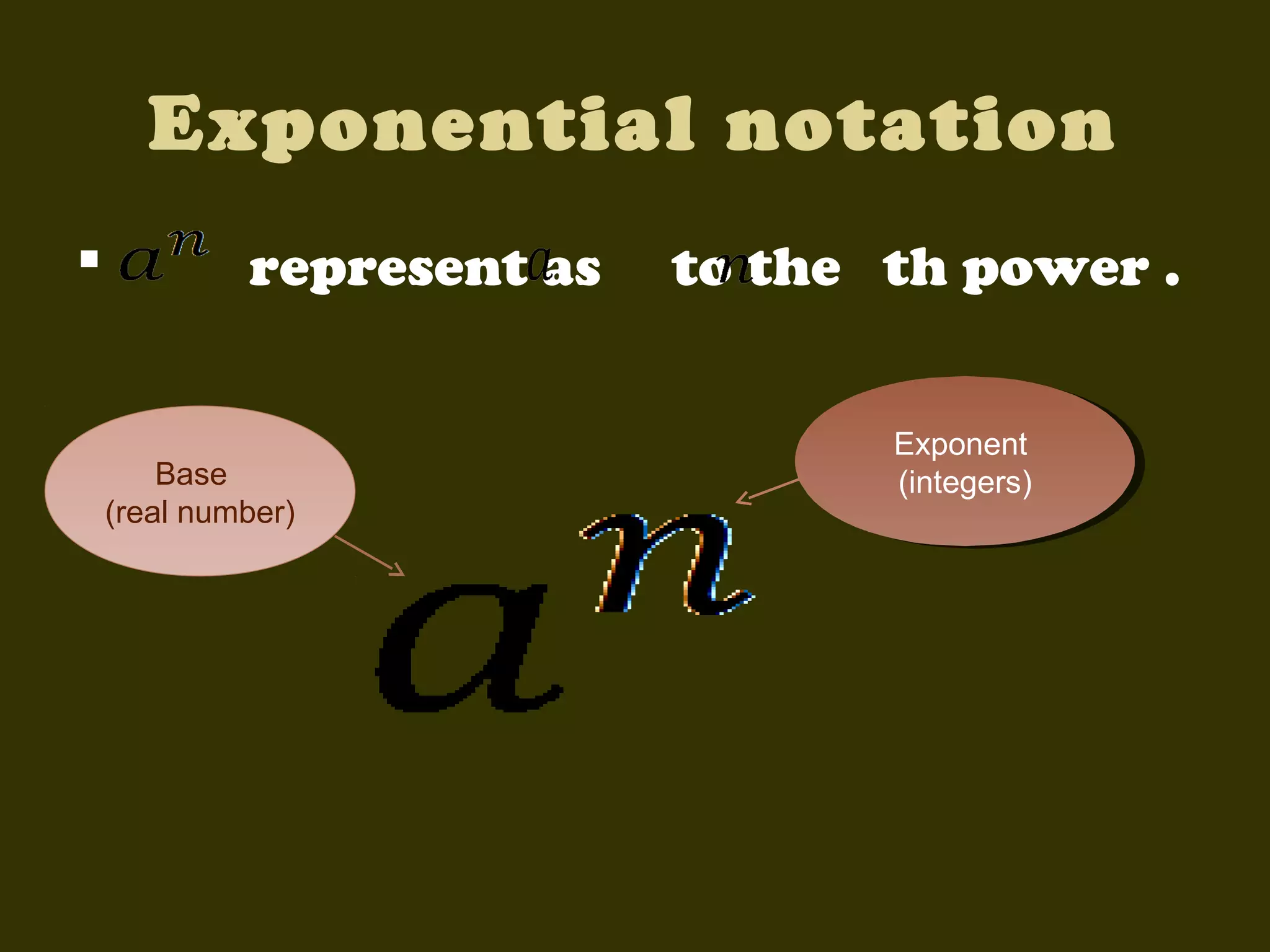
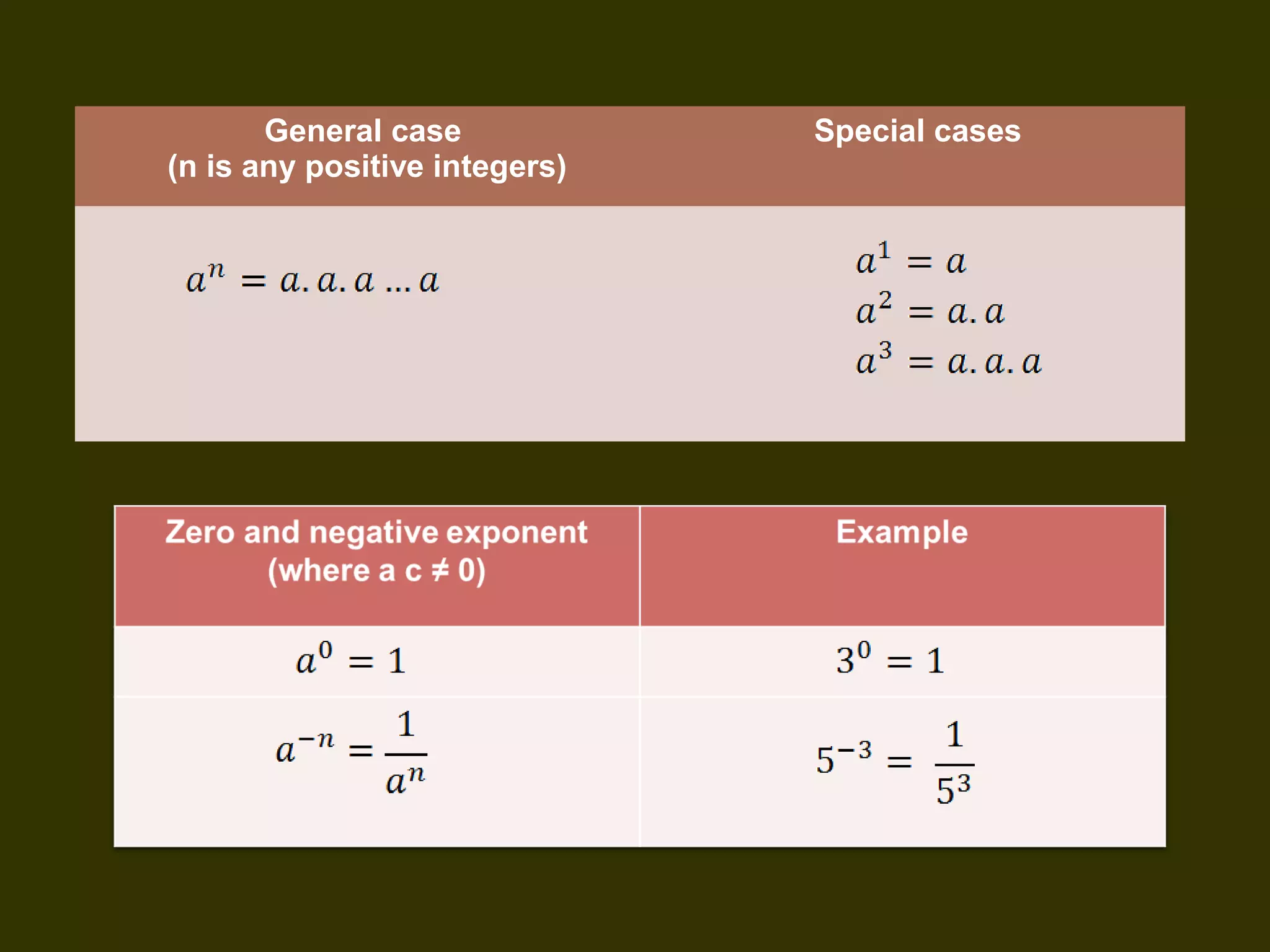
