how they work. The project involved simulating a wireless mesh network topology using NS-2 and evaluating the performance of the two protocols based on metrics like throughput, delay, and packet loss under varying conditions like number of hops and link distance. The results showed that TDMA performance was better than CSMA/CA. The conclusion recommends further analysis using directional antennas.







![Client Mesh [1]
Client meshing provides peer-to-peer networks among
client devices. Here no such mesh router is required. Client will
act like a mesh router by relaying the packets.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/final-141130144915-conversion-gate01/85/Performance-analysis-of-CSMA-CA-and-TDMA-MAC-protocols-in-Wireless-Mesh-Networks-9-320.jpg)


![Mac Protocols for WMN
• Objectives
o Maximize channel utilization.
o Minimize channel access delay.
• CSMA/CA : [4],[6],[8]
o It is a Random Access Protocol.
o It continuously senses the channel.
o Collision avoidance technique –
- Request to send/clear to send(RTS/CTS)
- Transmission](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/final-141130144915-conversion-gate01/85/Performance-analysis-of-CSMA-CA-and-TDMA-MAC-protocols-in-Wireless-Mesh-Networks-13-320.jpg)


![MAC protocols in WMN(cntd.)
TDMA: [3],[4],[7],[10]
• It is a channelization protocol.
• Each channel is allocated with a unique time slot.
• Three kinds of time slots-o
Control slots
o Contention slots
o Data slots](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/final-141130144915-conversion-gate01/85/Performance-analysis-of-CSMA-CA-and-TDMA-MAC-protocols-in-Wireless-Mesh-Networks-16-320.jpg)

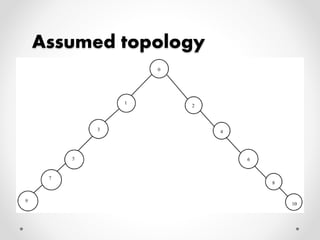
![Experimental Setup
• Performance of the assumed network topology has been
evaluated in terms of simulation in NS-2[5].
• The experiments were conducted to analyze the performance
of the CSMA/CA and TDMA MAC protocol.
• Table 1 specifies the various parameters considered along with
their values during the simulation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/final-141130144915-conversion-gate01/85/Performance-analysis-of-CSMA-CA-and-TDMA-MAC-protocols-in-Wireless-Mesh-Networks-21-320.jpg)










![REFERENCES
[1] Akyildiz, Ian F., XudongWang, and WeilinWang. "Wireless mesh networks: a survey." Computer networks
47.4 (2005): 445-487.
[2] Ian F. Akyildiz and Xudong Wang ,”Wireless Mesh Networks”:JohnWiley and Sons ,Ltd Publication
[3] Mihail L. Sichitiu,”Wireless Mesh Networks: Opportunities and Challenges”
[4] IEEE Standard for Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications,
Nov. 1997,P802.11.
[5] “Network Simulator- ns2.” http://www.isi.edu/nsnam/ns.
[6] Manshaei, H., et al. "Performance analysis of the IEEE 802.11 MAC and physical layer protocol." World of
Wireless Mobile and Multimedia Networks, 2005. WoWMoM 2005. Sixth IEEE International Symposium on a.
IEEE, 2005.
[7] Akyildiz, Ian F., et al. "Medium access control protocols for multimedia traffic in wireless
networks." Network, IEEE 13.4 (1999): 39-47.
[8] Bianchi, Giuseppe, Luigi Fratta, and Matteo Oliveri. "Performance evaluation and enhancement of the
CSMA/CA MAC protocol for 802.11 wireless LANs."Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications,
1996. PIMRC'96., Seventh IEEE International Symposium on. Vol. 2. IEEE, 1996.
[9] Perkins, Charles E. Ad hoc networking. Addison-Wesley Professional, 2008.
[10] Sen, Sayandeep, and Bhaskaran Raman. "Long distance wireless mesh network planning: problem
formulation and solution." Proceedings of the 16th international conference on World Wide Web. ACM, 2007.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/final-141130144915-conversion-gate01/85/Performance-analysis-of-CSMA-CA-and-TDMA-MAC-protocols-in-Wireless-Mesh-Networks-35-320.jpg)
