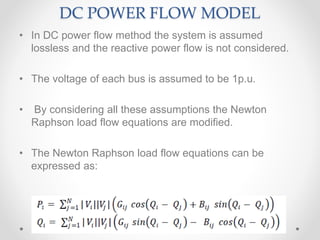
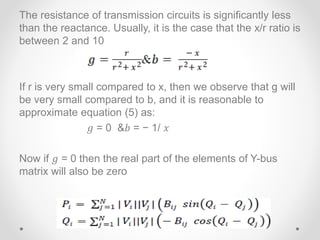
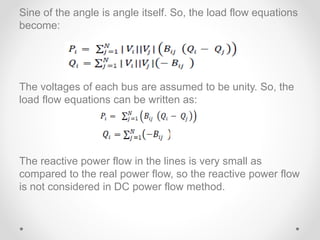
This document discusses available transfer capability (ATC) and methods for calculating ATC. It begins by defining ATC according to NERC as the remaining transmission capacity for commercial activity over already committed uses. It then lists three main methods for calculating ATC: (1) continuation power flow, (2) optimal power flow, and (3) repeated power flow. The document goes on to provide more details about each method, including their strengths and weaknesses. It also discusses AC and DC power flow methods for calculating ATC, noting the DC method only considers real power flow while AC incorporates reactive power as well.