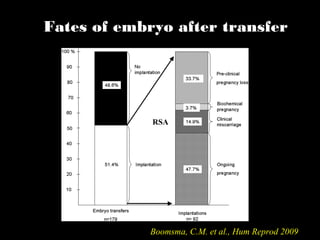
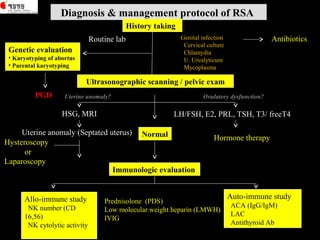
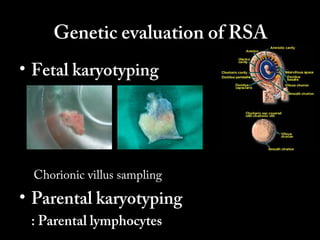
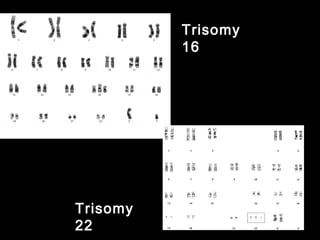
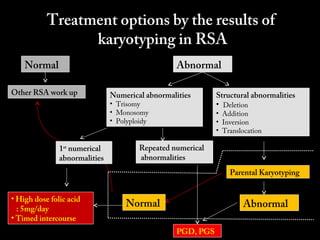
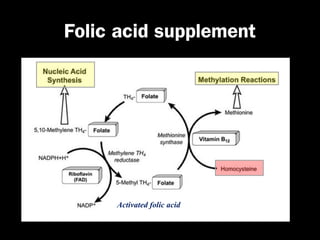
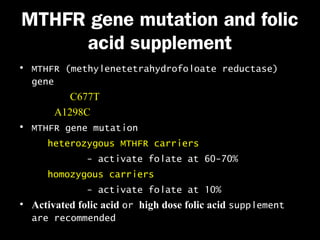
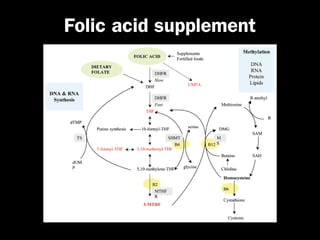
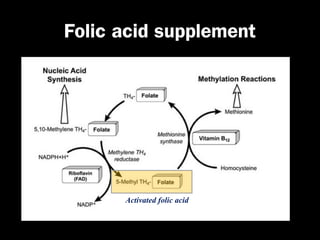
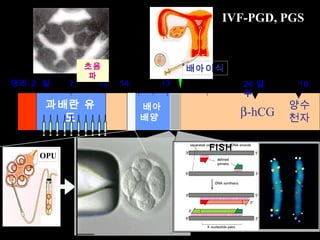
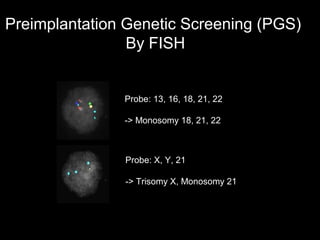
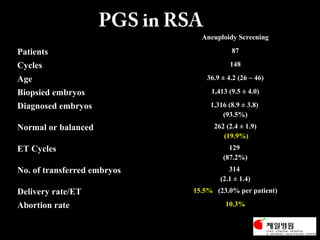
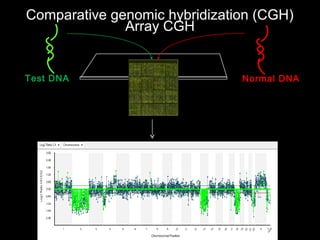
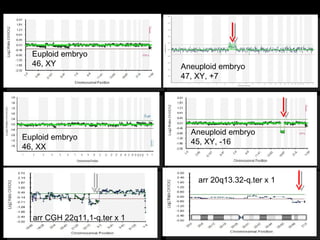
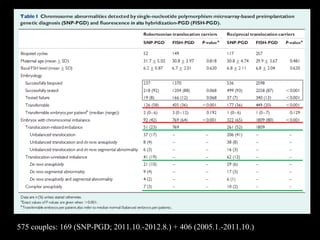
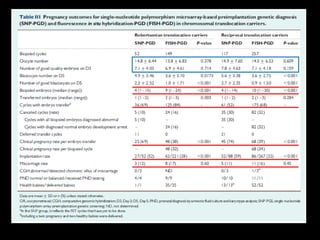
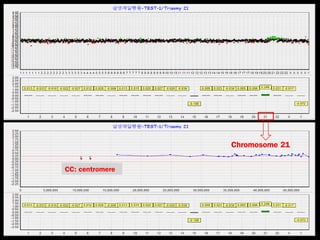
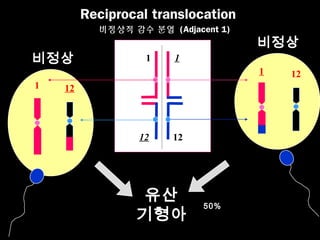
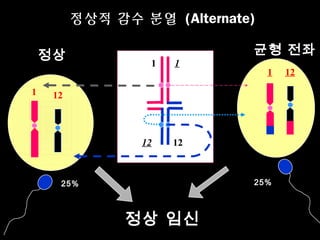
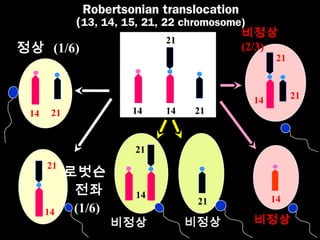
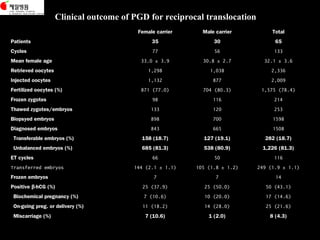
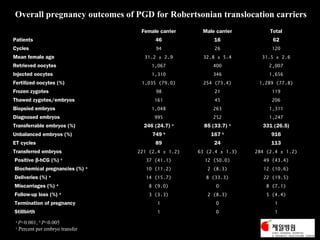
This document discusses the genetic causes and management of recurrent spontaneous abortion (RSA). It defines RSA as three or more pregnancy losses before 20 weeks. Around 50% of RSA cases are considered unexplained. Genetic factors, including balanced translocations, account for around 2-5% of cases. Karyotyping of abortus and parental testing can identify chromosomal abnormalities. For repeated aneuploid miscarriages, high dose folic acid supplementation and timed intercourse may help prevent further aneuploid conceptions. Preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) and screening (PGS) using technologies like comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) and array CGH can identify and select euploid embryos for transfer in cases involving