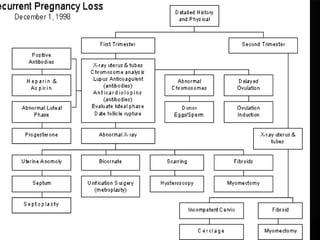
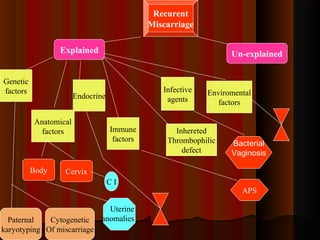
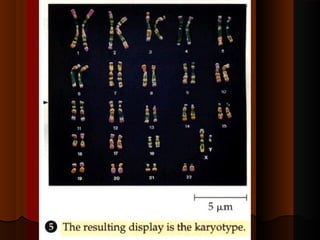
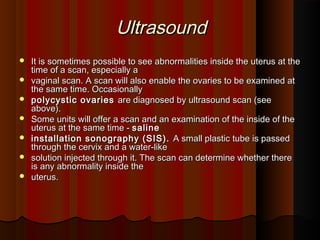
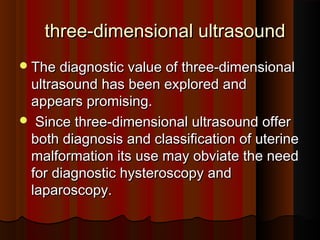
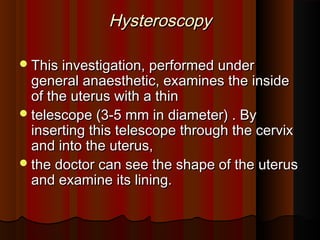
Recurrent miscarriage is defined as 3 or more consecutive spontaneous pregnancy losses under 20 weeks gestation. It affects 1% of women and can be caused by many potential genetic, anatomical, hormonal, and immunological factors. Evaluation involves testing the parents' chromosomes through karyotyping of their blood, testing the chromosomes of miscarried fetal tissue when possible, and examining the uterus and fallopian tubes through ultrasound, hysterosalpingogram, hysteroscopy, or laparoscopy to check for anatomical abnormalities. Finding the cause helps guide treatment such as surgery to remove uterine anomalies which may improve future pregnancy outcomes.







































![ TORCH (toxoplasmosis rubella,TORCH (toxoplasmosis rubella,
cytomegalovirus and herpes simplexcytomegalovirus and herpes simplex
virus), other [congenital syphilis andvirus), other [congenital syphilis and
viruses], screening is unhelpful in theviruses], screening is unhelpful in the
investigation of recurrent miscarriage.investigation of recurrent miscarriage.
For an infective agent to be implicated in theFor an infective agent to be implicated in the
aetiology of repeated pregnancy loss, it mustaetiology of repeated pregnancy loss, it must
be capable of persisting in the genital tract andbe capable of persisting in the genital tract and
avoiding detection or must cause insufficientavoiding detection or must cause insufficient
symptoms to disturb the women.symptoms to disturb the women.
Toxoplasmosis, rubella, cytomegalovirus,Toxoplasmosis, rubella, cytomegalovirus,
herpes and listeria infections do not fulfil theseherpes and listeria infections do not fulfil these
criteria and routine TORCH screening shouldcriteria and routine TORCH screening should
be abandonebe abandone](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recurrent-miscarriage-guidelines-160907232126/85/Recurrent-miscarriage-guidelines-46-320.jpg)