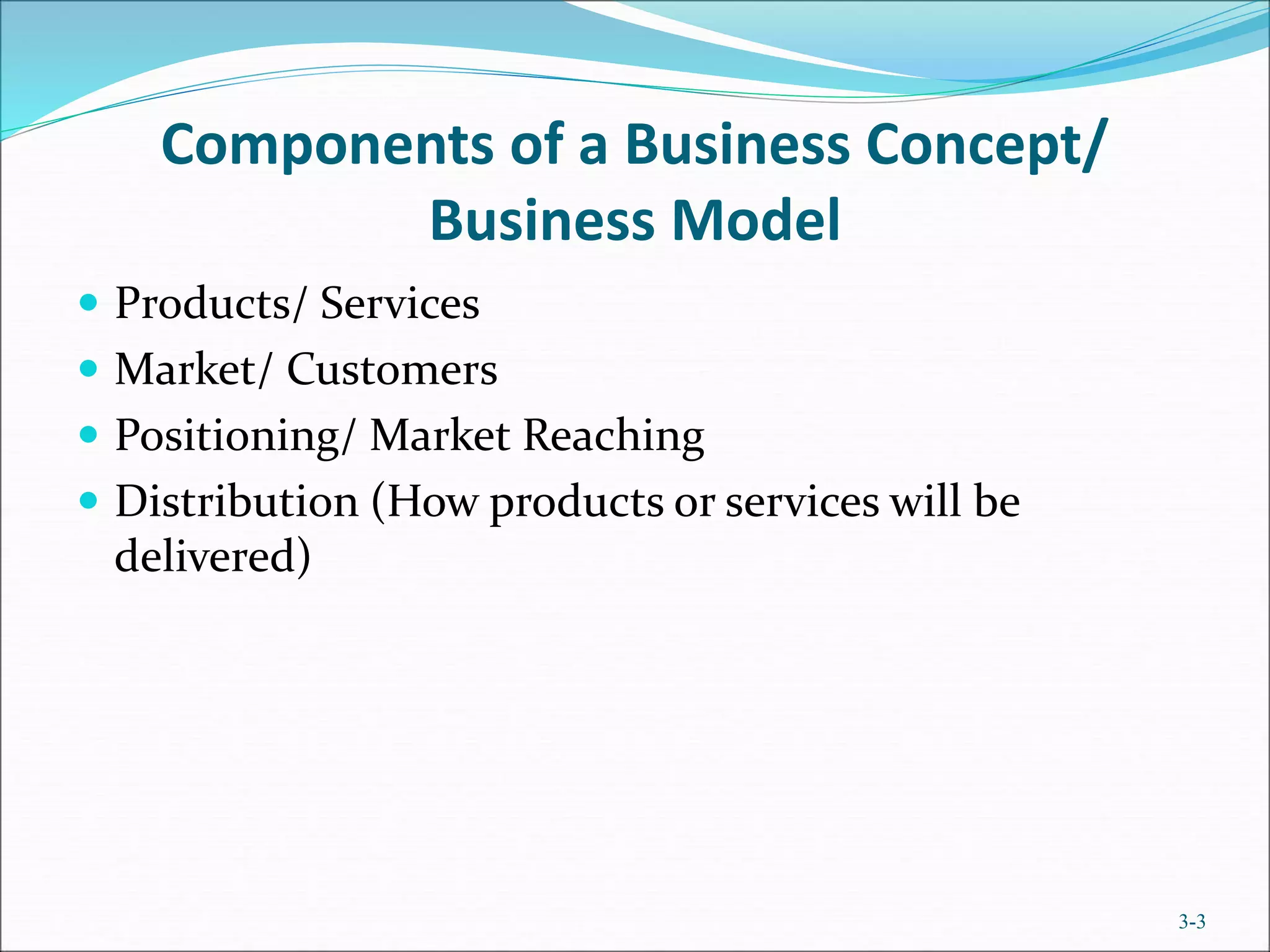
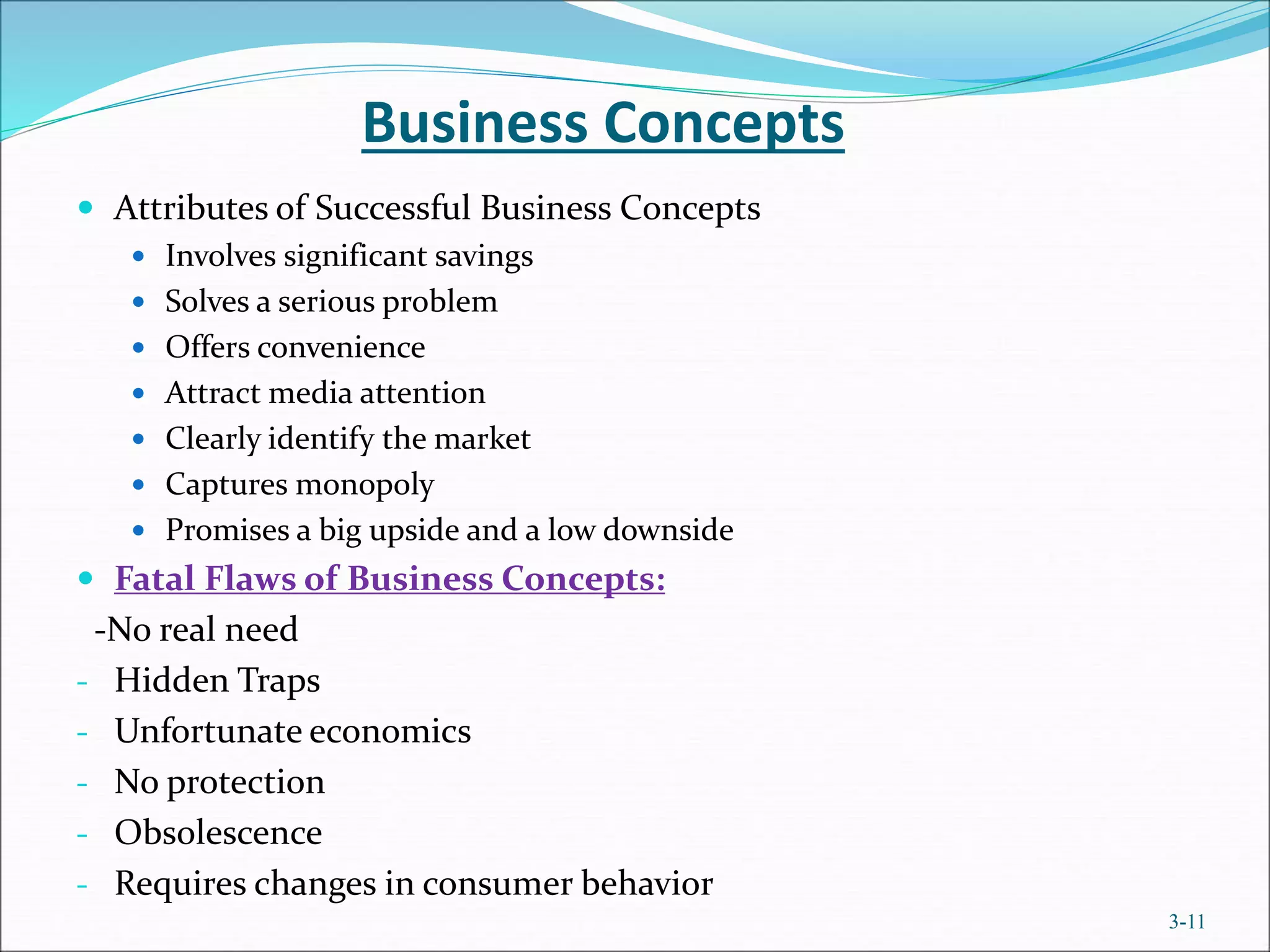
The document outlines the essential components of defining a business concept, which is a cohesive set of ideas for creating and delivering market value. It emphasizes the importance of developing a unique business model that addresses customer needs and effectively positions products or services. Additionally, it highlights the necessity of conducting thorough research in various areas like industry, market, and competition to ensure the business concept's success.