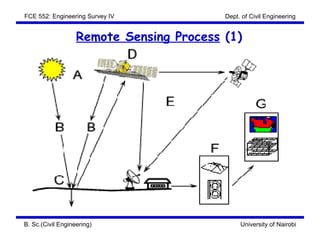
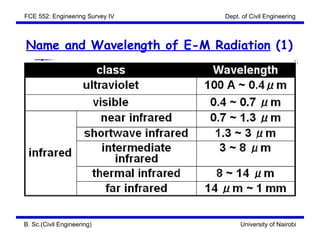
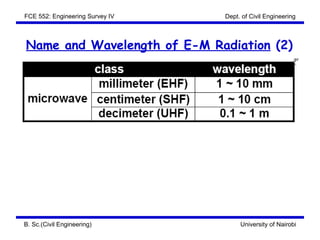
This document discusses the fundamentals of remote sensing. It covers the concept of remote sensing, the characteristics of electromagnetic radiation, the classification of EM radiation, and types of remote sensing. The concept section defines remote sensing and describes the flow and process. It involves an energy source, interaction with the target, sensor recording, transmission and processing, interpretation and analysis, and application. Characteristics of EM radiation include wavelength, frequency and speed. Classification involves the different names and wavelengths that make up the EM spectrum, as well as the principal atmospheric windows and bands used in remote sensing. Types of remote sensing are also addressed.