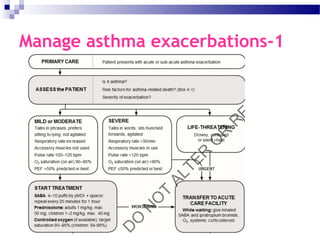
This document provides an in-depth overview of asthma, detailing its definitions, phenotypes, diagnostic criteria, and management strategies, including medications and assessments. It highlights various risk factors for asthma exacerbations, potential medication side effects, and specific considerations during pregnancy. Additionally, the document emphasizes the importance of a stepwise approach to treatment and proper inhaler technique for effective asthma management.