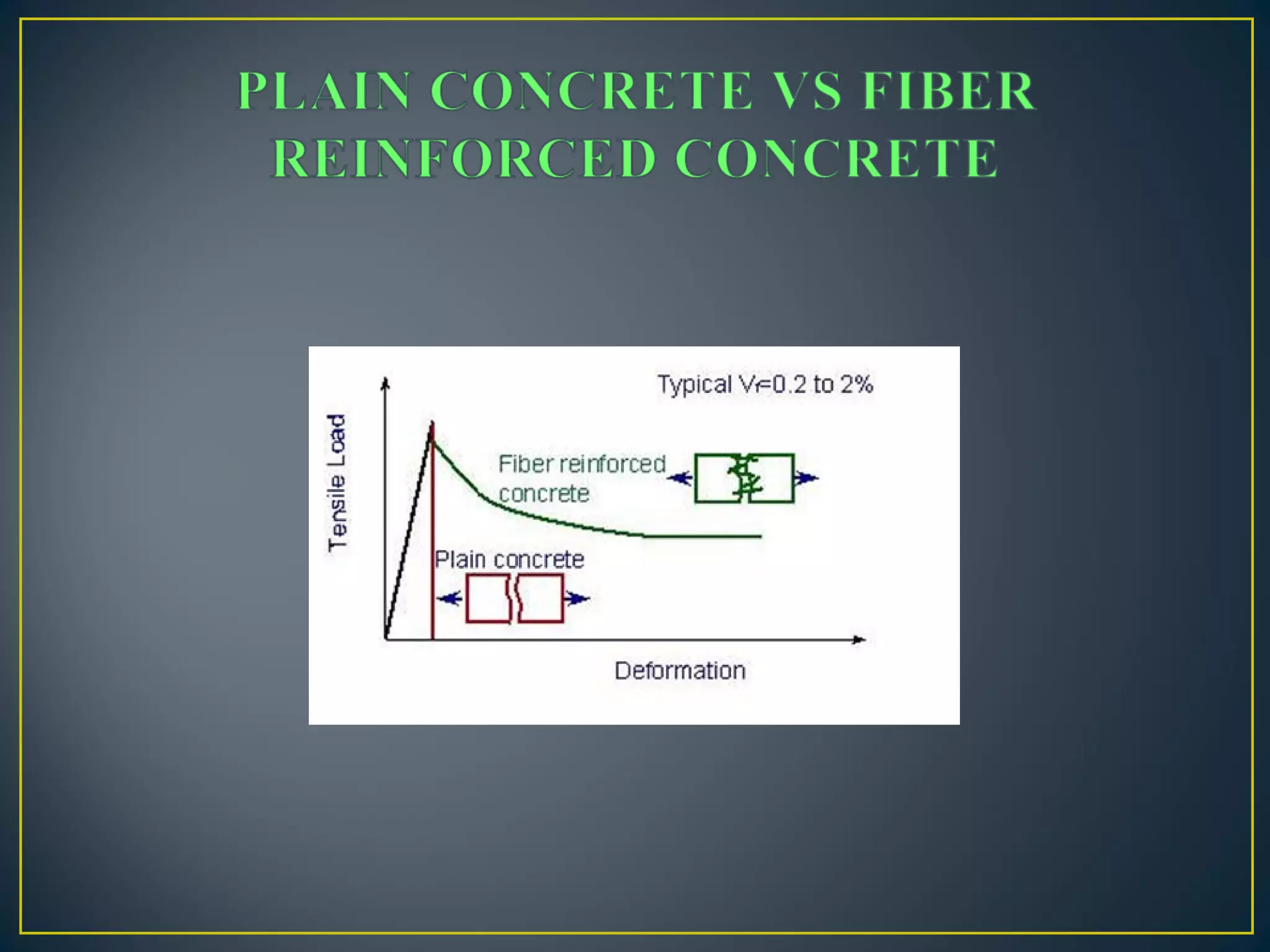
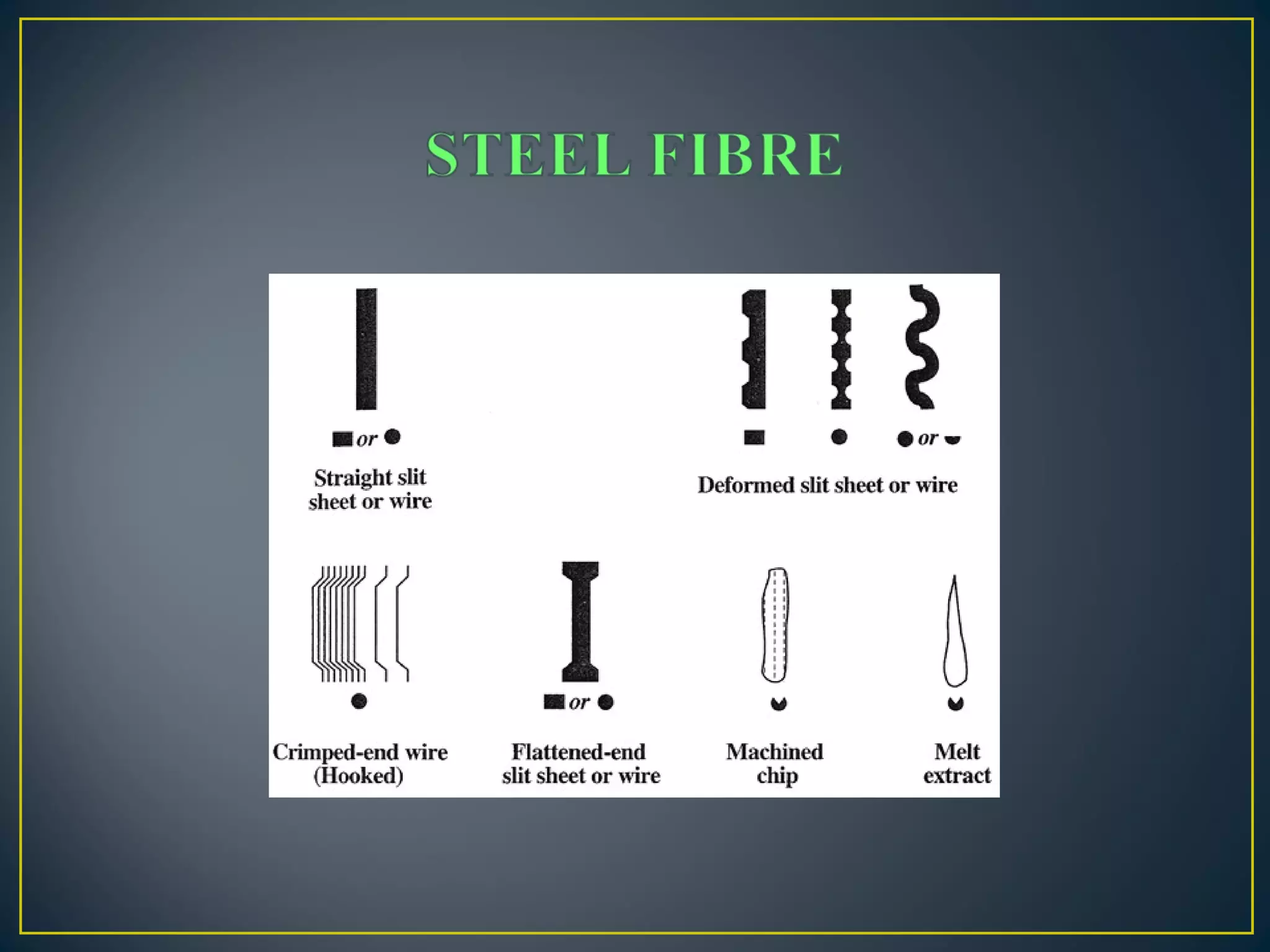
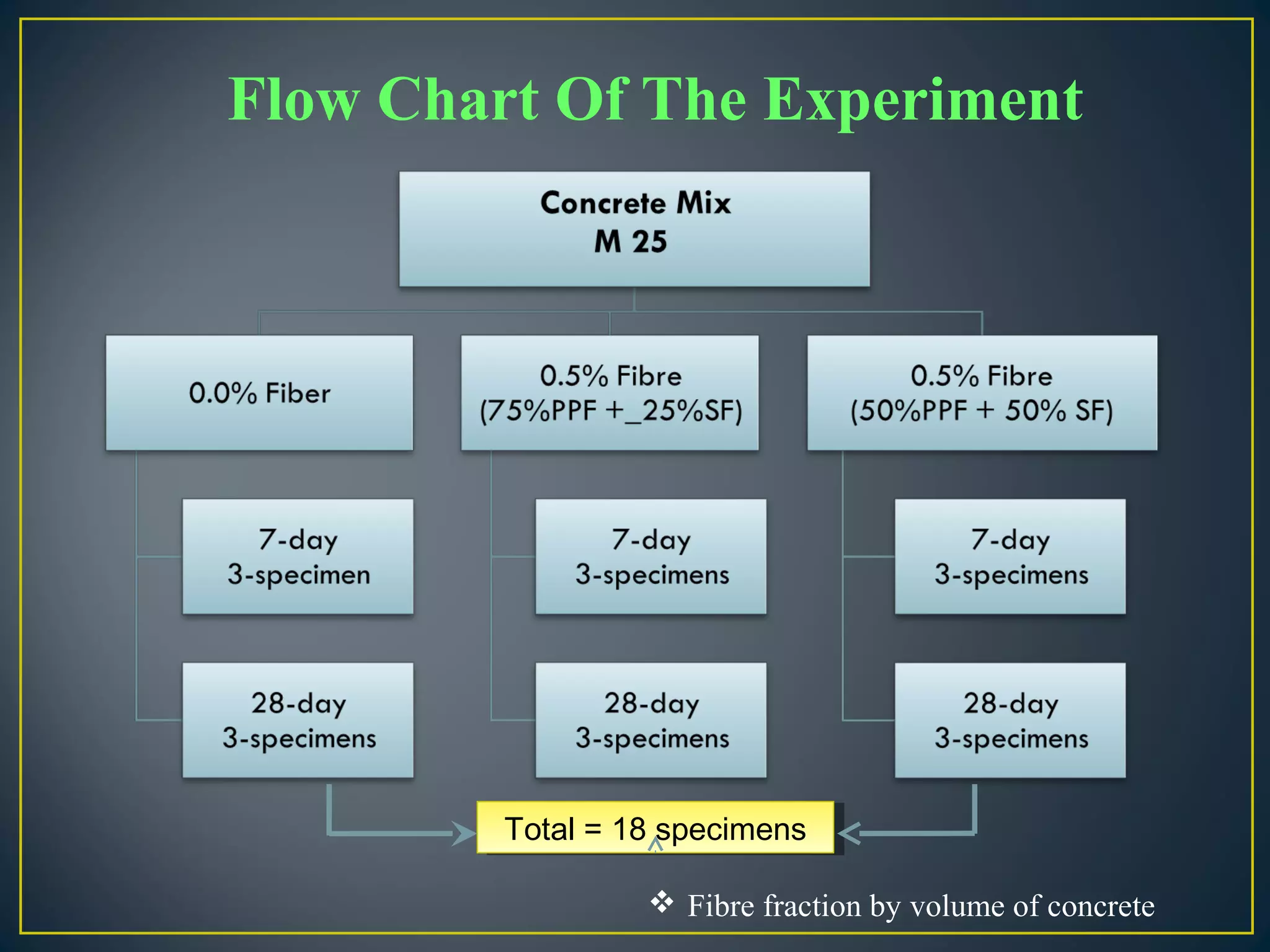
