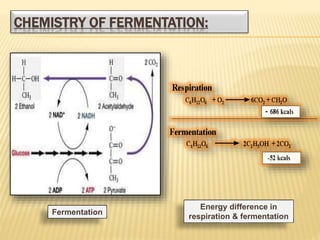
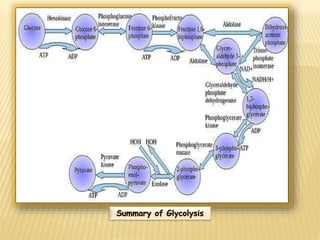
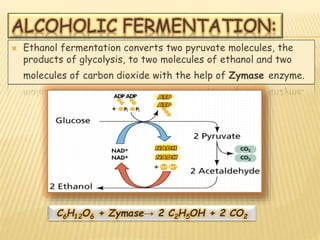
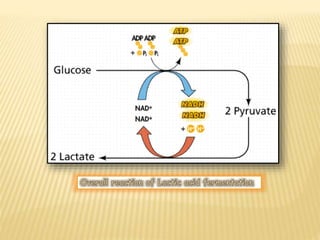
Fermentation is the conversion of carbohydrates into alcohols, carbon dioxide, or organic acids by microorganisms like yeast and bacteria in anaerobic conditions. It results in less energy production than aerobic respiration. Louis Pasteur first investigated fermentation chemistry in 1860. Key steps include glycolysis, which converts glucose to pyruvate, and alcoholic fermentation, which converts pyruvate to ethanol and carbon dioxide. Fermentation is used to produce foods and beverages like beer, wine, yogurt and cheese, as well as treat wastewater.