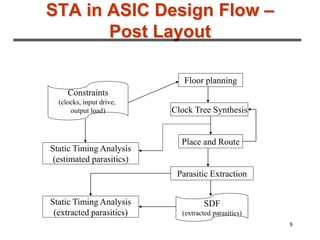
1. Static timing analysis is a methodology for verifying timing characteristics of a design without test vectors, which is faster than simulation and guarantees 100% coverage of timing paths.
2. It involves breaking a circuit into timing paths, calculating the delay of each path, and checking if delays meet constraints. Timing paths are grouped by controlling clocks.
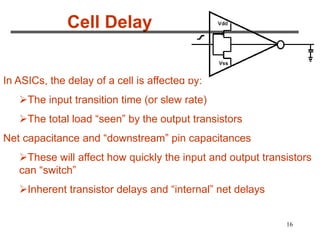
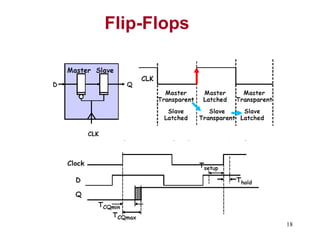
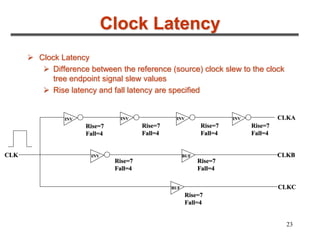
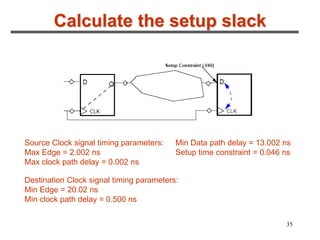
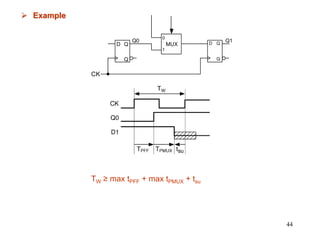
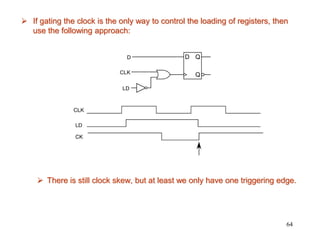
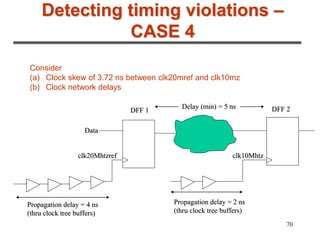
3. The maximum clock frequency is limited by flip-flop and gate delays. Clock skew between flip-flops must be less than the minimum setup/hold times to meet timing.