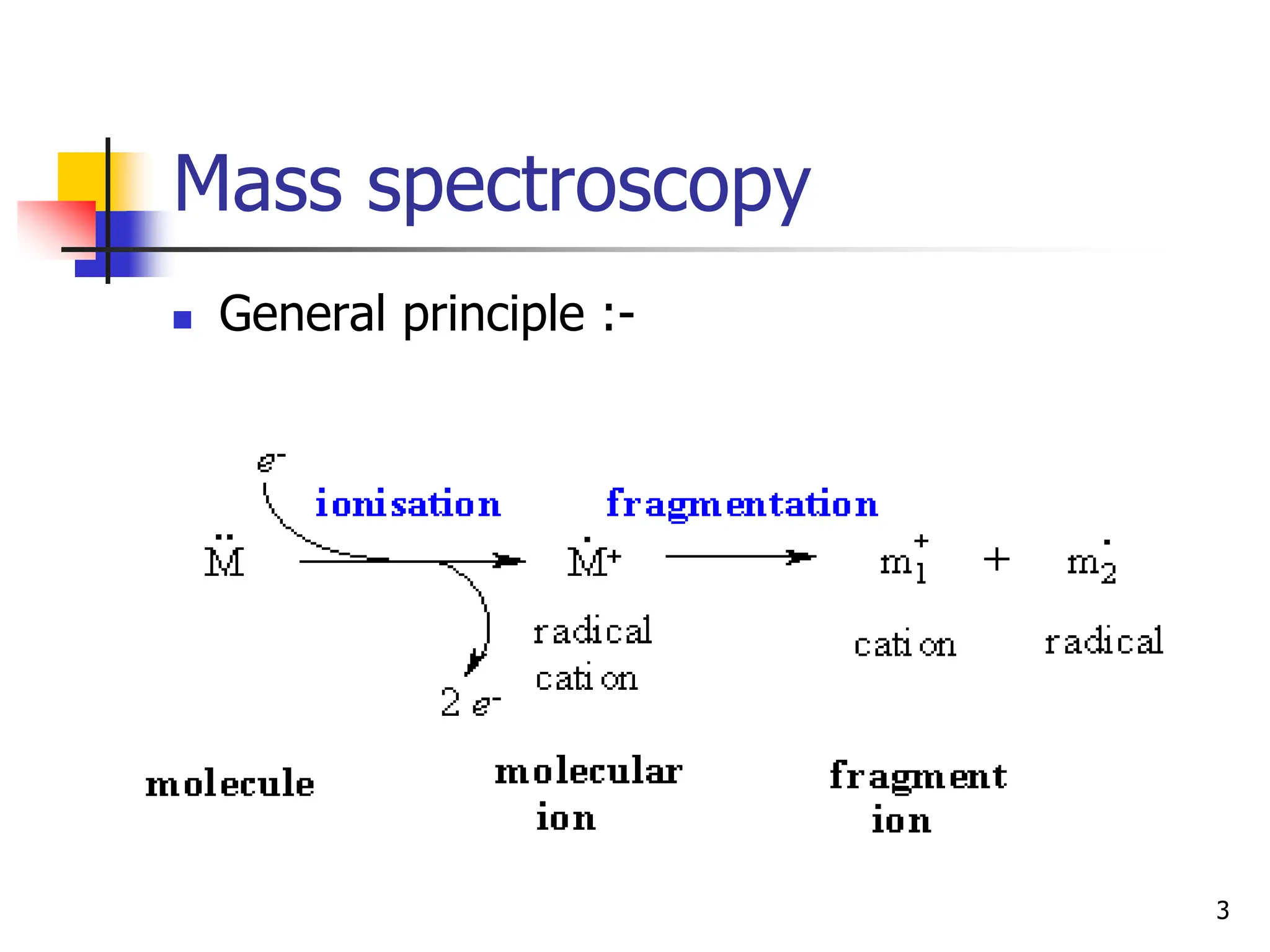
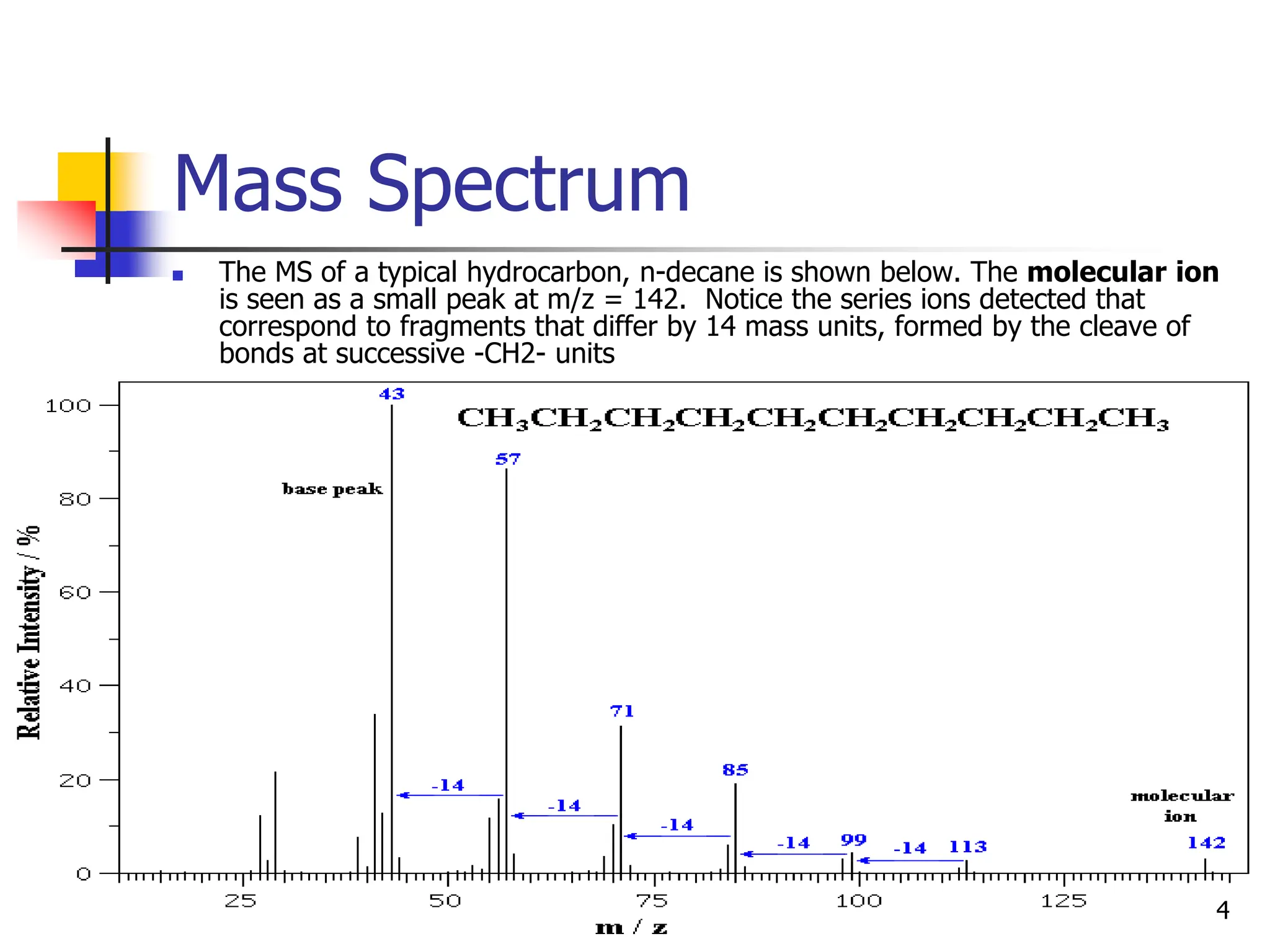
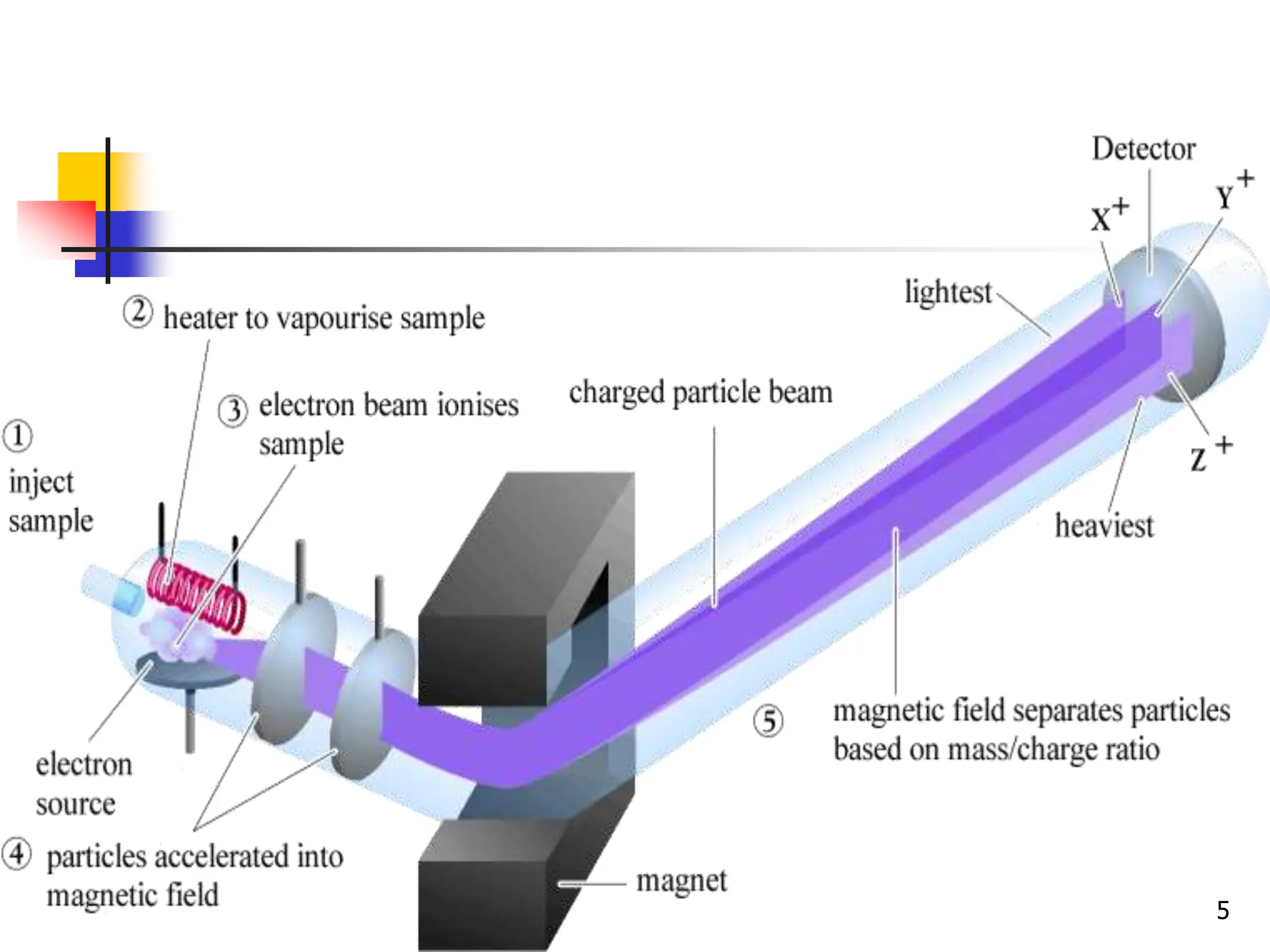
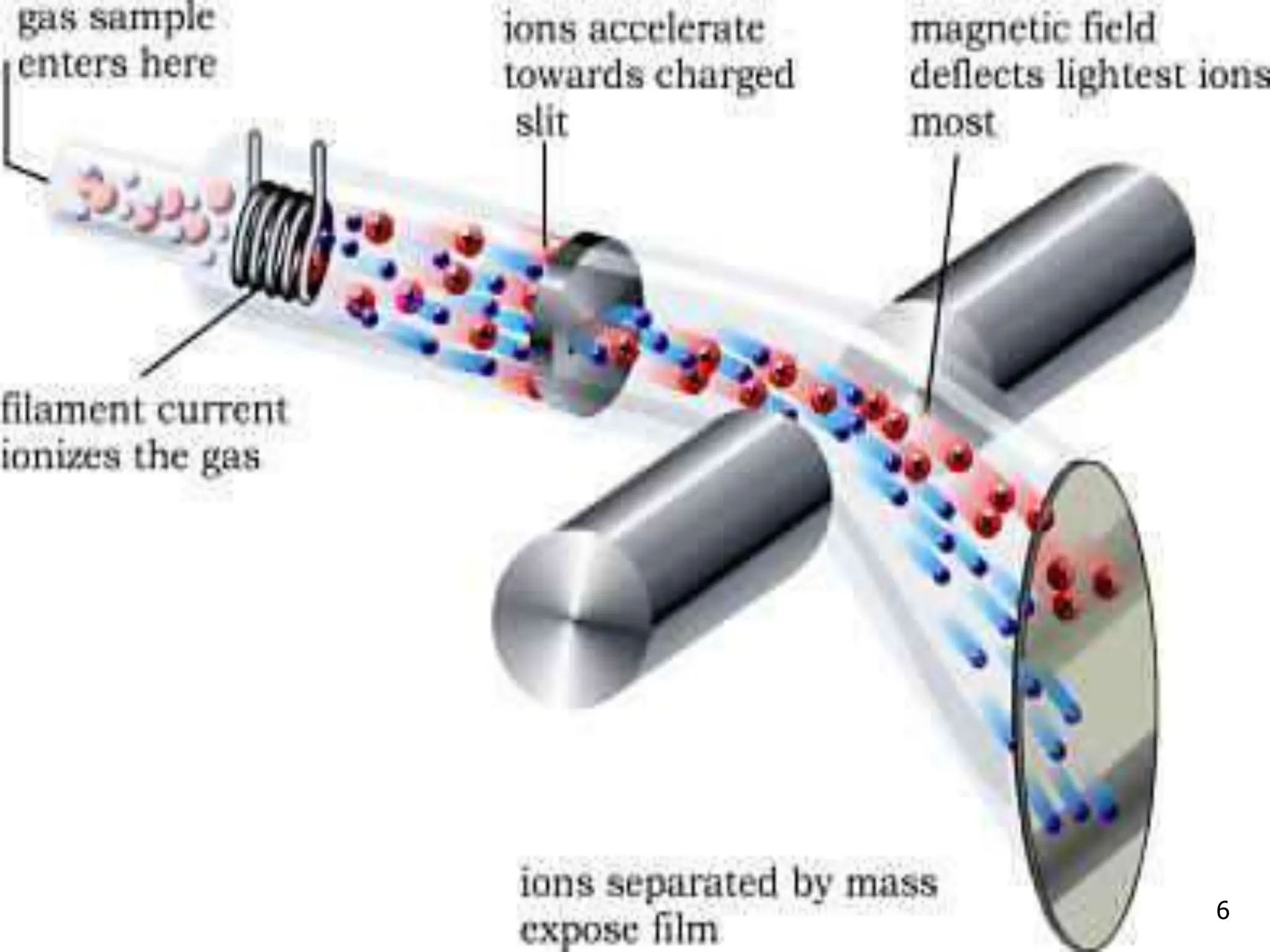