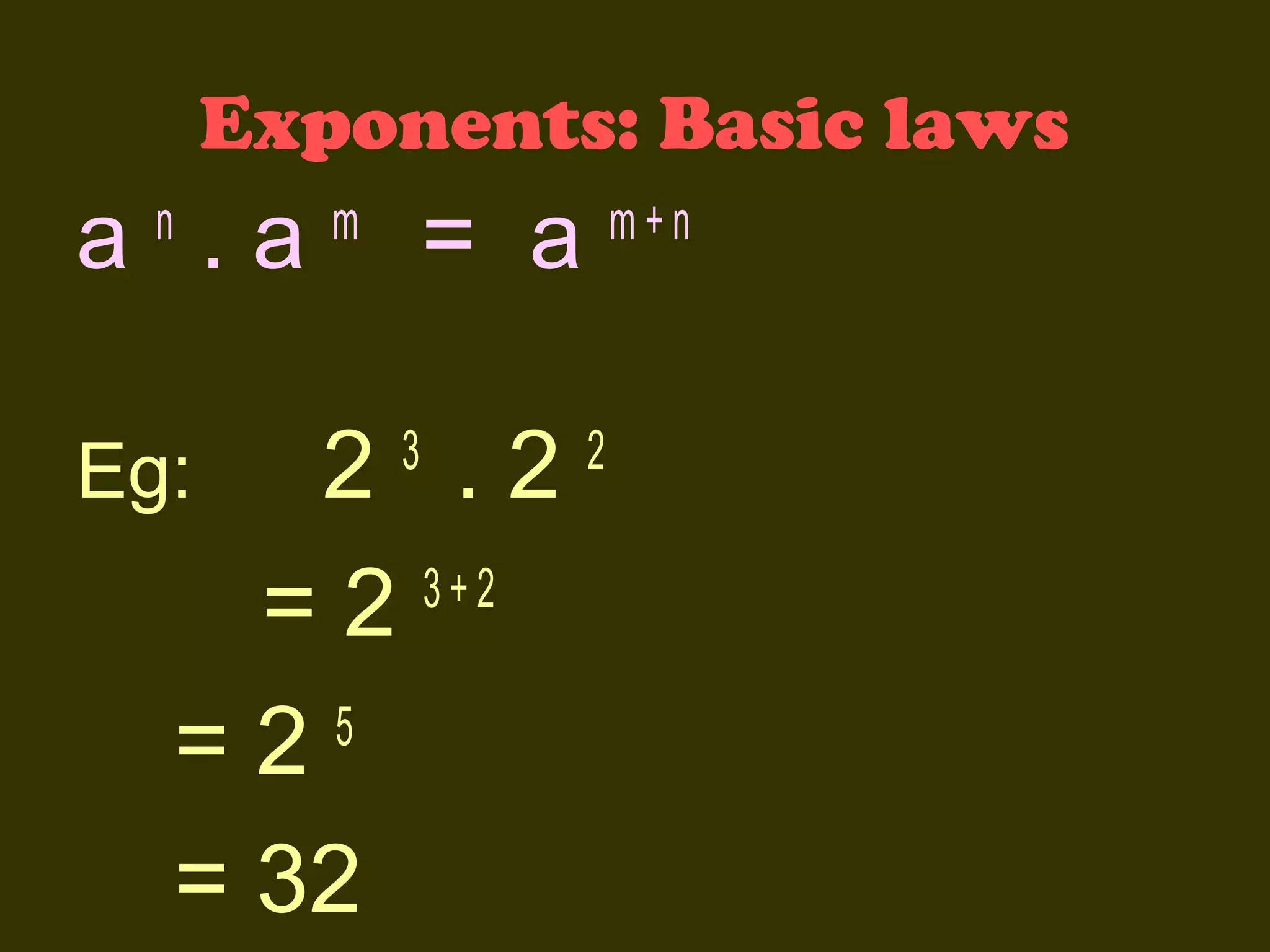
