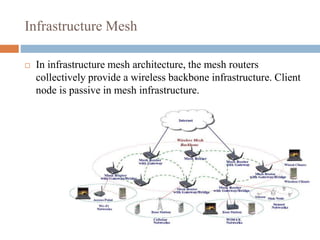
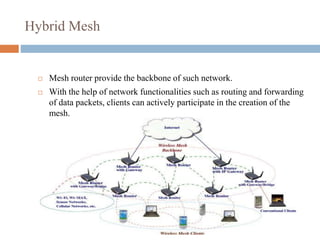
This document provides an overview of wireless mesh networks (WMNs). It discusses the types of nodes in WMNs including wireless mesh routers and mesh clients. It describes the different architectures of WMNs and characteristics such as low cost, integration capabilities, and applications like broadband networking. Key challenges are also addressed around developing high-capacity radio interfaces and resource management. The document serves as an introduction to WMNs covering topics from architecture and standards to research opportunities.