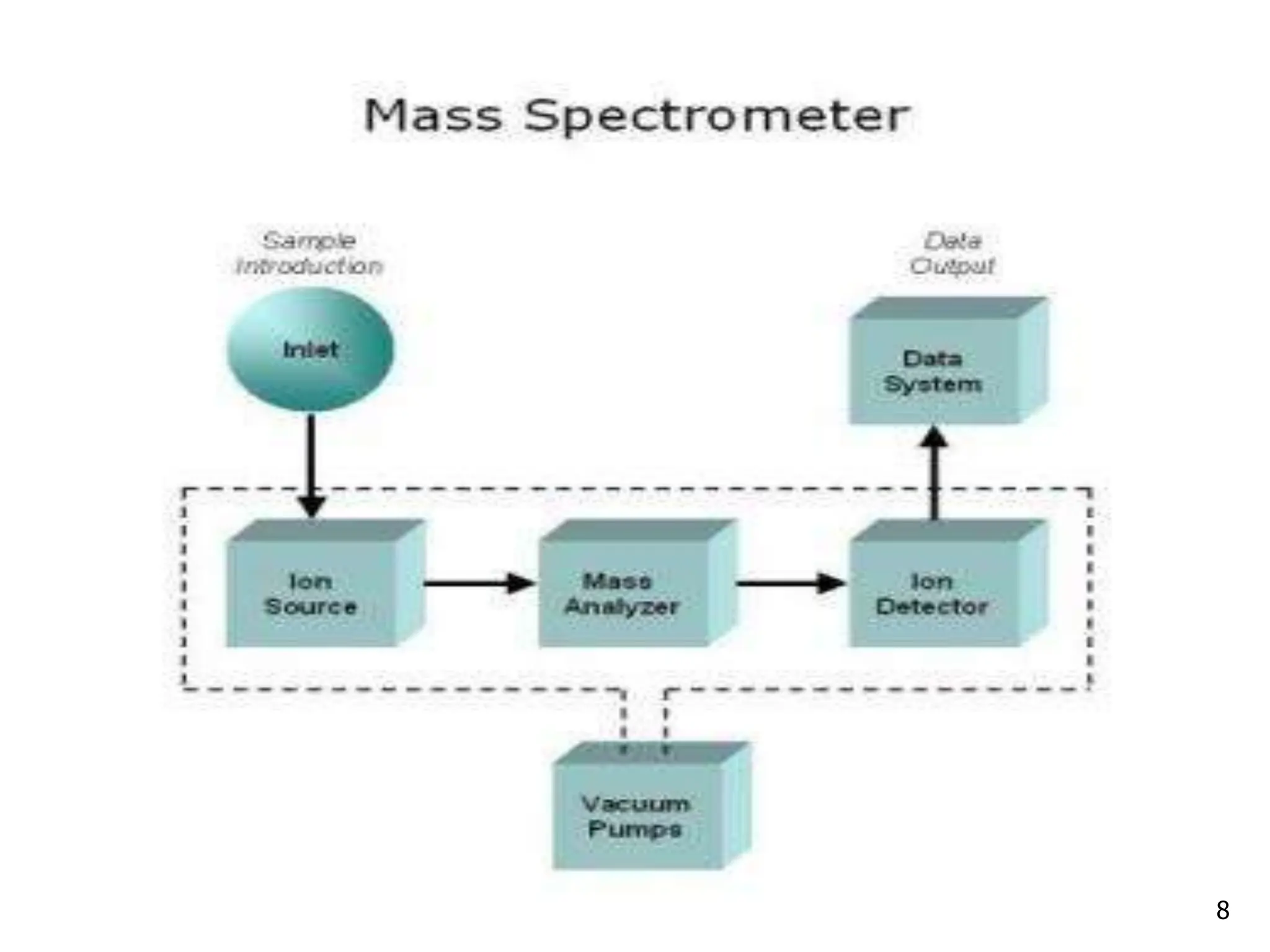
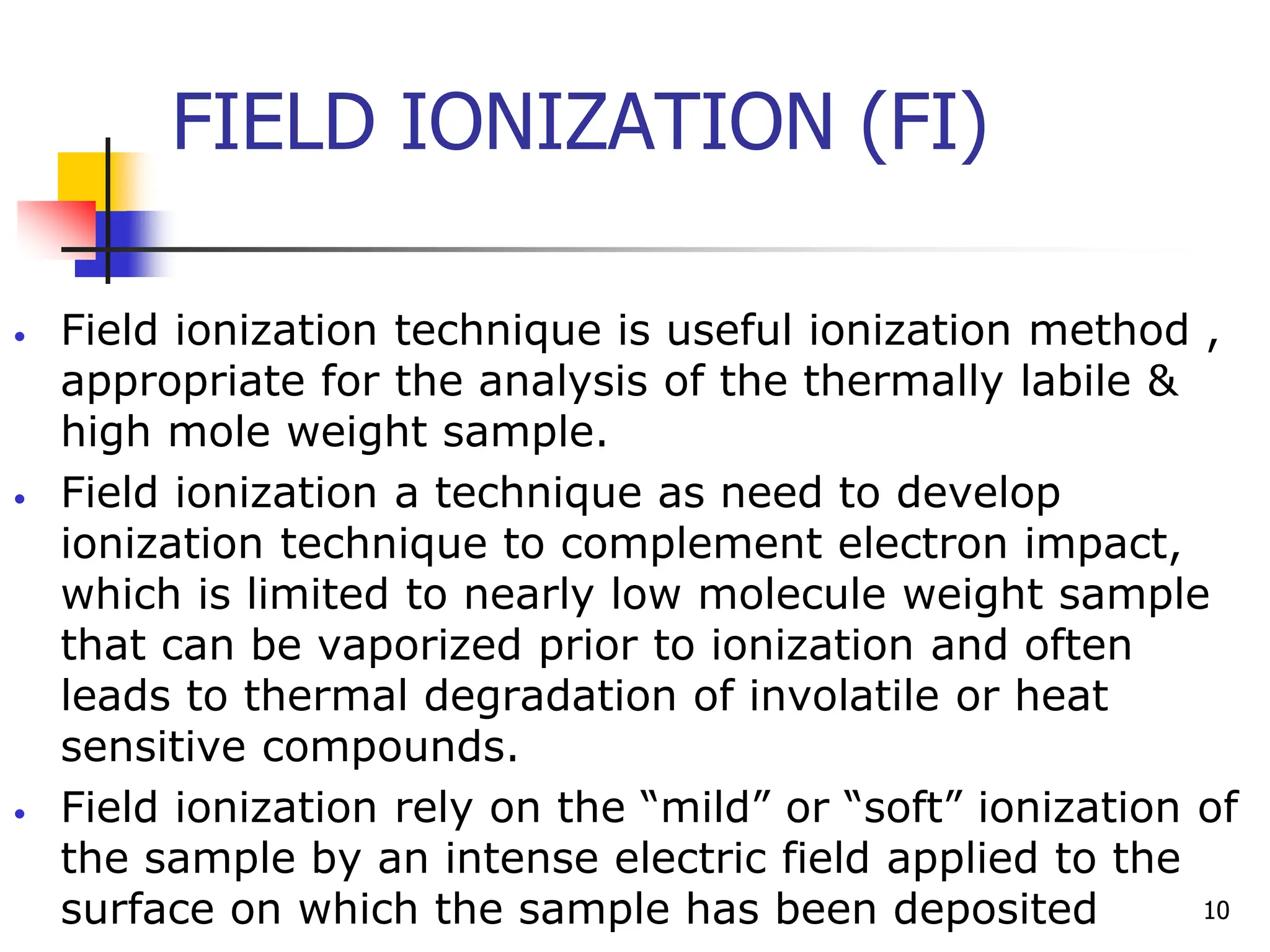
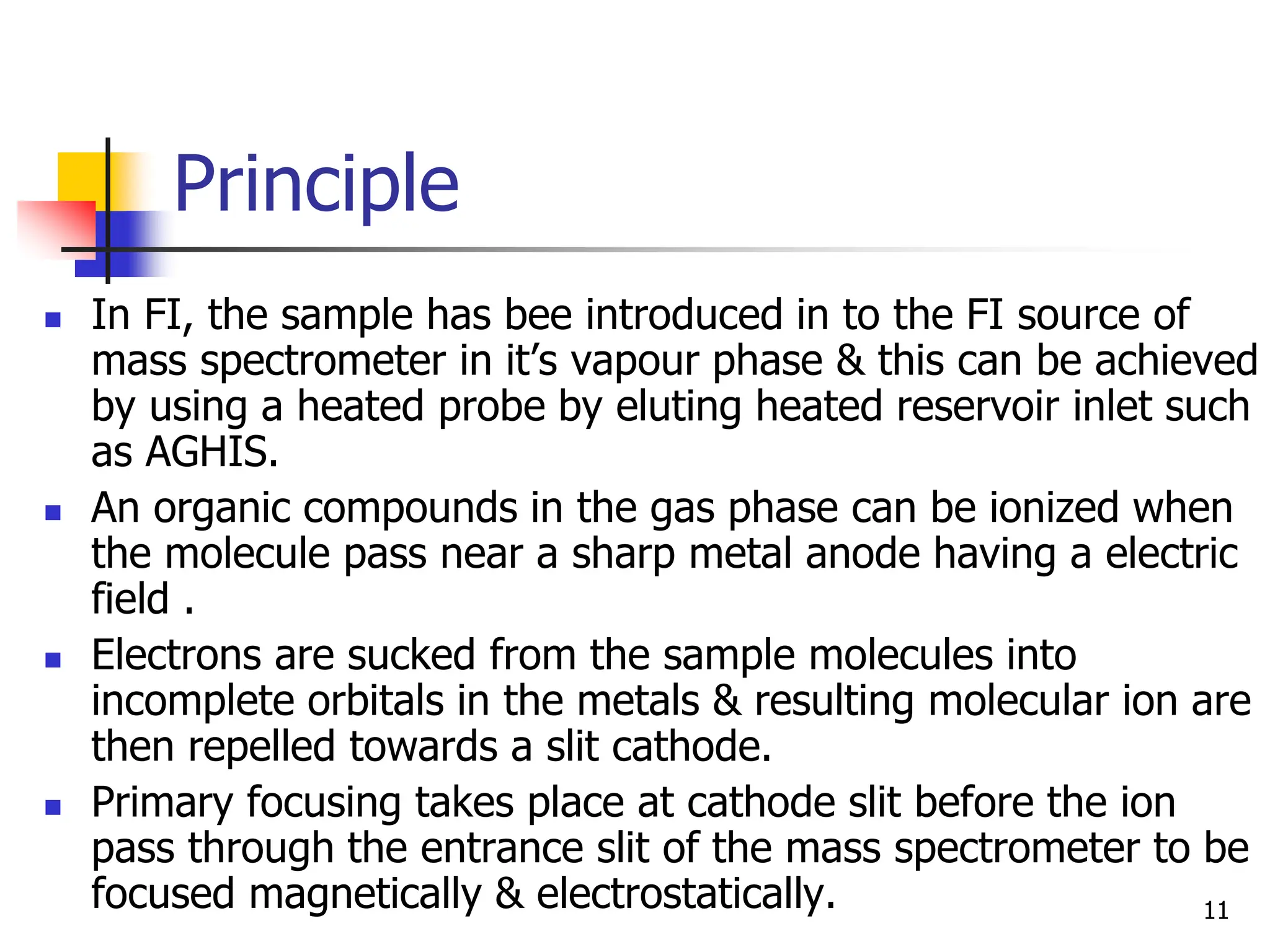