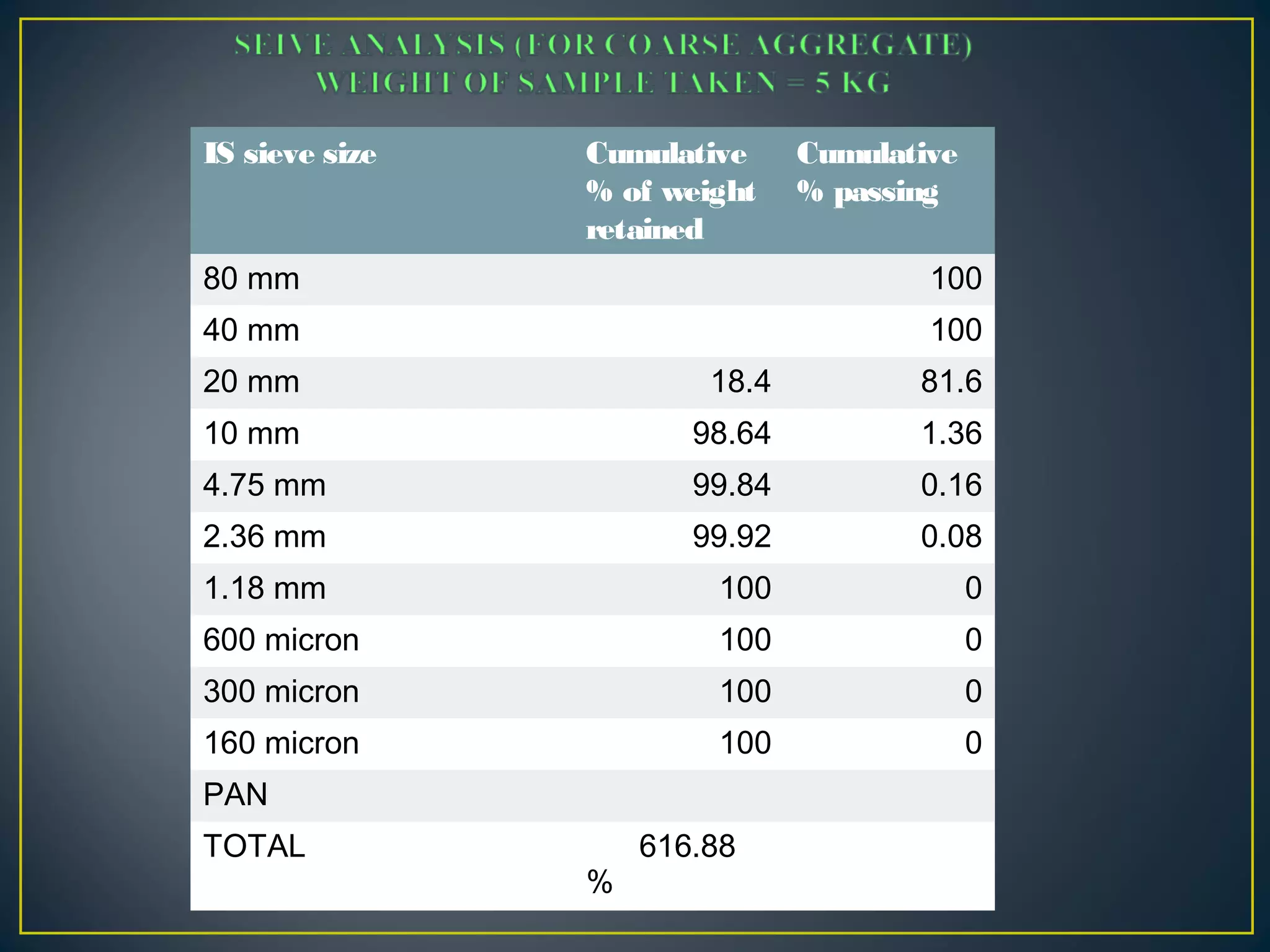
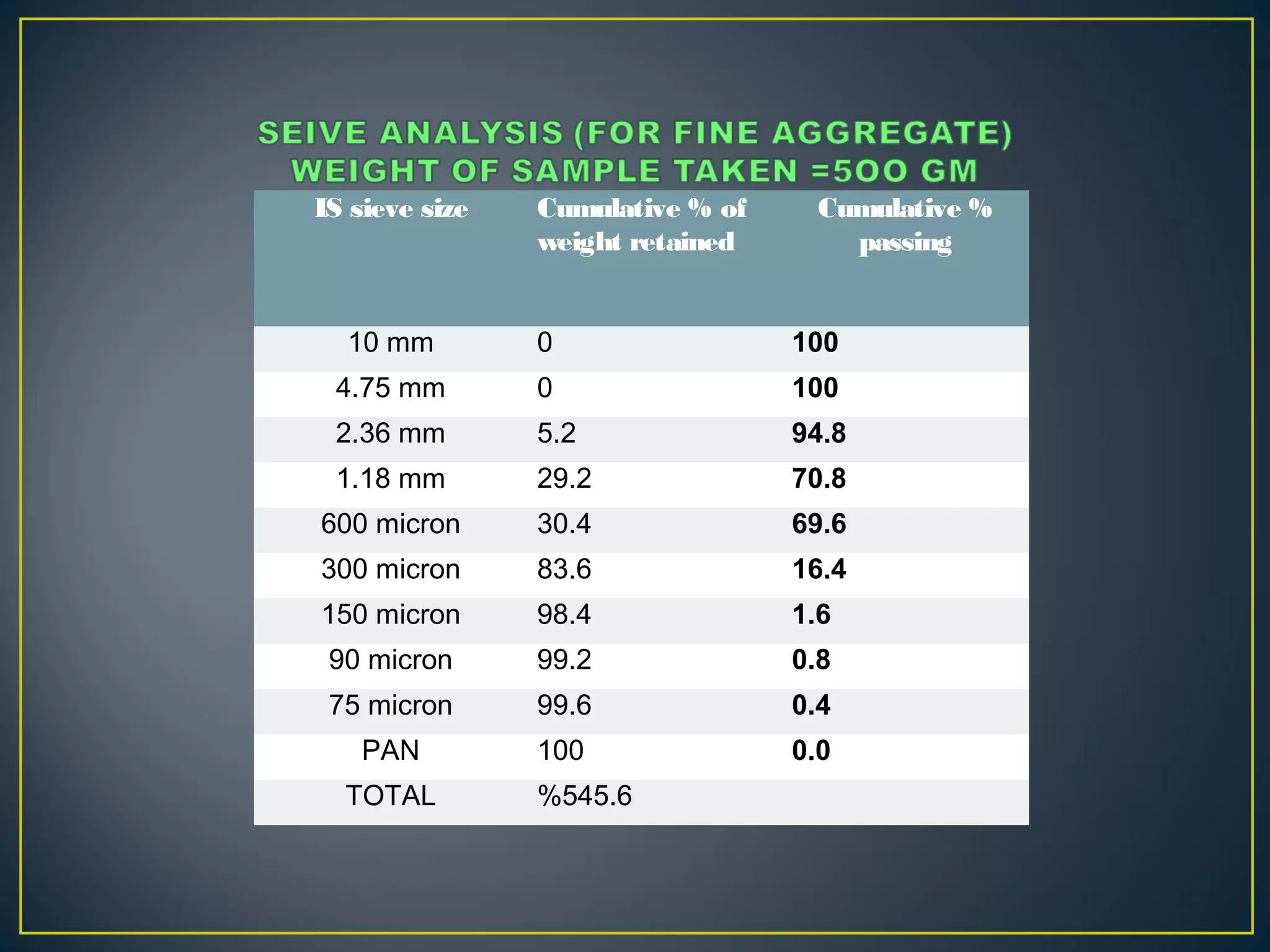
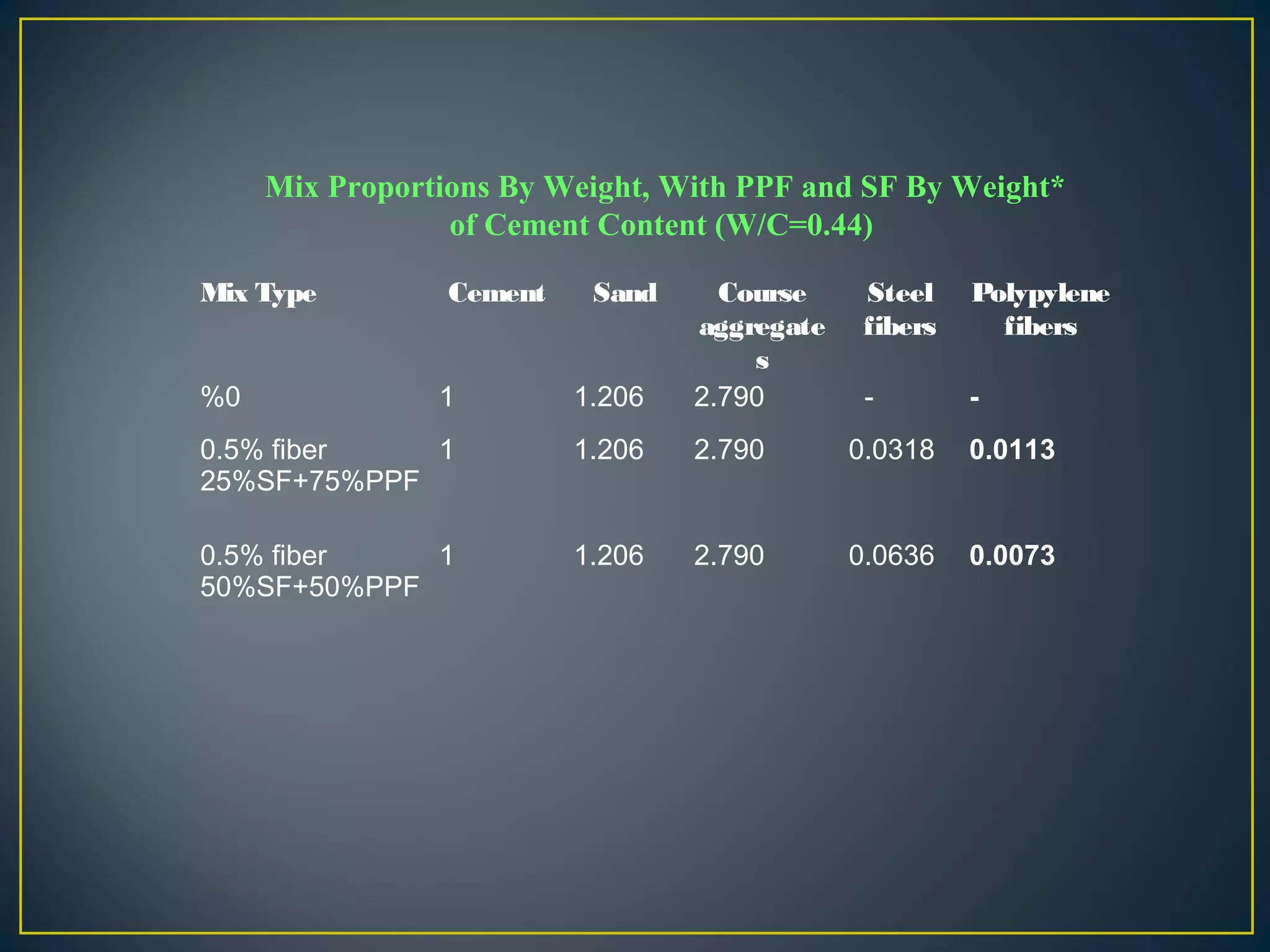