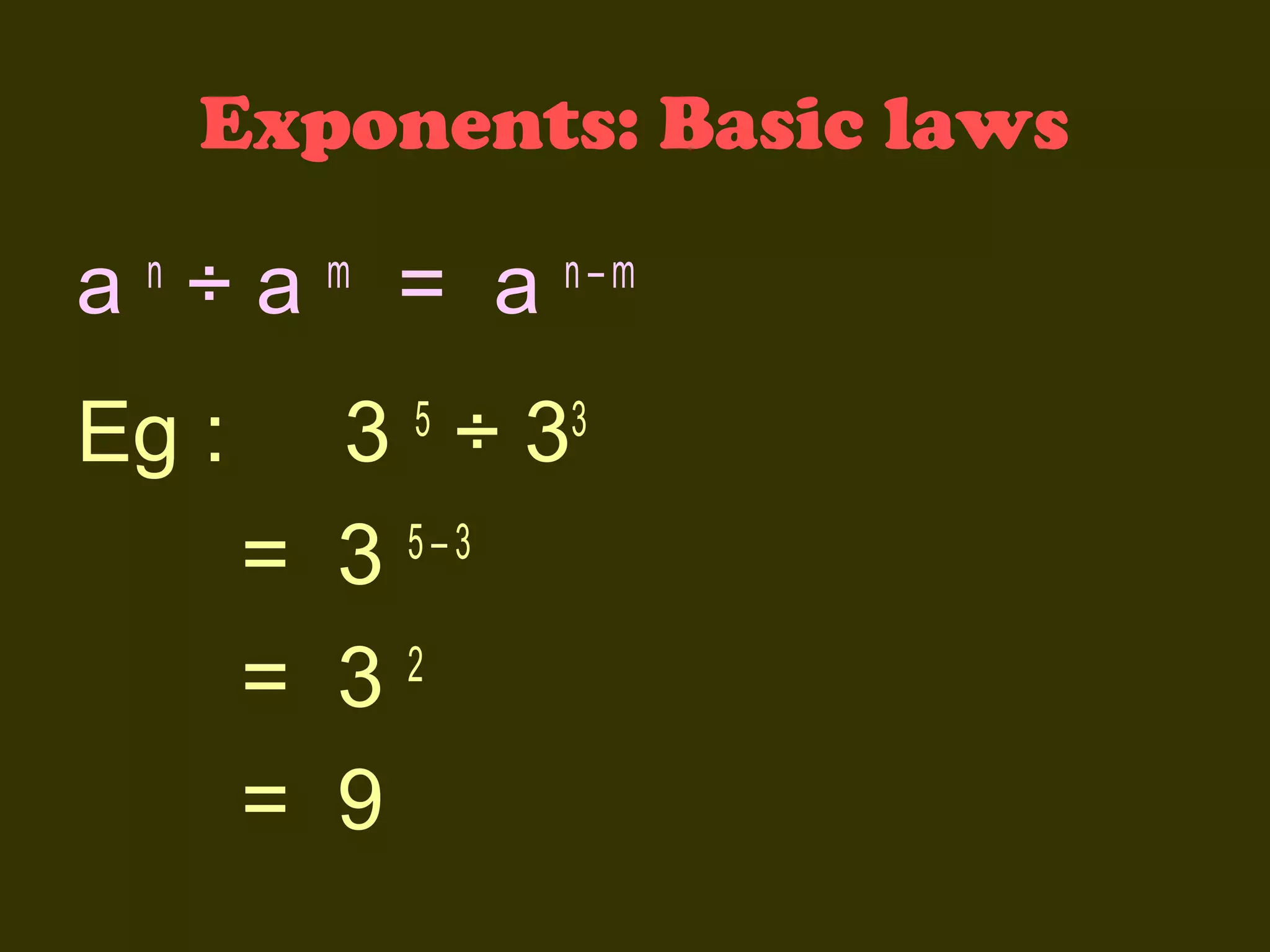
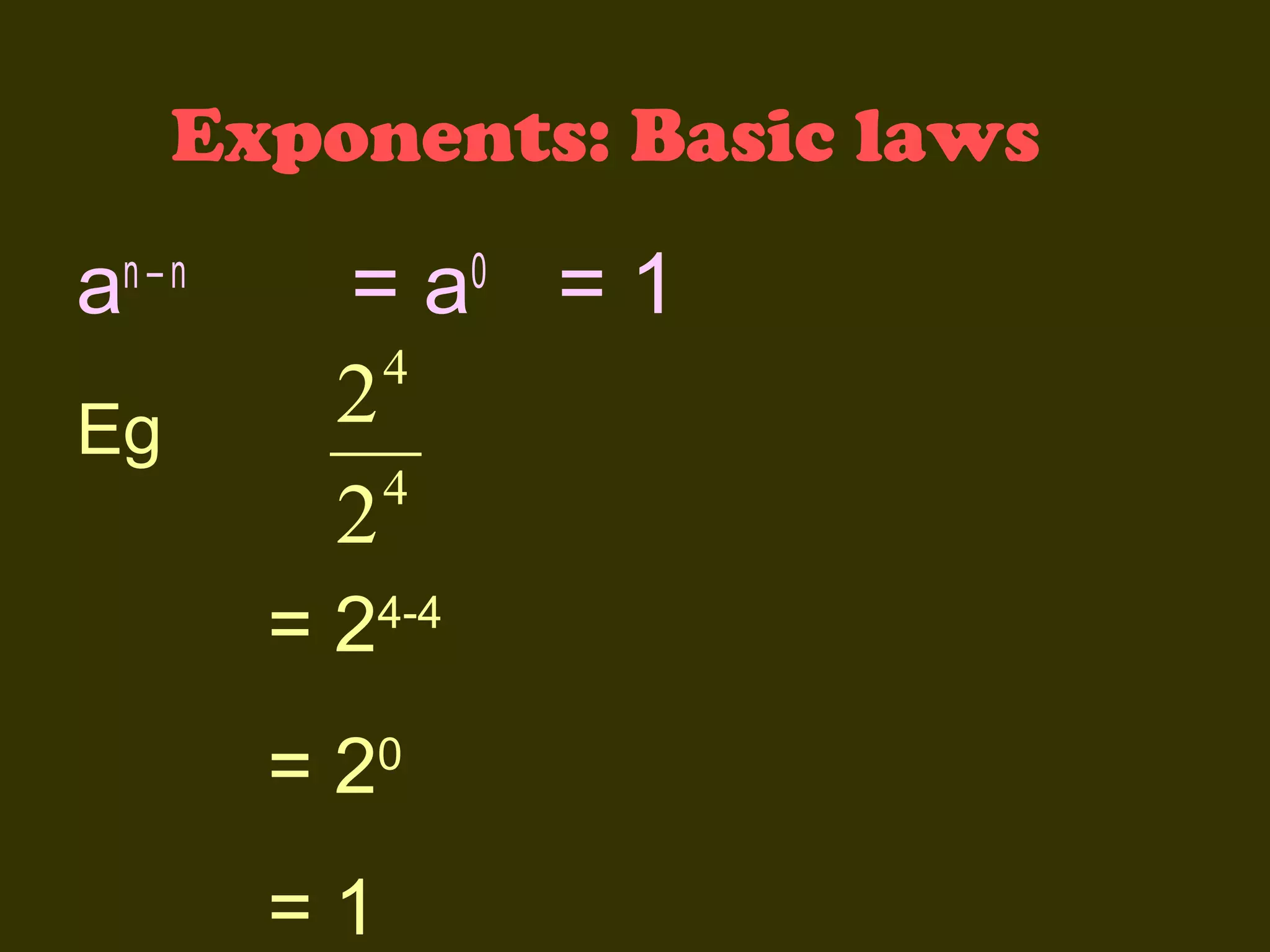
