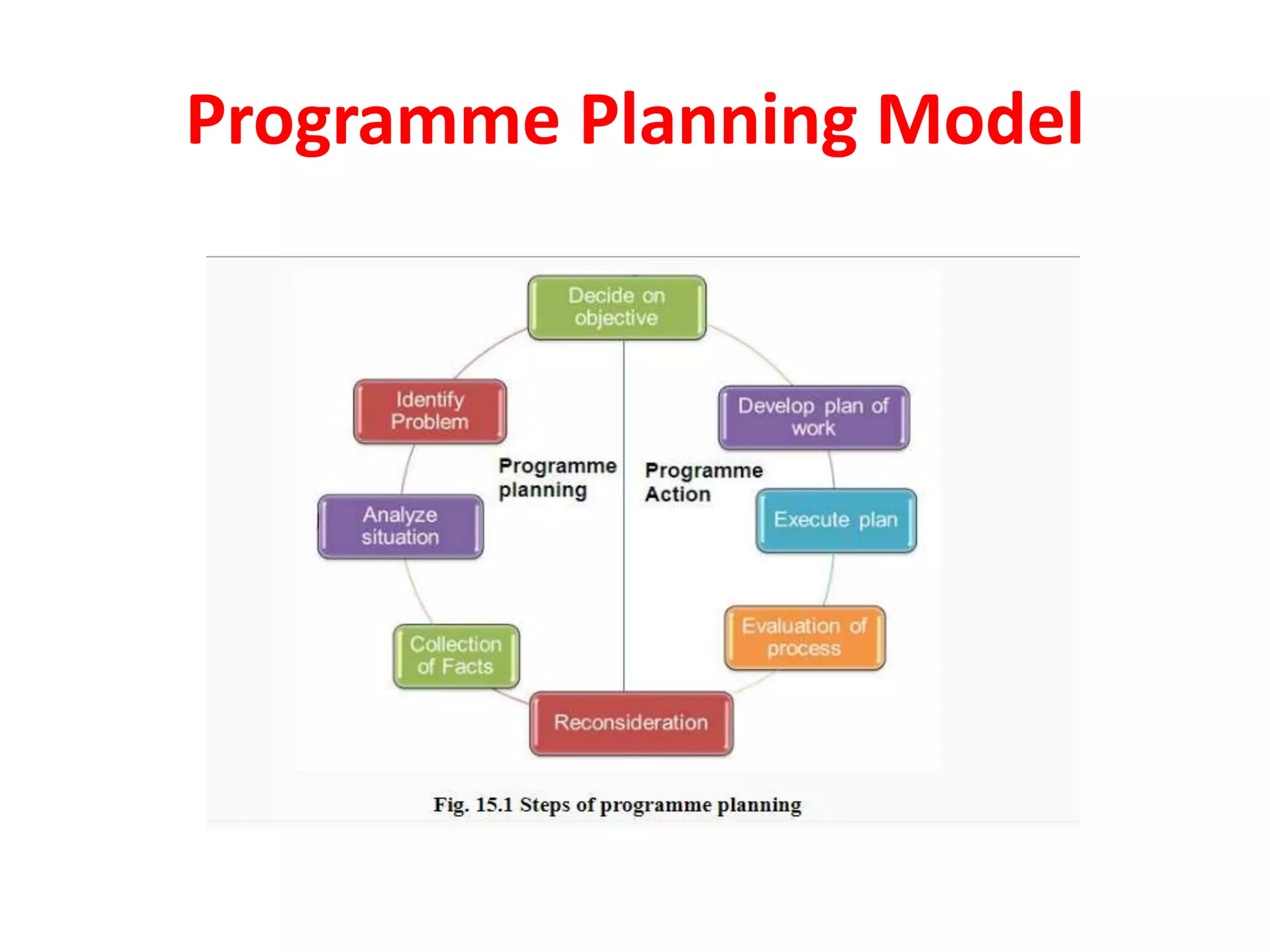
The document outlines extension programme planning, which involves designing a course of action for well-defined target groups through a series of organized activities. It emphasizes the importance of this planning to avoid resource wastage, provide guidance, and foster local support, while introducing a six-phased planning model. Key principles of effective programme planning are also discussed, highlighting the need for flexibility, joint participation, and continuous evaluation.