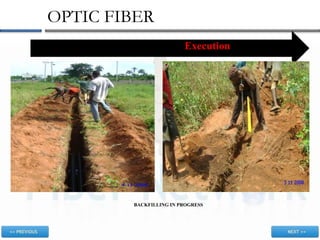
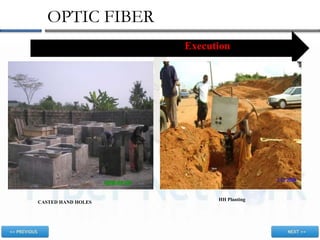
This document discusses optic fiber networks. It begins by explaining what optic fiber is, how it works, and its advantages over traditional metal cables. Next, it discusses the history of optic fiber technology and its development over time. It then explains why fiber networks are useful and lists some of their applications. Finally, it outlines the key stages involved in executing and implementing a fiber network project, including planning, construction, installation, and commissioning.

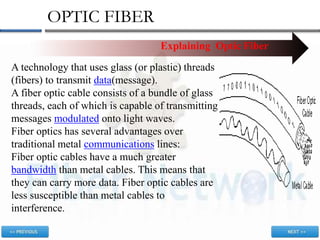


![OPTIC FIBER
History
Modern optical fibers, where the glass fiber is coated with a
transparent cladding to offer a more suitable refractive index,
appeared later in the decade. Development then focused on
fiber bundles for image transmission. Robust modern optical
fiber uses glass for both core and sheath, and is therefore less
prone to aging. It was invented by Gerhard Bernsee of Schott
Glass in Germany in 1973.
The emerging field of photonic crystals led to the
development in 1991 of photonic-crystal fiber,[21] which
guides light by diffraction from a periodic structure, rather
than by total internal reflection. The first photonic crystal
fibers became commercially available in 2000.Photonic
crystal fibers can carry higher power than conventional fibers
and their wavelength-dependent properties can be
manipulated to improve performance](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/99dbc3d3-8a58-4c0a-9f0f-21632f3a1155-151022101401-lva1-app6892/85/Fiber-Network-Deployment-8-320.jpg)