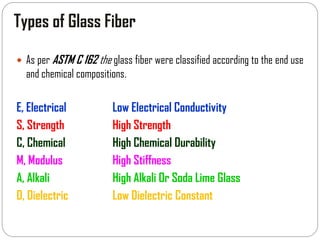
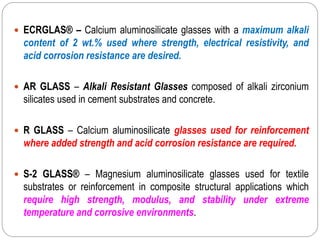
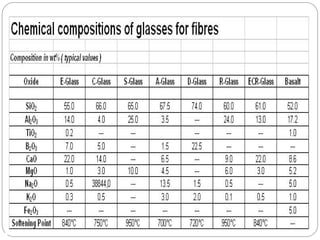
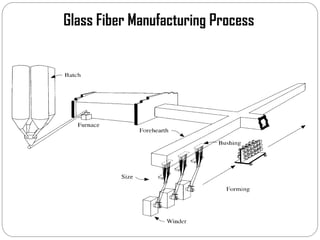
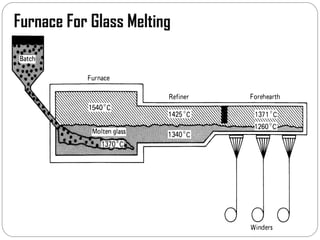
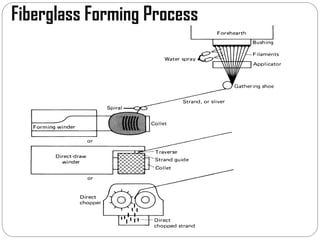
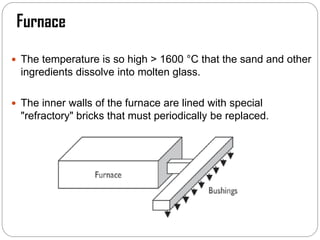
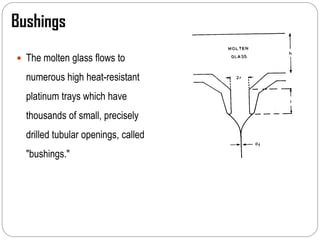
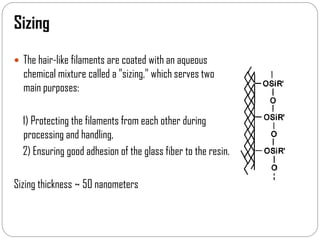
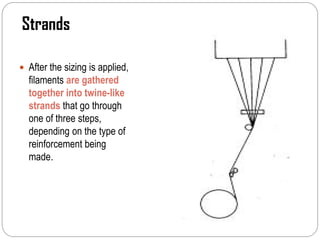
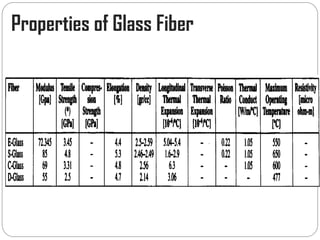
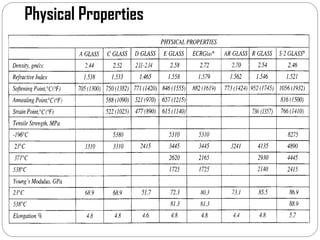
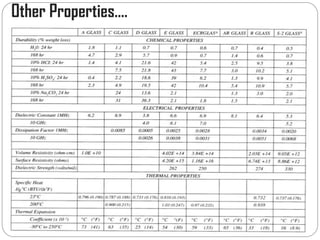
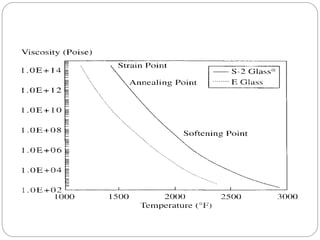
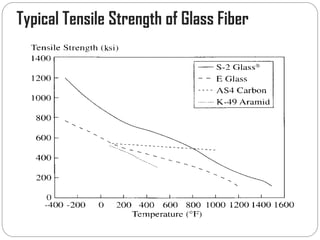
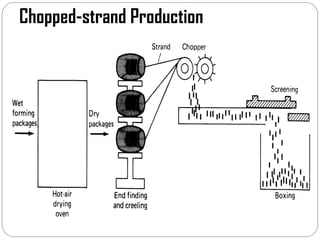
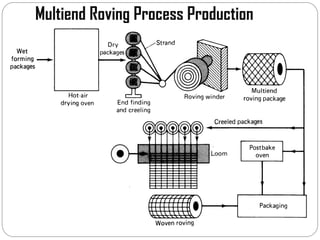
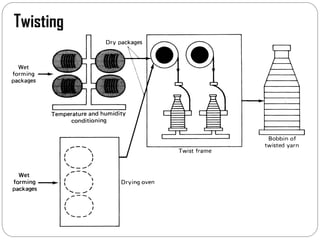
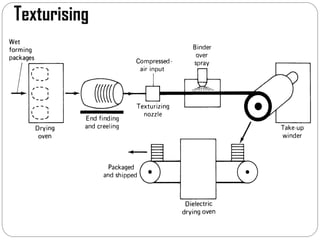
Glass fibers are manufactured through a process of melting raw materials and drawing them into fine fibers for various applications. Raw materials such as silica, alumina and boron are melted together and refined before flowing through bushings with small holes to produce thin glass filaments. These filaments are drawn, quenched, coated with a sizing and gathered into strands. Glass fibers have properties including high strength, stiffness, chemical resistance and stability that make them useful for insulation, reinforcement, filtration and optical applications. Common types include E, S, C and D glass formulated for different end uses.