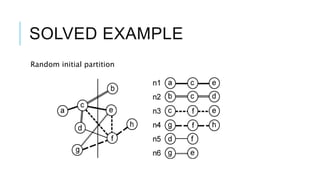
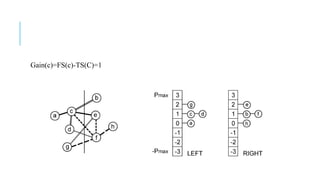
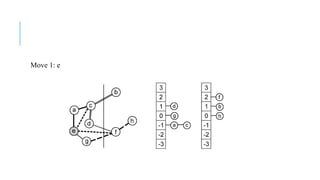
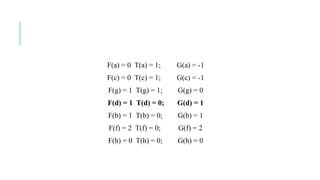
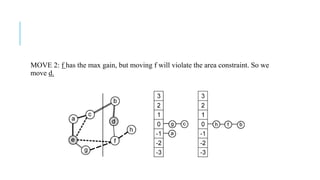
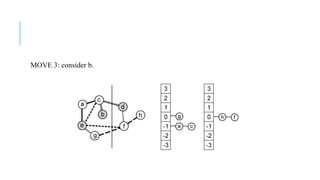
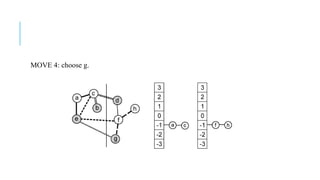
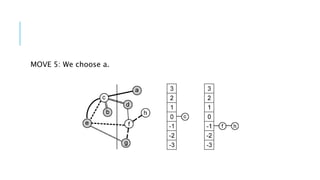
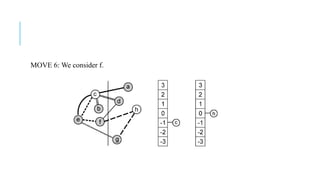
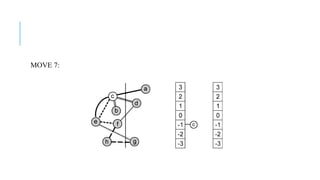
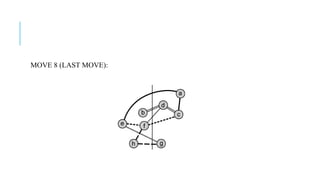
The Fiduccia-Mattheyses algorithm is an iterative partitioning algorithm that aims to reduce the net cut cost of a weighted graph. It works by computing the gain of moving each vertex to the opposite partition and iteratively moving the vertex with the highest gain. This continues until all vertices are locked in and the algorithm terminates. The key steps are to initially compute gains, select the highest gain move, update all affected gains, and repeat until done. An example run on a sample graph demonstrates computing initial gains and making moves until the algorithm converges.