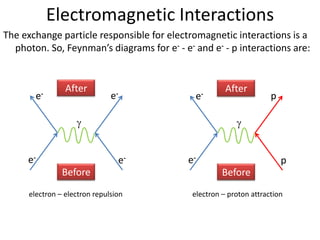
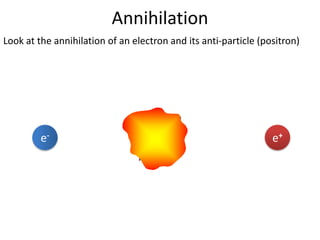
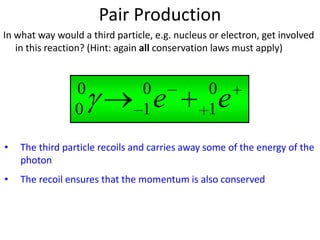
Richard Feynman developed diagrams to illustrate particle interactions through the exchange of other particles. His diagrams use straight lines for particles and curved lines for the exchanged particles. The diagrams must conserve charge at interaction points. Electromagnetic interactions exchange photons, while weak interactions exchange W bosons. Annihilation occurs when a particle collides with its antiparticle and they destroy each other, producing gamma rays. Pair production is the reverse, where a high energy photon transforms into a particle-antiparticle pair.