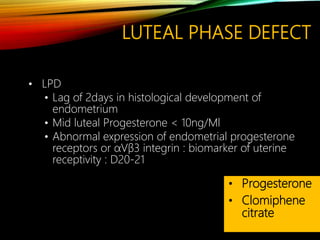
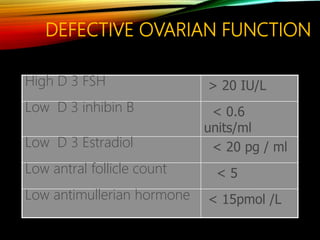
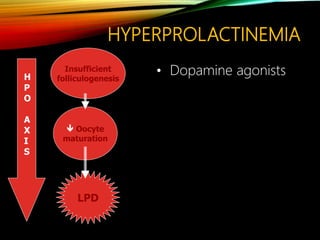
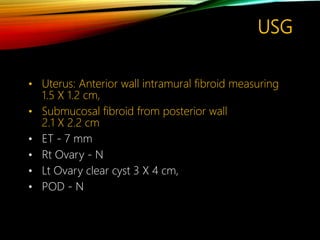
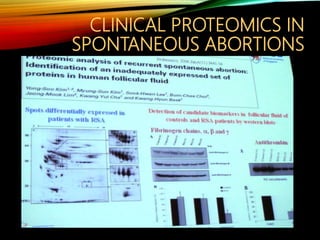
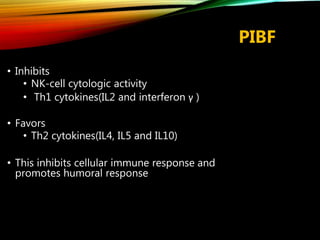
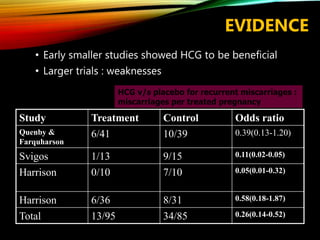
This document discusses recurrent pregnancy loss and provides information on definitions, incidence, causes, investigations, and guidelines. Some key points:
- Recurrent pregnancy loss is defined as 3 or more clinically recognized pregnancy losses before 20 weeks. The incidence is about 1 in 300 pregnancies.
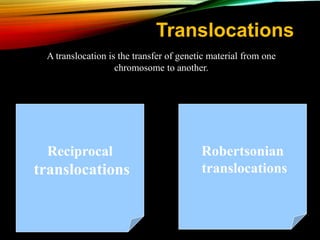
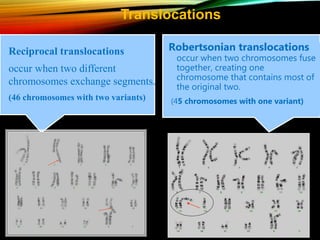
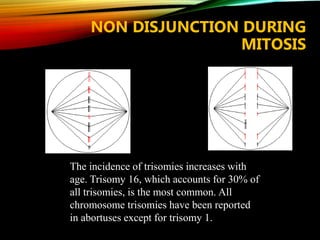
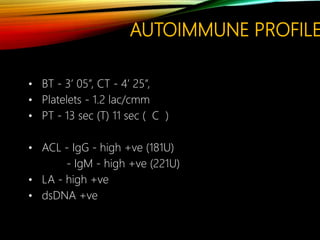
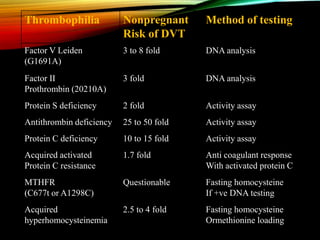
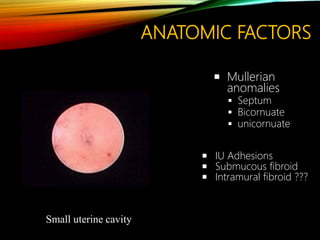
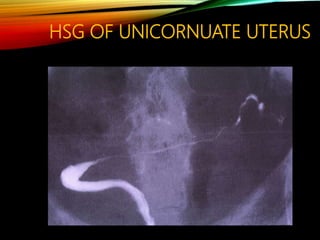
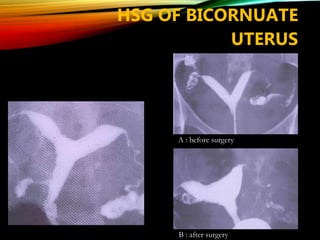
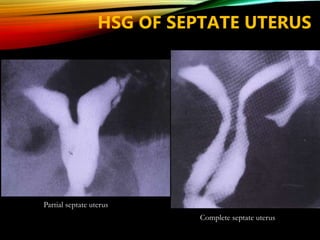
