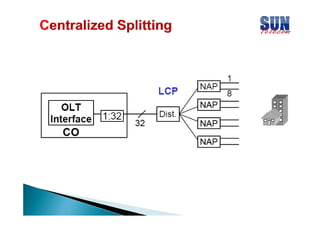
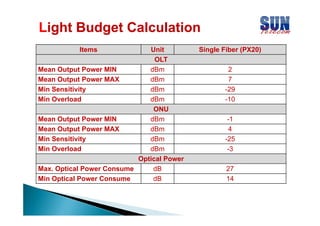
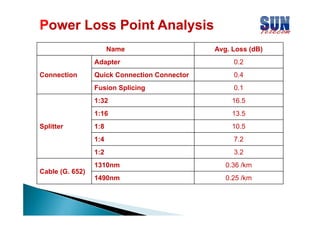
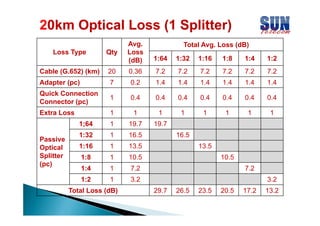
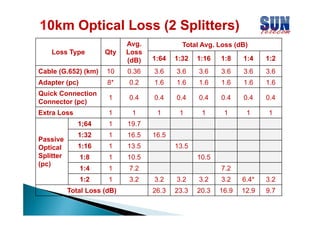
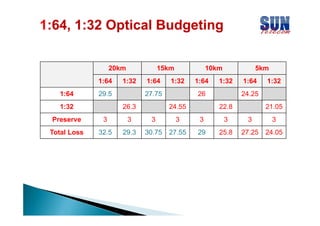
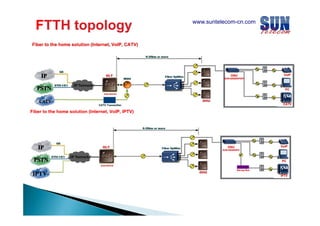
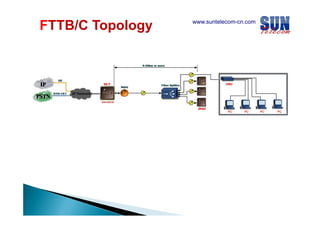
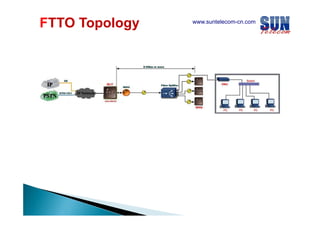
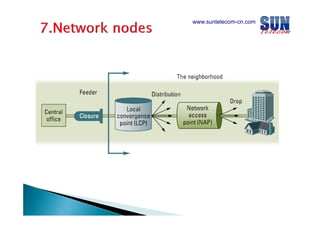
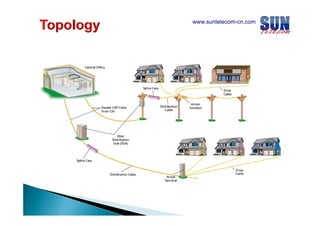
The document discusses considerations for designing an EPON network. It covers bandwidth requirements, splitting architecture options including 1-stage and 2-stage splitting, maximum transmission distances depending on splitting ratios, calculating the optical power budget, services that can be provided over EPON including FTTH and FTTB/C, upgrading existing networks, required network nodes and equipment, and cable types.