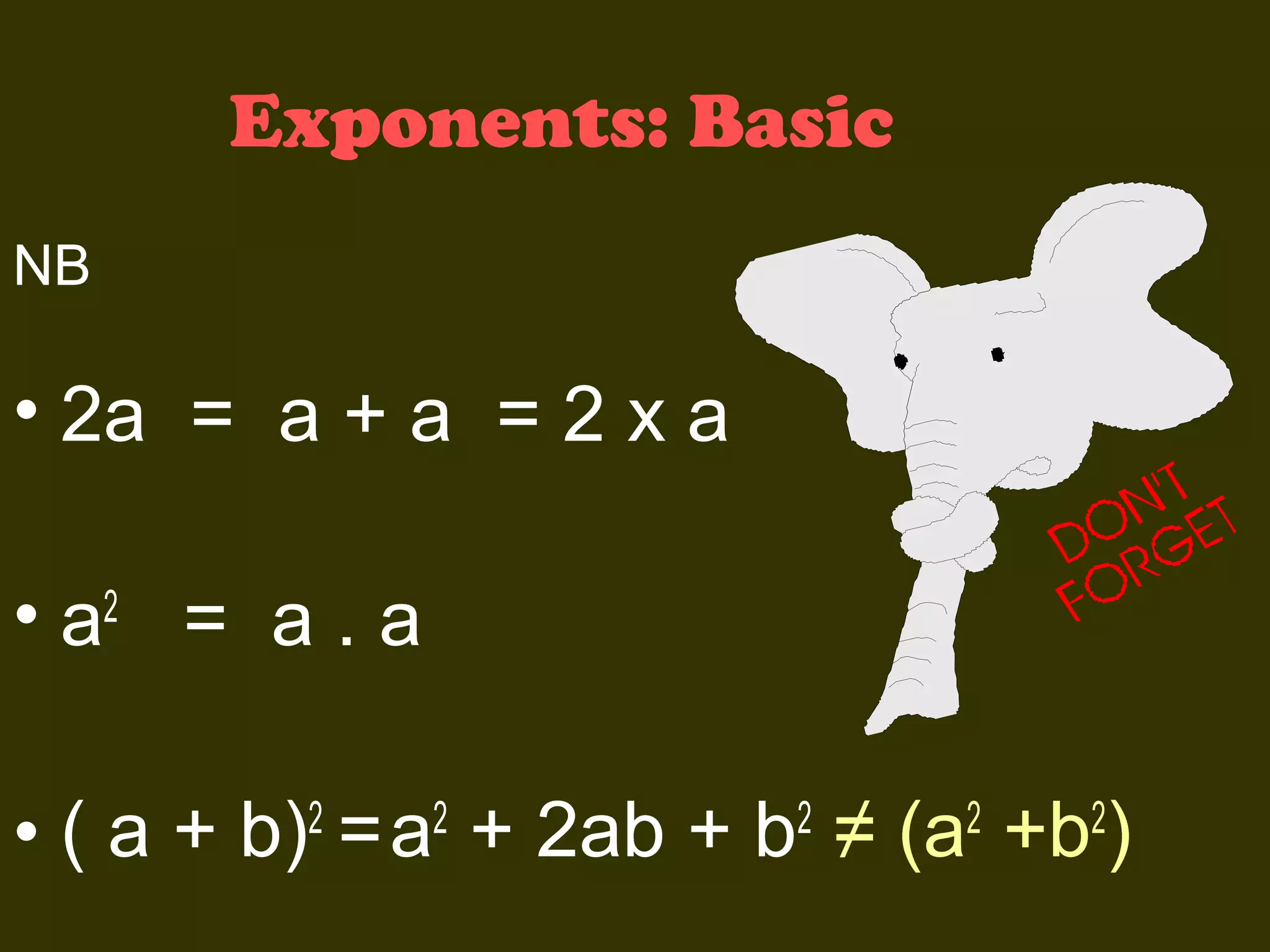