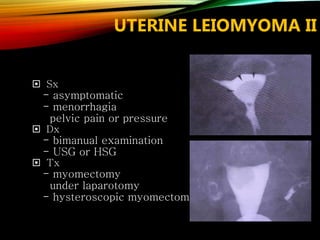
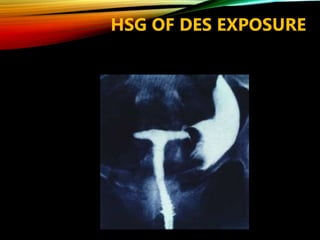
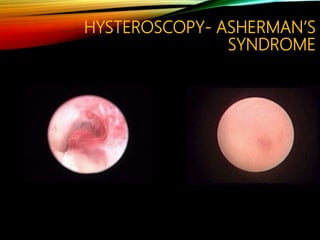
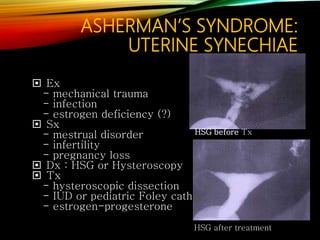
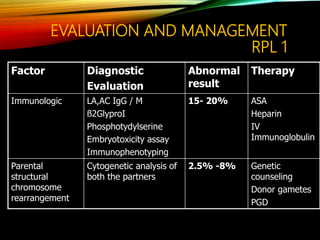
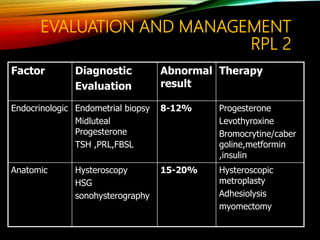
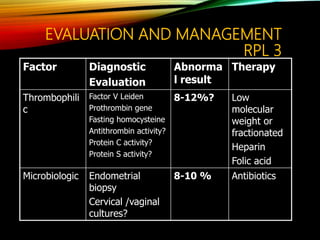
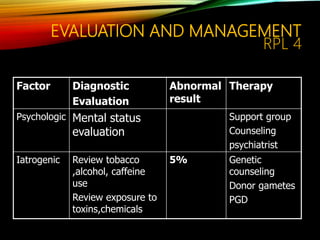
- Common causes include genetic factors in the parents or embryo, anatomic abnormalities, endocrine/immune/infectious factors, and inherited thrombophilias.
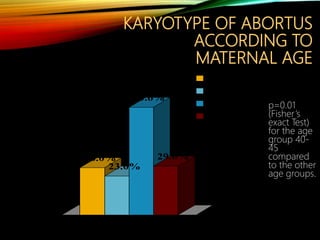
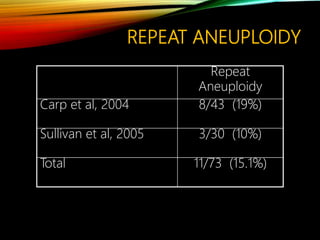
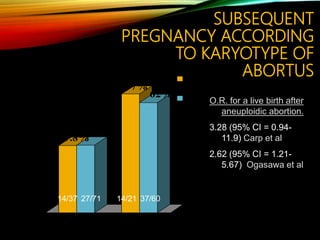
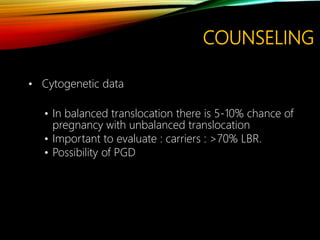
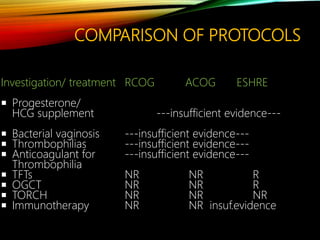
- Investigations should include parental karyotyping after 2 losses, and karyotyping of pregnancy tissues is recommended by RCOG guidelines to provide counseling and predict outcomes of future pregnancies.
- Biomarkers and ultrasound can provide information on predicting outcomes,