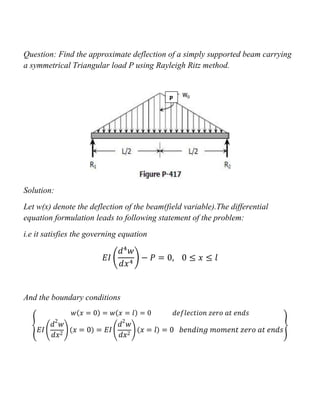
(1) The document solves for the approximate deflection of a simply supported beam carrying a symmetrical triangular load P using the Rayleigh Ritz method.
(2) It models the deflection w(x) and derives equations for the total potential energy Π and moment of inertia I2 in terms of w(x).
(3) By taking the derivative of Π with respect to the constants C1 and C2 and setting them to zero, it arrives at the solution for the deflection w(x) = (Pl^3/48EI)(4x^3/l^3 - 3x^2/l^2) which matches the exact solution.

![Total energy i.e. potential energy of the system is given below:
Π= ∫ [ ( ) ( )]
Replace P=8
( )
( )
( )
9
Π= [∫ { ( ) ( )} ∫ { ( ) (
( )
)} ]
Where E=Young’s Modulus
I=Moment of inertia, l=length of beam, P=load on beam
Now we are integrating above equation denoted in different color
separately.
Let here w(x)=
( ) ( ) , where C1 and C2 are constant
After using the value of and w in above equation we have,
∫ 0 ( ( ) ( ) ) .
( )
/1
∫ 6 2 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 3
4
( )
57 ( )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/femproblemofelasticity-130607011015-phpapp01/85/FEM-problem-of-elasticity-3-320.jpg)
![We know that, ∫ 2 3
∫
Therefore, equation (1) becomes
2 ( ) ( ) 3 ∫ 64
( )
57
2 ( ) ( ) 3 ∫ 64
( )
57 ( )
∫ [ ∫ ∫ ( ) ]
[ ∫ ( ) ]
0 ( ) ( )1
0( ) 1
Similarly
∫ ( )
Now equation (2) becomes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/femproblemofelasticity-130607011015-phpapp01/85/FEM-problem-of-elasticity-4-320.jpg)
![2 ( ) ( ) 3 0 ( ) ( ) 1 ( )
∫ * ( ) (
( )
)+ = ∫ * ( ) ( )+
∫ 6 . / 8 ( )
( )
97
∫ [ ∫ ∫ ( ) ]
[ ∫ ( ) ]
[ ∫ ( ) ]
[ ( ) ]
Similarly,
∫ 0 ( ) 1
Therefore, I2 now becomes after substituting the value
{ ( ) ( ) } , - 0 2 ( ) 3
{ ( ) }1…… (4)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/femproblemofelasticity-130607011015-phpapp01/85/FEM-problem-of-elasticity-5-320.jpg)
![Therefore, Π= [ ]
i.e. Π= 0 , ( ) ( ) - * ( ) ( ) + , ( )
( ) - , - * , ( ) - , ( ) -+1
where C1 and C2 are independent constant. For the minimum of π we have
{ ( ) } , - =0
{ ( ) }=0
Therefore,
( ) , which is the deflection of beam.
The deflection of beam at the middle point of beam(i.e. at l/2) is given by
( ) ( )
which compare with the exact solution](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/femproblemofelasticity-130607011015-phpapp01/85/FEM-problem-of-elasticity-6-320.jpg)