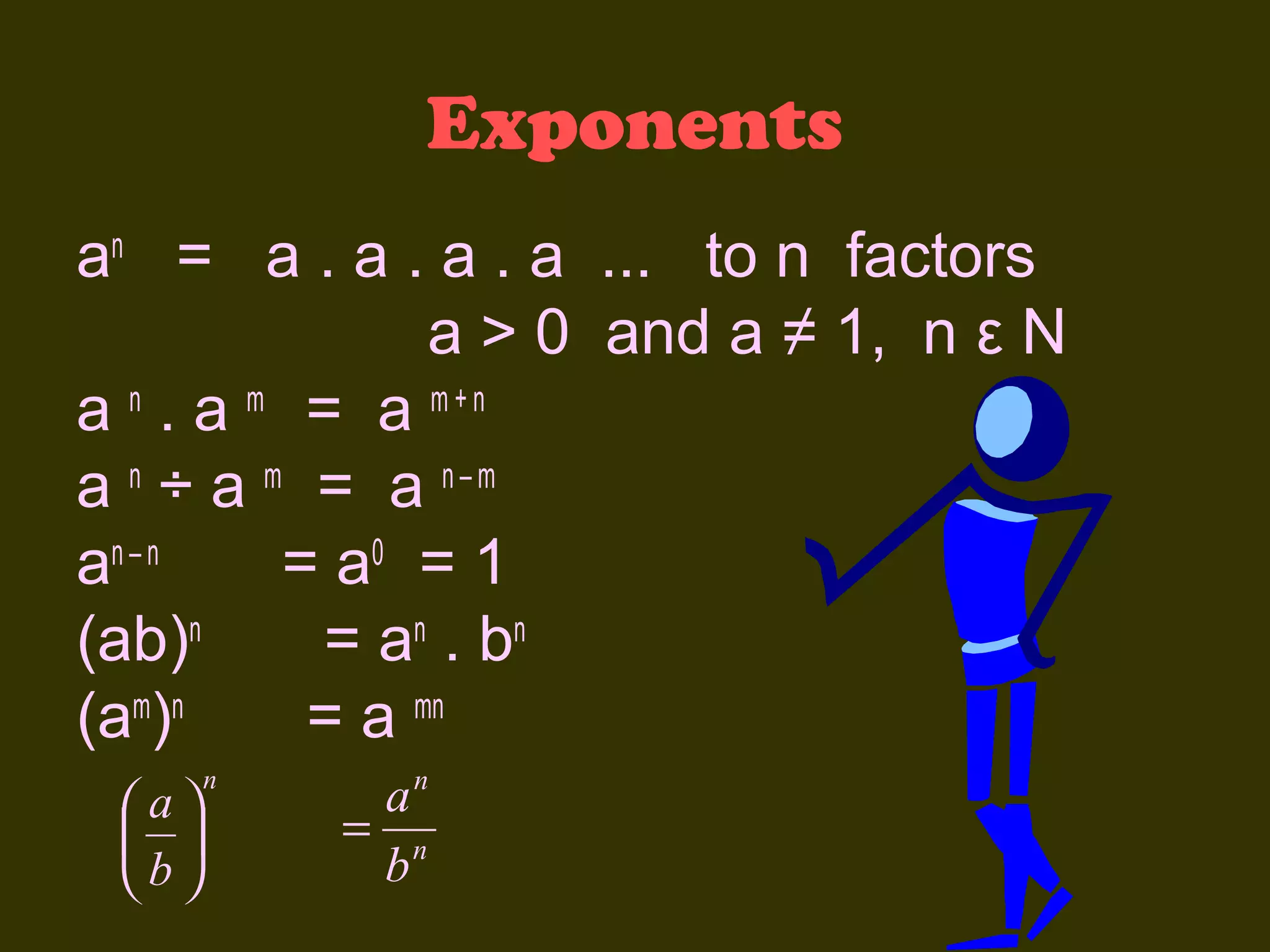
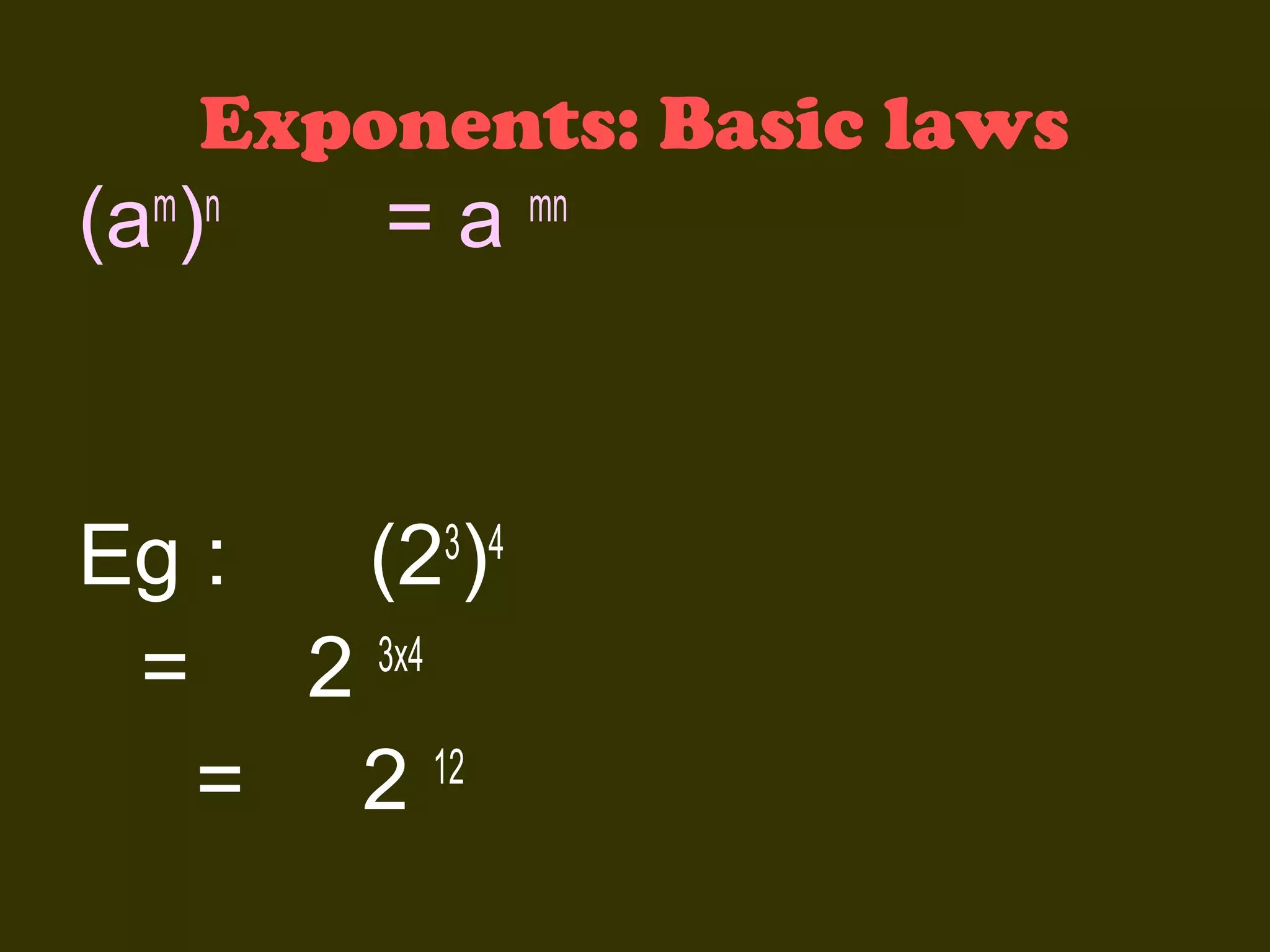