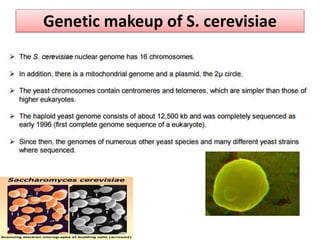
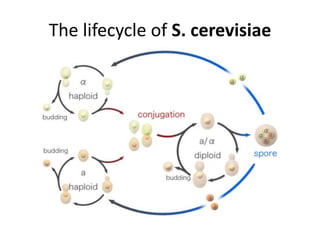
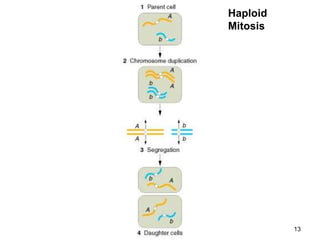
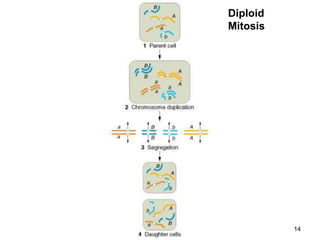
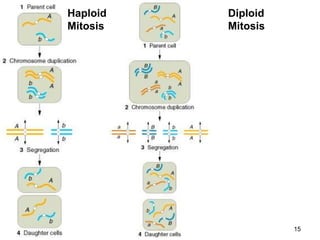
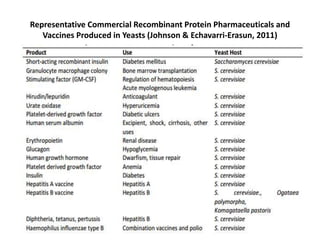
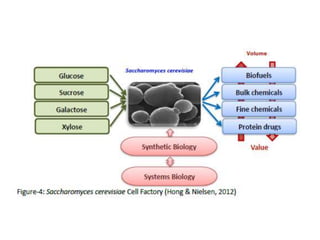
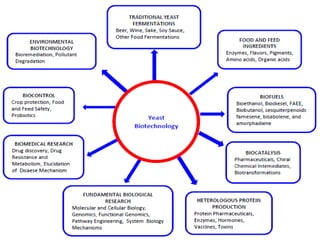
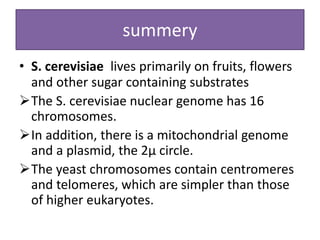
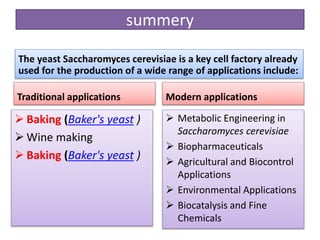
Saccharomyces cerevisiae, commonly known as baker's yeast, is a single-celled eukaryote and the first domesticated fungus. It has a globular shape and lives primarily on sugars, fermenting glucose to ethanol and carbon dioxide. S. cerevisiae has 16 chromosomes and is used traditionally in baking, brewing, and winemaking due to its carbon dioxide production. Modern applications include metabolic engineering, production of biopharmaceuticals, and use as a cell factory for industrial chemicals.