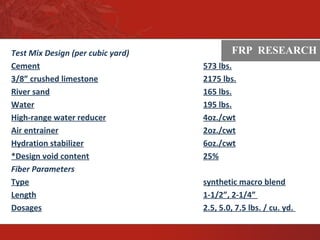
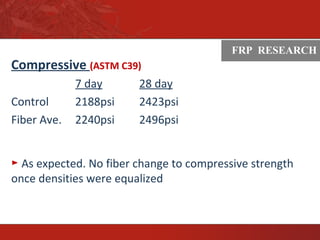
This document summarizes research on using fiber reinforced polymers (FRP) to improve the durability of pervious concrete. Laboratory testing found that higher dosages of longer macro-fibers significantly increased tensile strength, reduced raveling and abrasion, and dramatically improved freeze-thaw durability. Specifically, mixes with 7.5 lbs/yd of 2.25" fibers saw a 44% increase in tensile strength, 15-30% reduction in abrasion losses, and up to 3 times greater freeze-thaw durability compared to plain pervious concrete. The research demonstrates that FRP fibers can enhance the long-term performance of pervious concrete pavements.