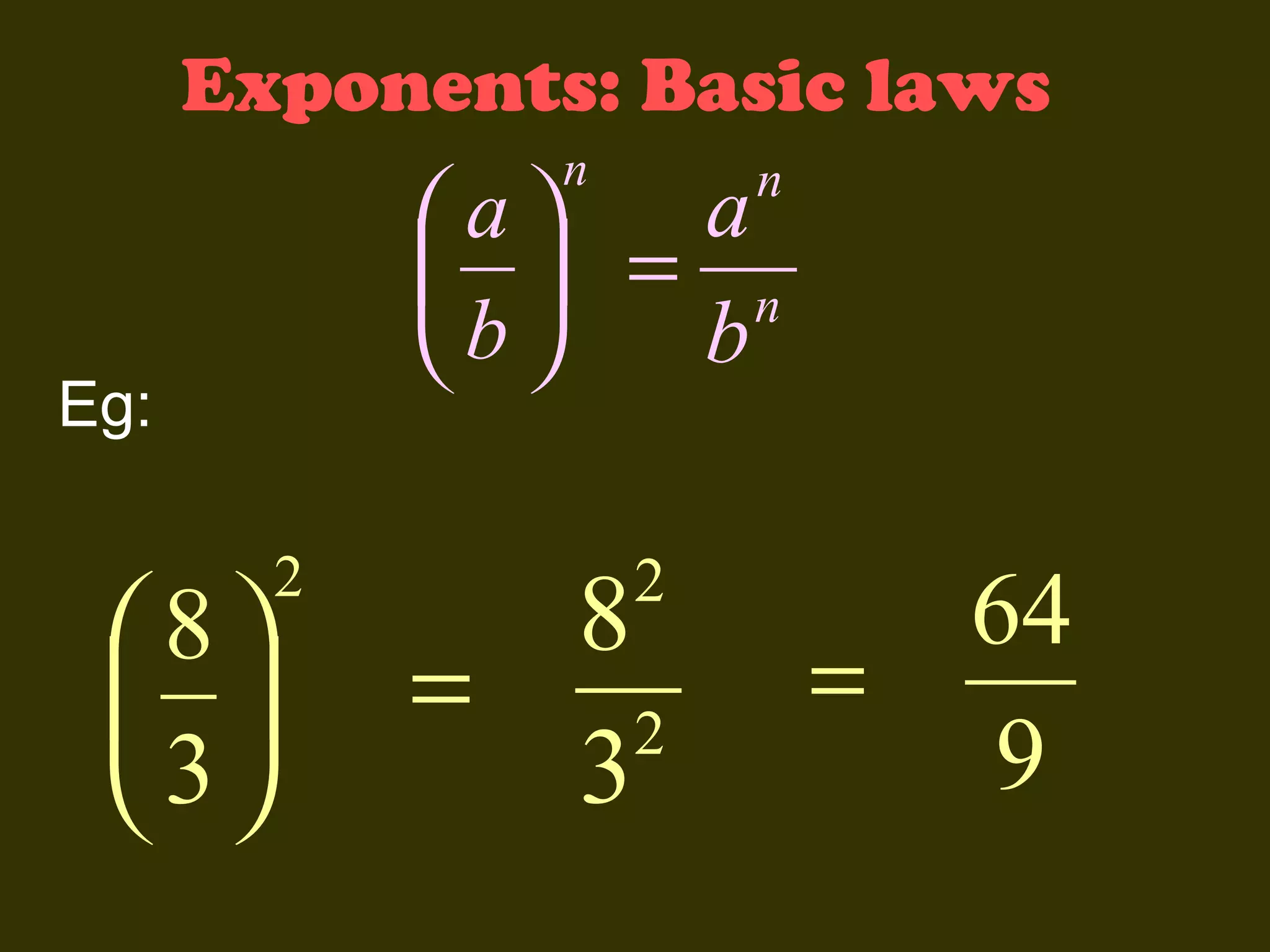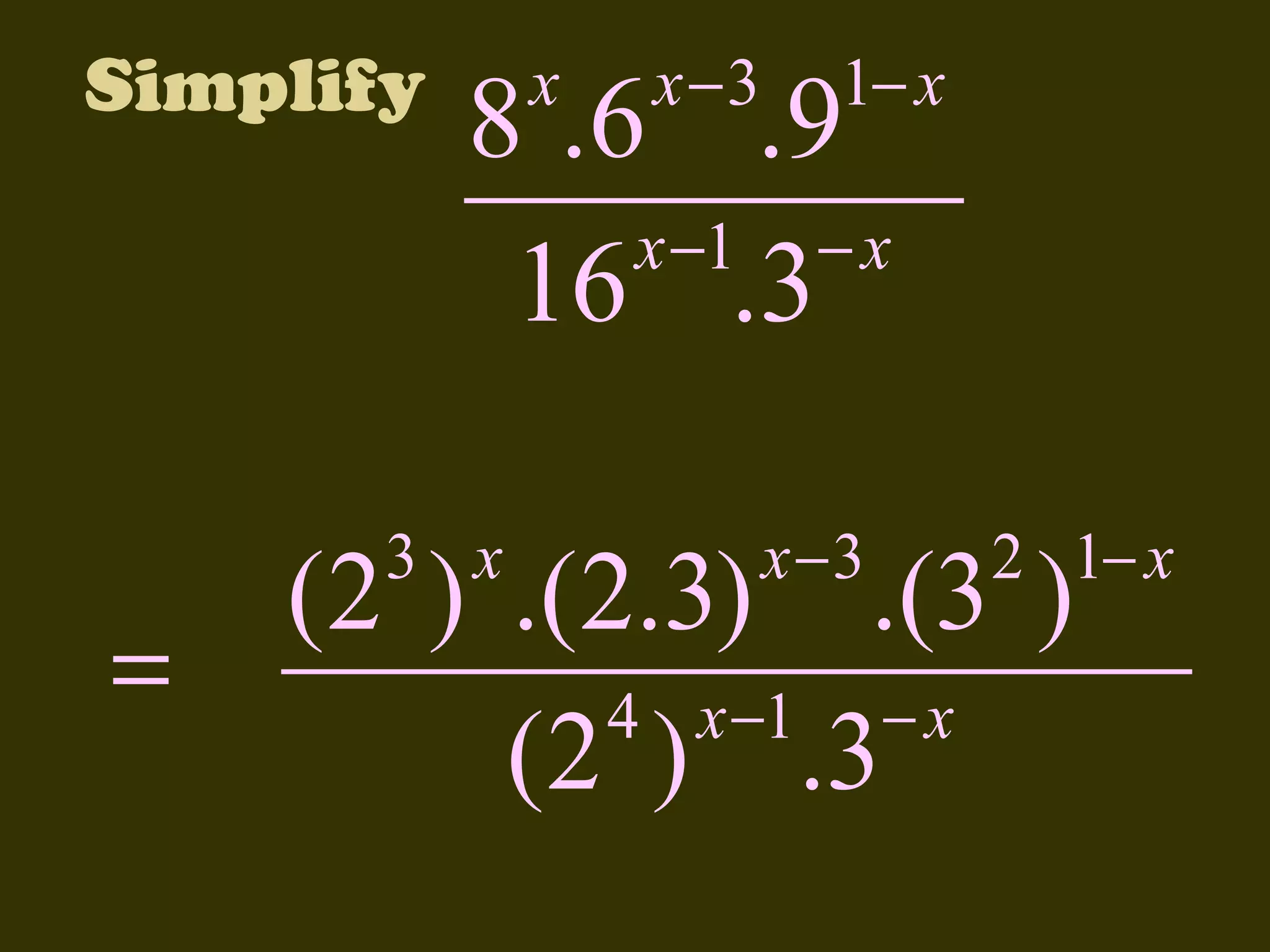