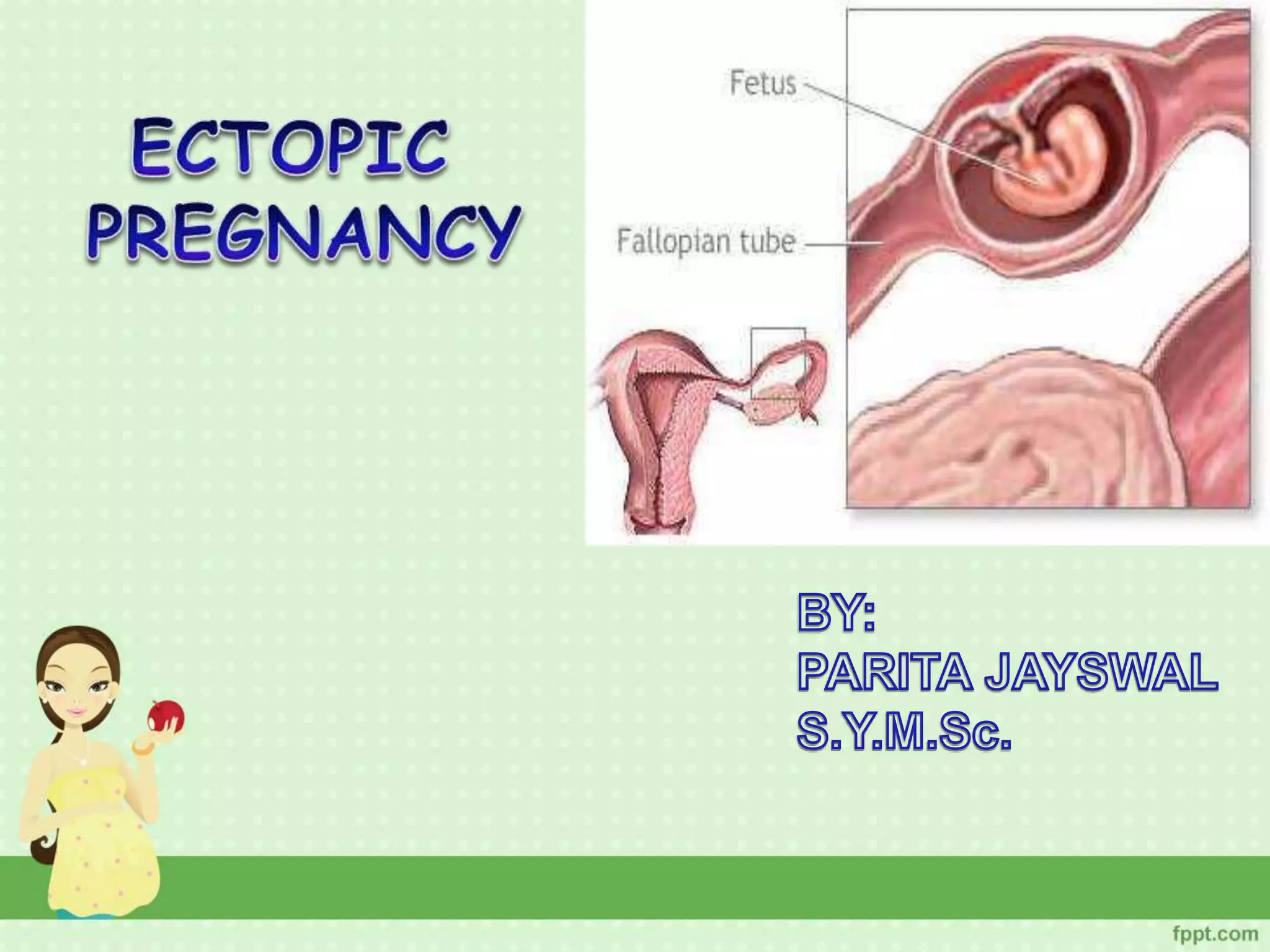
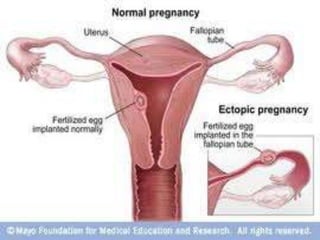
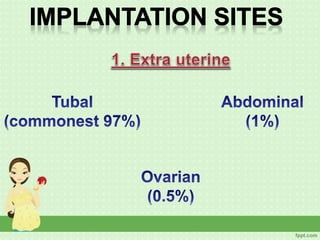
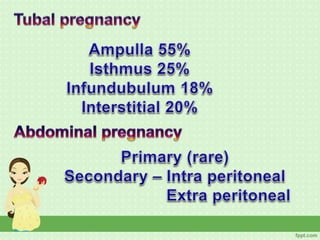
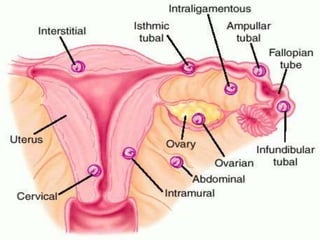
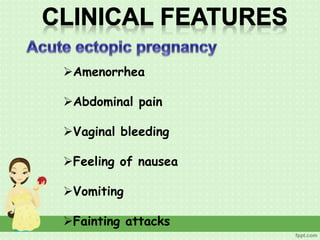
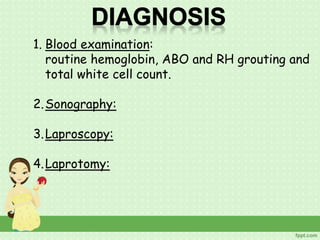
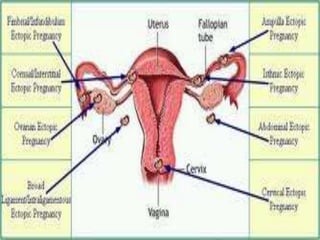
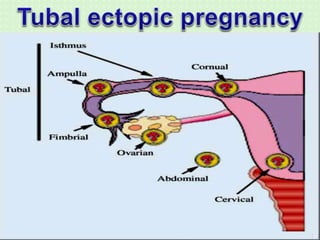
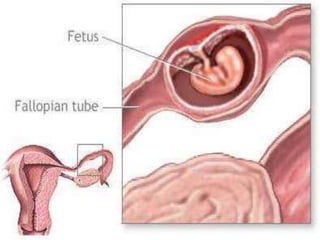
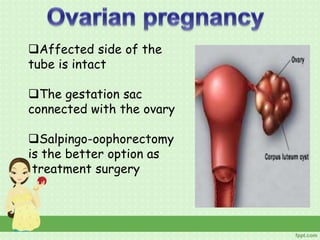
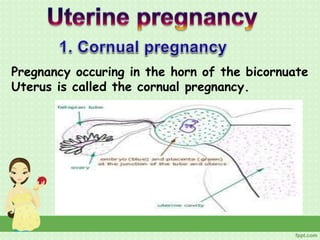
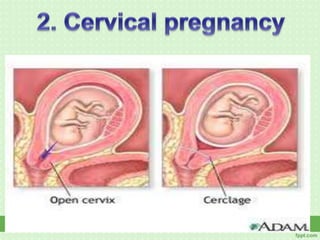
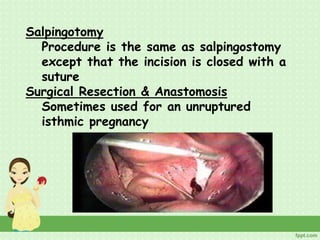
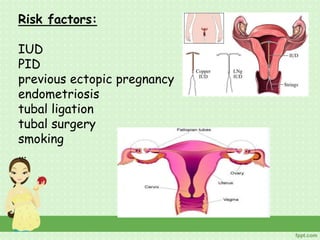
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, usually in a fallopian tube. Common symptoms include missed period, abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, nausea and fainting. Diagnosis involves blood tests, ultrasound and laparoscopy. Treatment depends on factors like size and location of ectopic pregnancy, and may involve surgery like salpingostomy or salpingectomy, or medication like methotrexate. Risk factors include prior pelvic infections, IUD use, tubal surgery or damage from endometriosis. Managing ectopic pregnancies helps preserve fertility whenever possible.