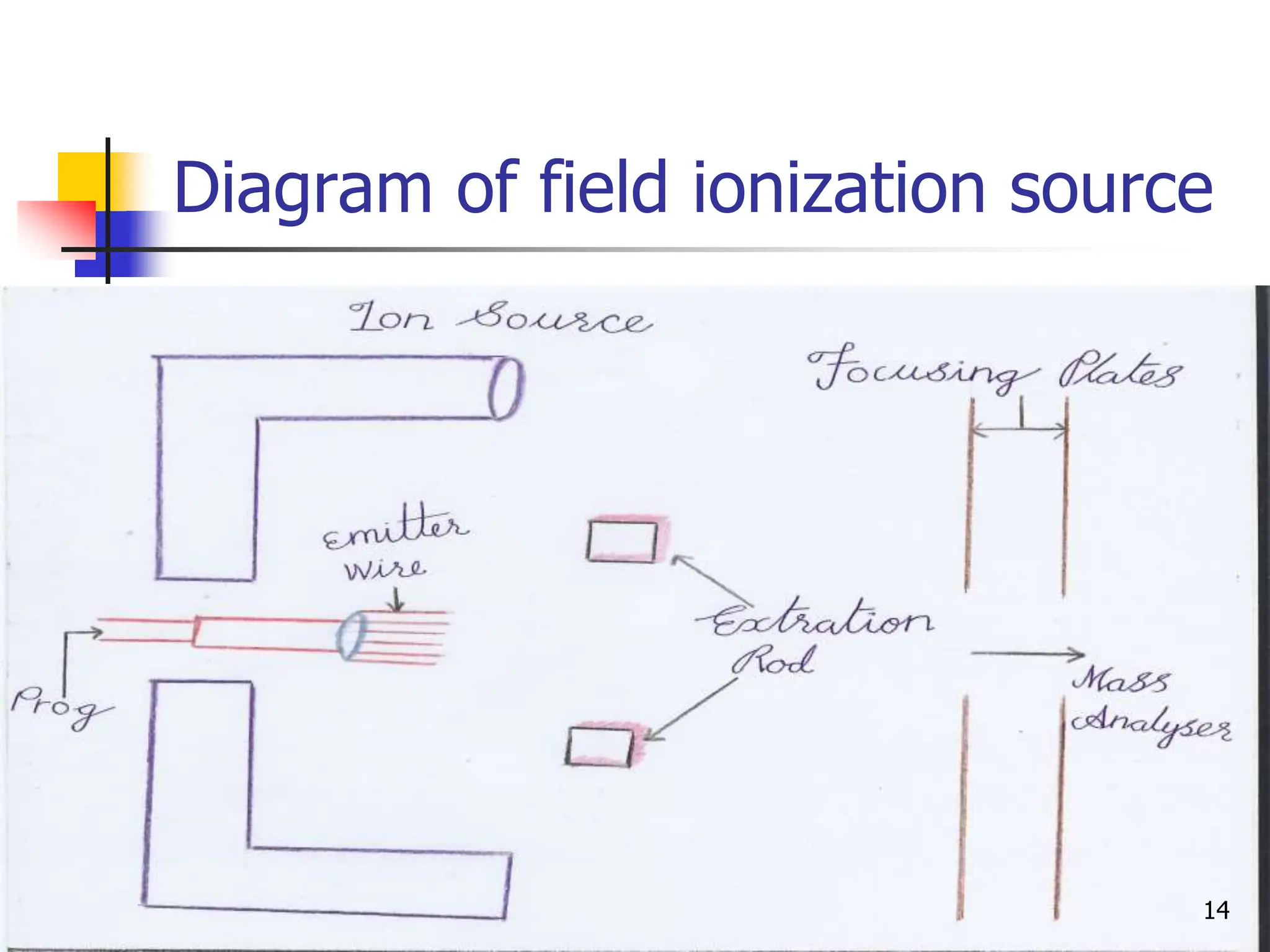
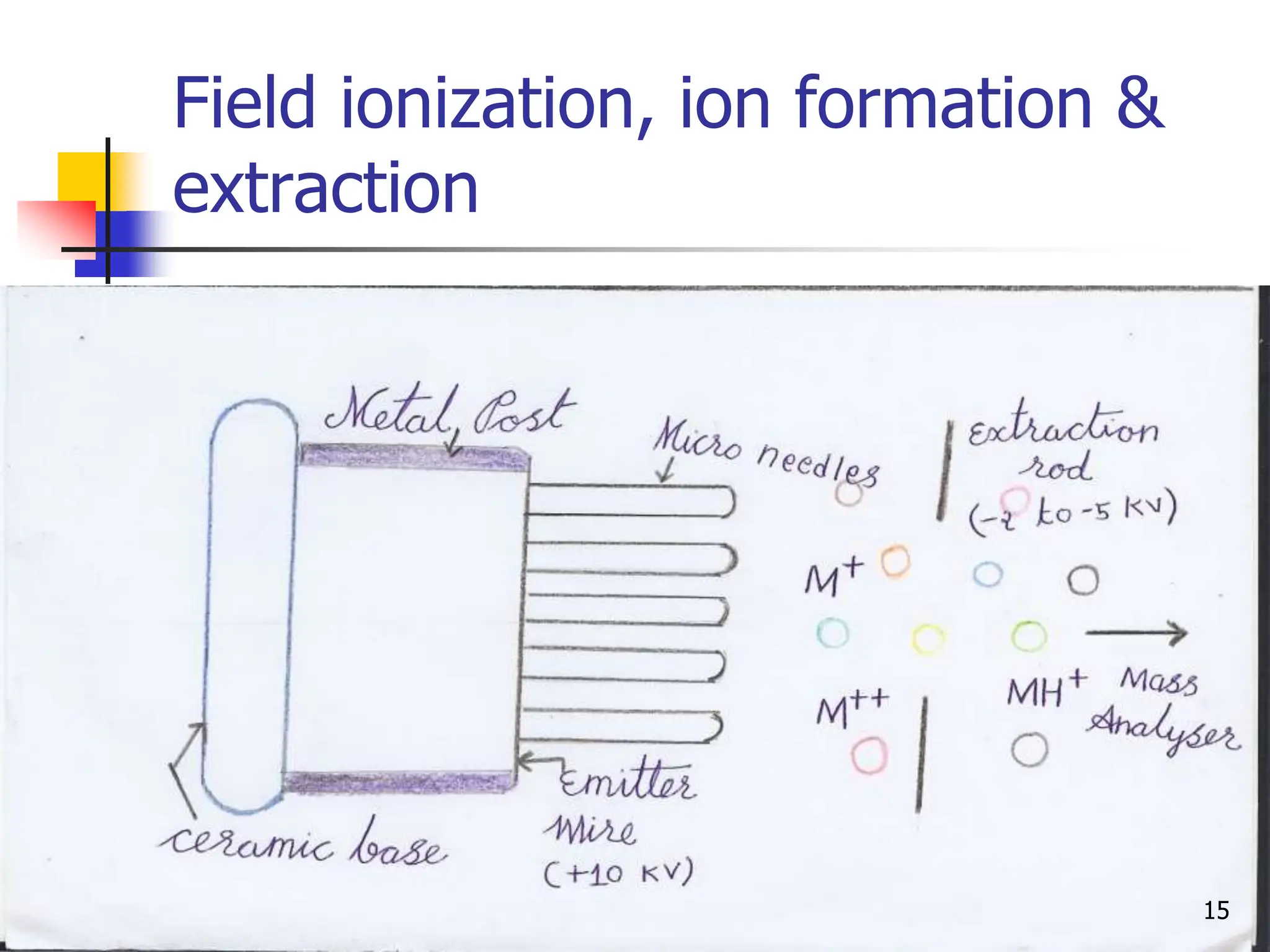
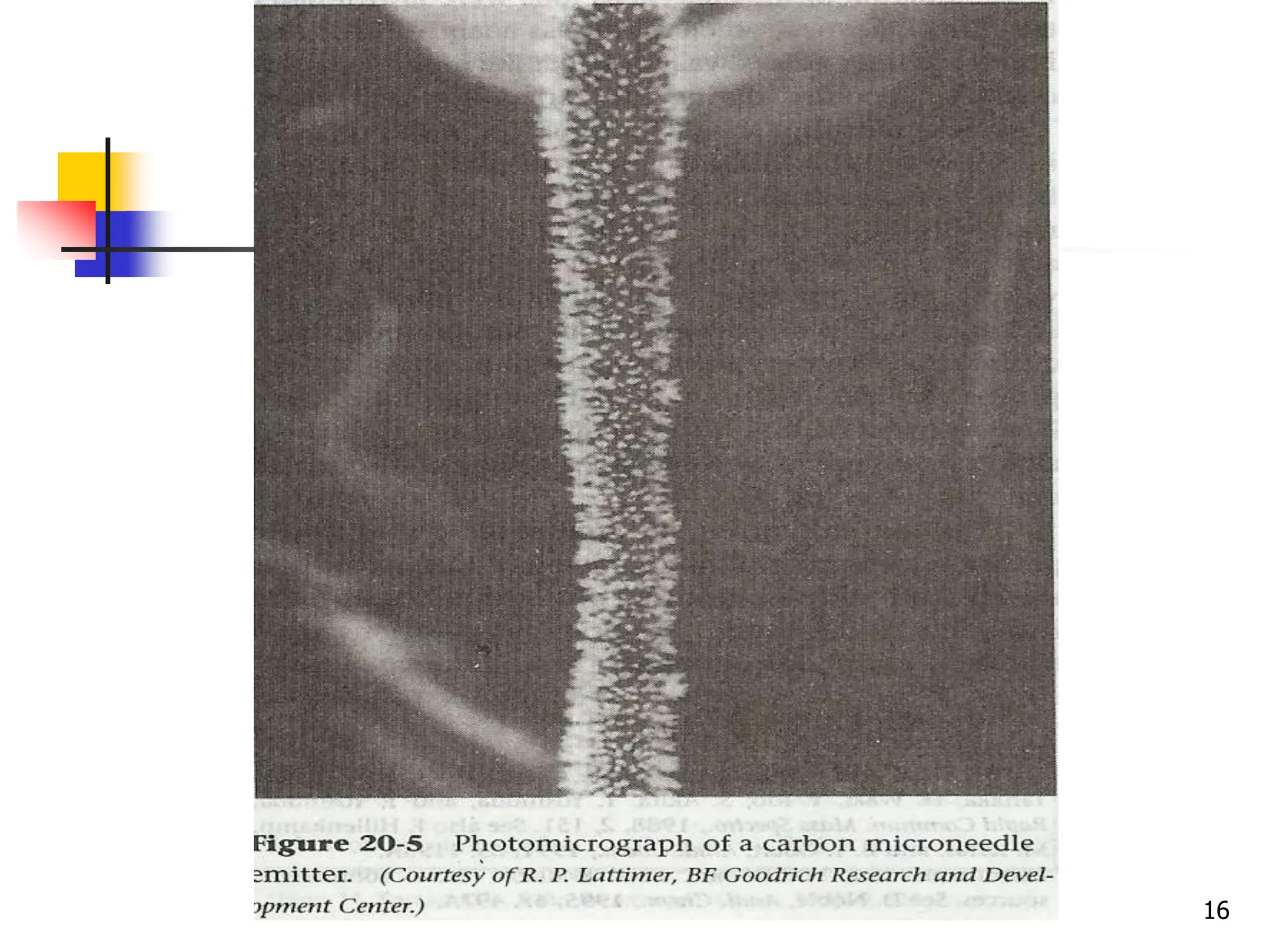
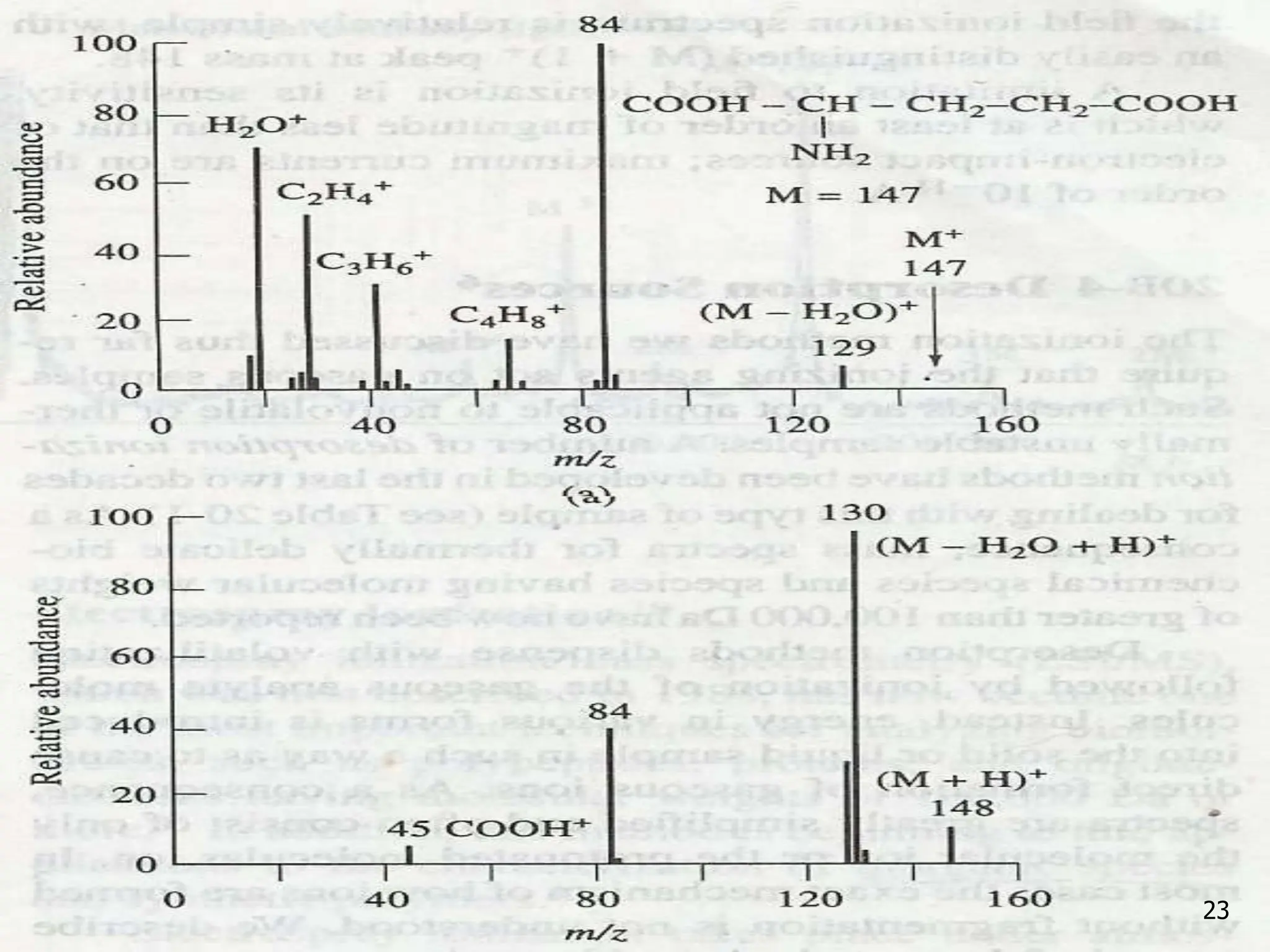
This document discusses field ionization (FI) as an ionization method in mass spectroscopy. FI allows for the ionization of thermally labile and high molecular weight samples. It works by subjecting the sample, in vapor phase, to an intense electric field near a sharp metal tip, causing ionization through quantum tunneling. FI produces predominantly molecular ions with little fragmentation, making it useful for analyzing compounds that are difficult to analyze via electron impact ionization. However, FI has lower sensitivity and resolution compared to other methods. Its applications include analysis in biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, clinical settings, and environmental and geological analyses.