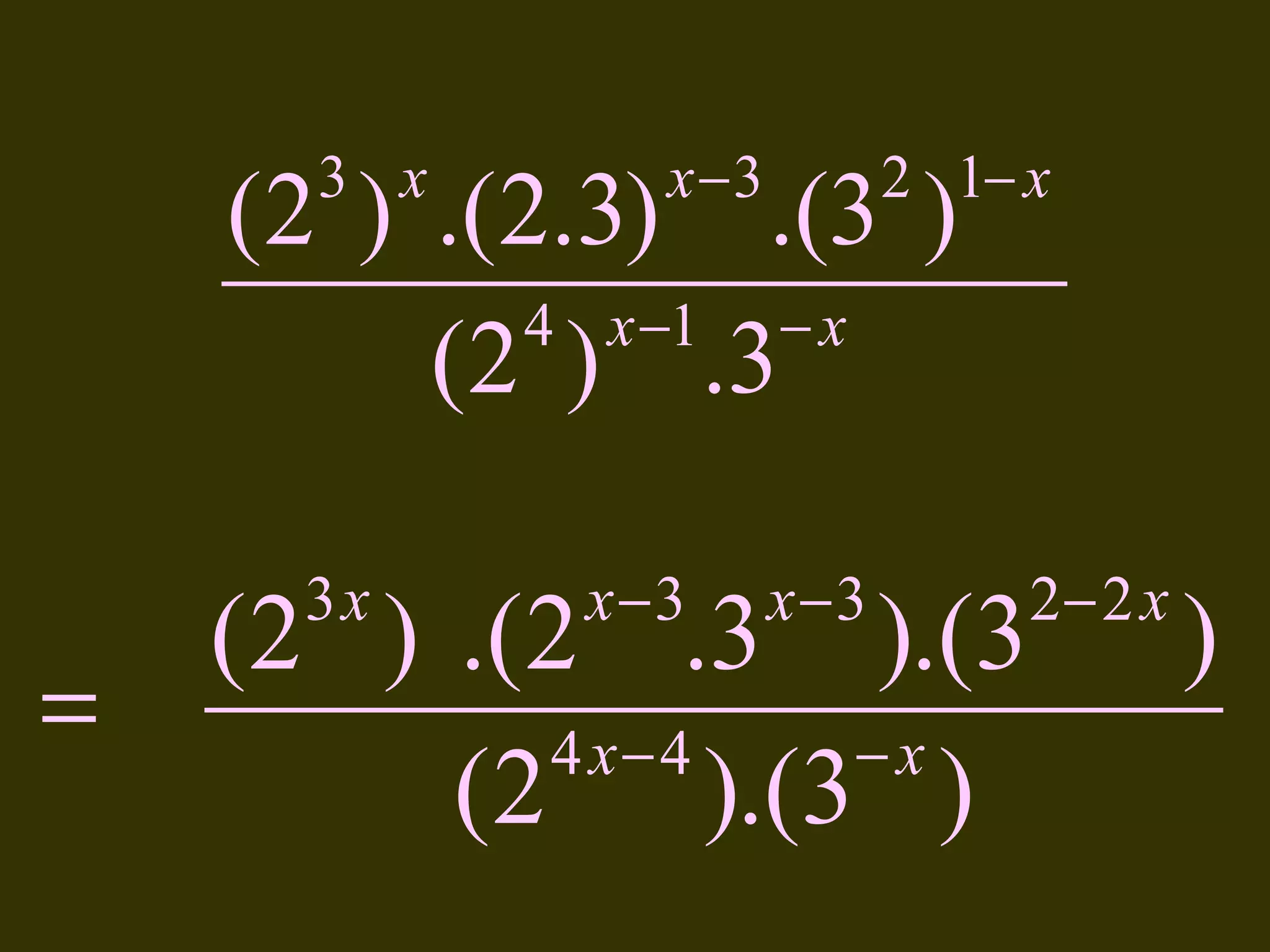