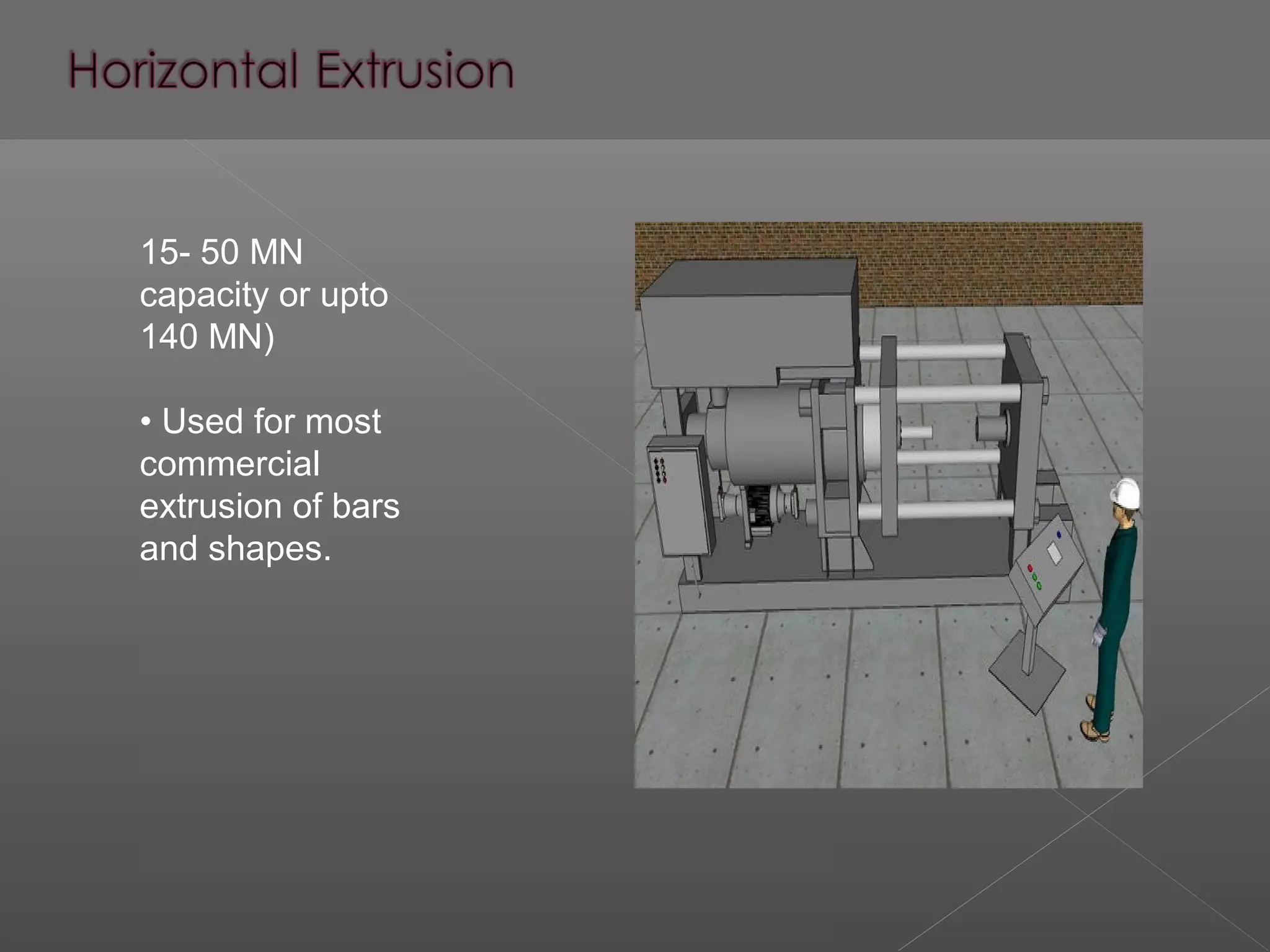
This document provides an overview of the manufacturing process of extrusion. It discusses direct and indirect extrusion as well as hot and cold extrusion. Hot extrusion is performed at elevated temperatures to reduce work hardening and make the material easier to push through the die. Common applications of extrusion include automotive and construction parts. The document also compares the advantages and disadvantages of hot and cold extrusion such as their costs, shape complexity, and environmental impact.