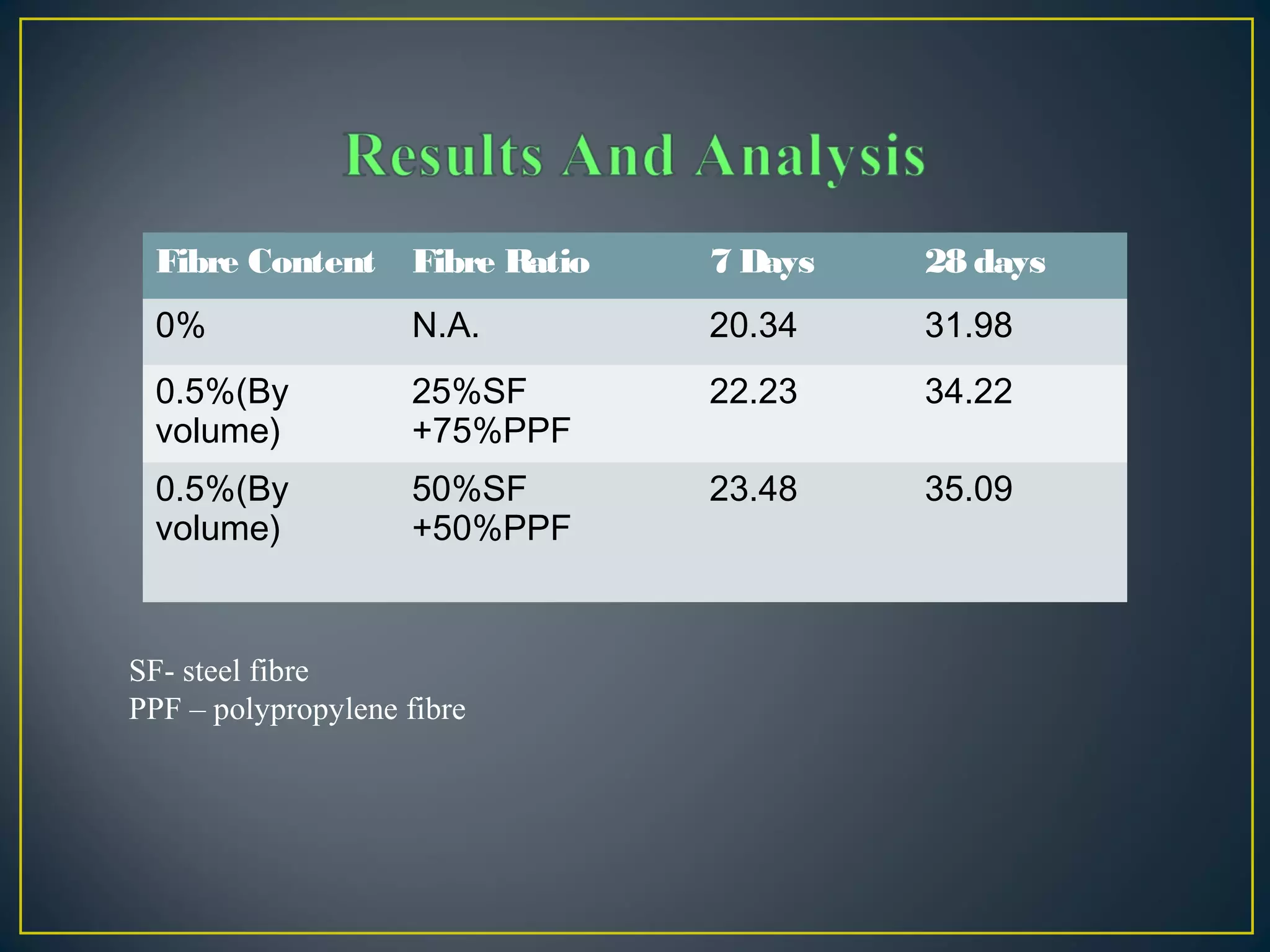
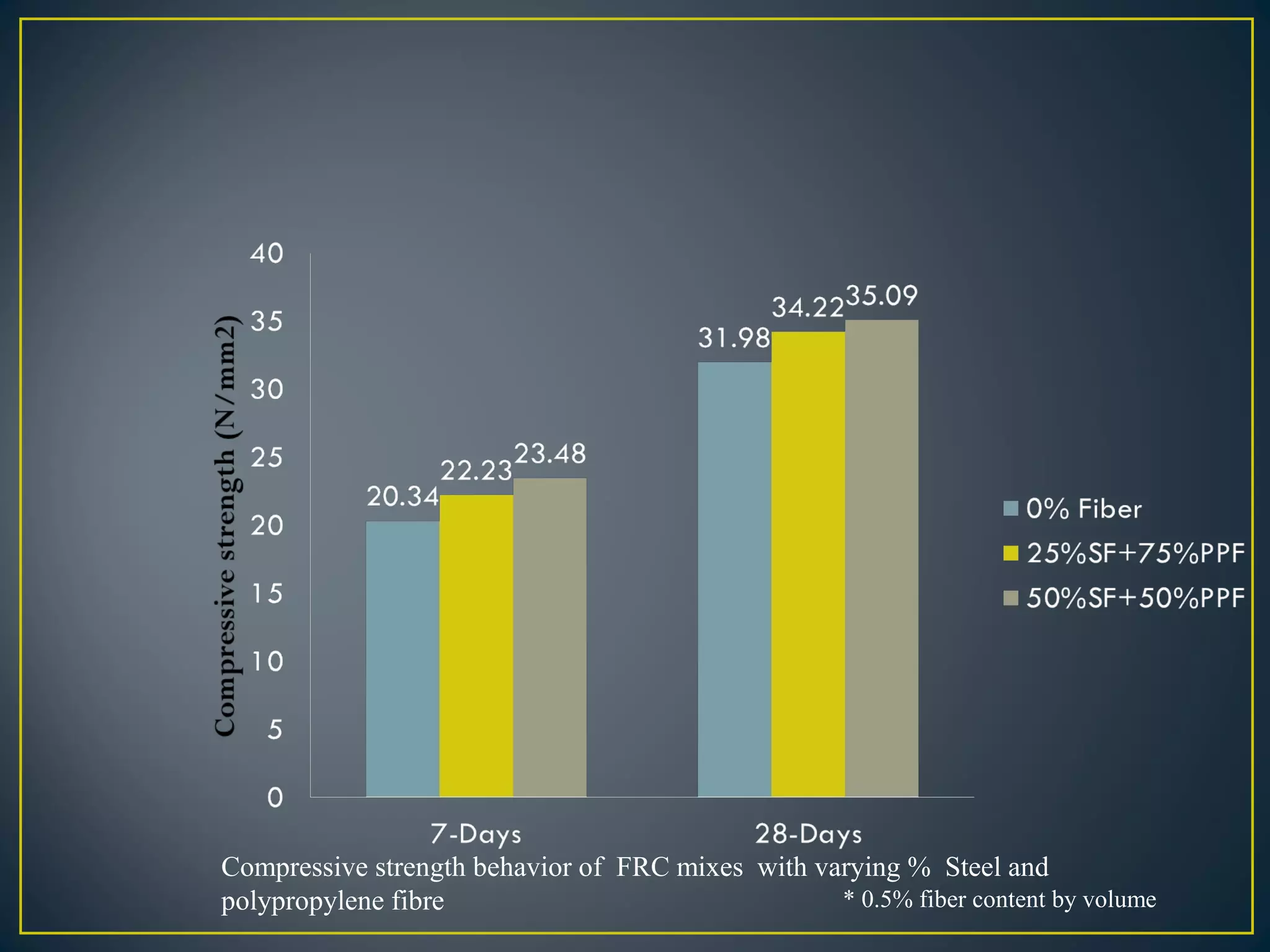
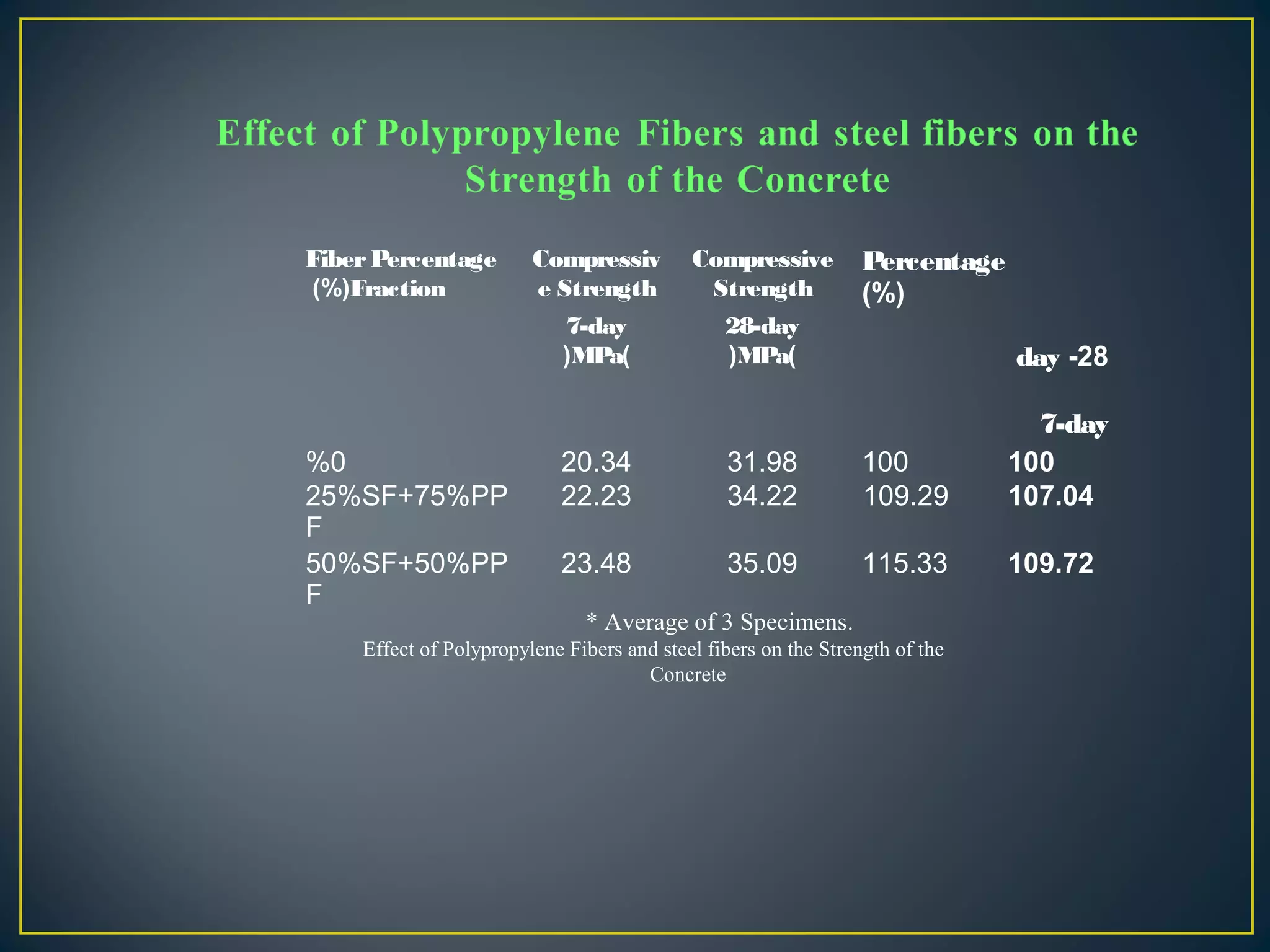
This document discusses a study on improving the properties of concrete by adding fibers. It summarizes that concrete is strong in compression but weak in tension. It then discusses different types of fibers that can be added like steel fibers, polypropylene fibers, carbon fibers, and glass fibers. The study focuses on adding steel fibers and polypropylene fibers to concrete mixtures to test their effect on compressive and tensile strength. The results showed that mixtures with both steel and polypropylene fibers had higher strengths compared to plain concrete at 7 and 28 days. Applications of fiber reinforced concrete included industrial floors, building structures, tunnels and more.