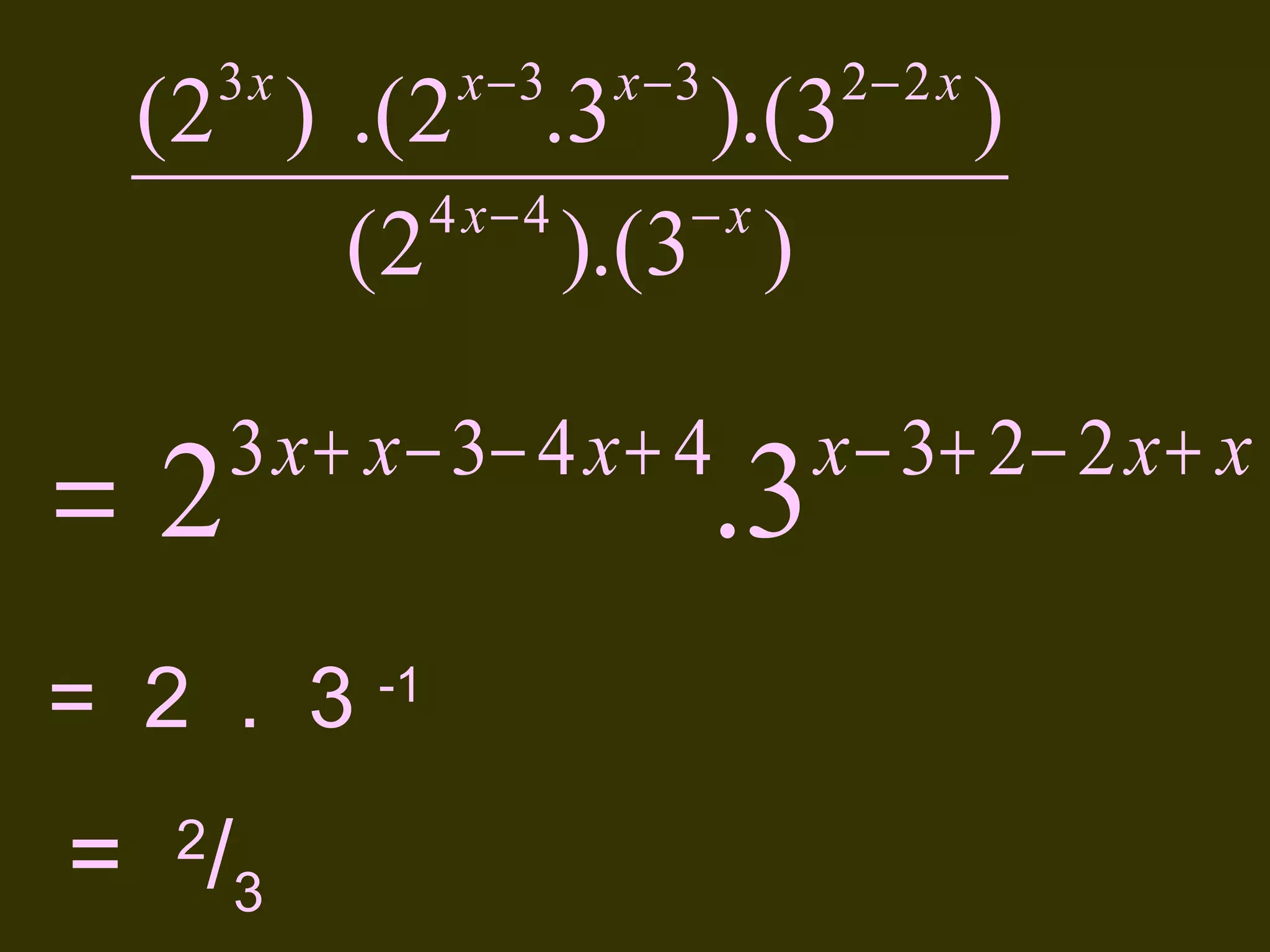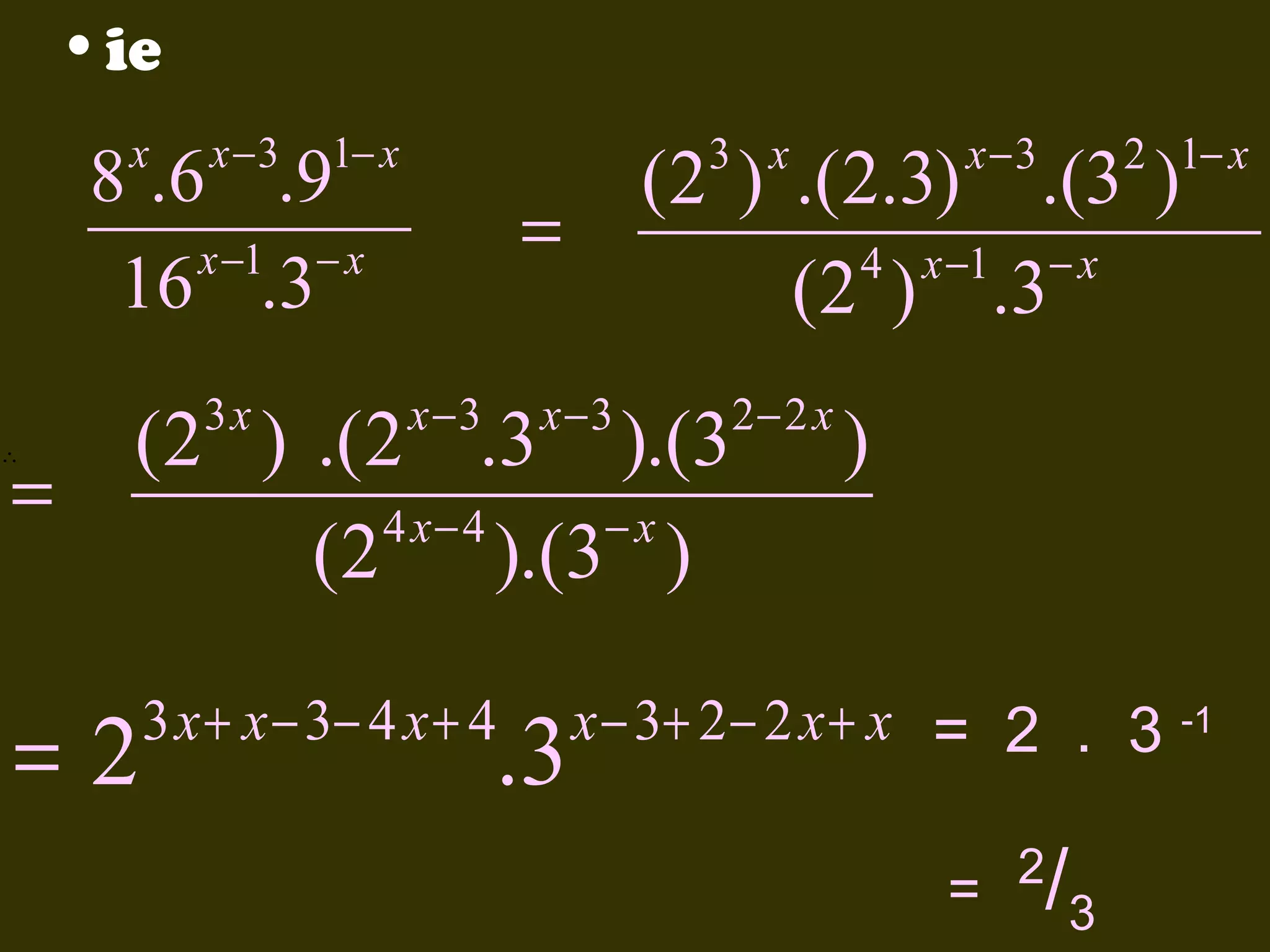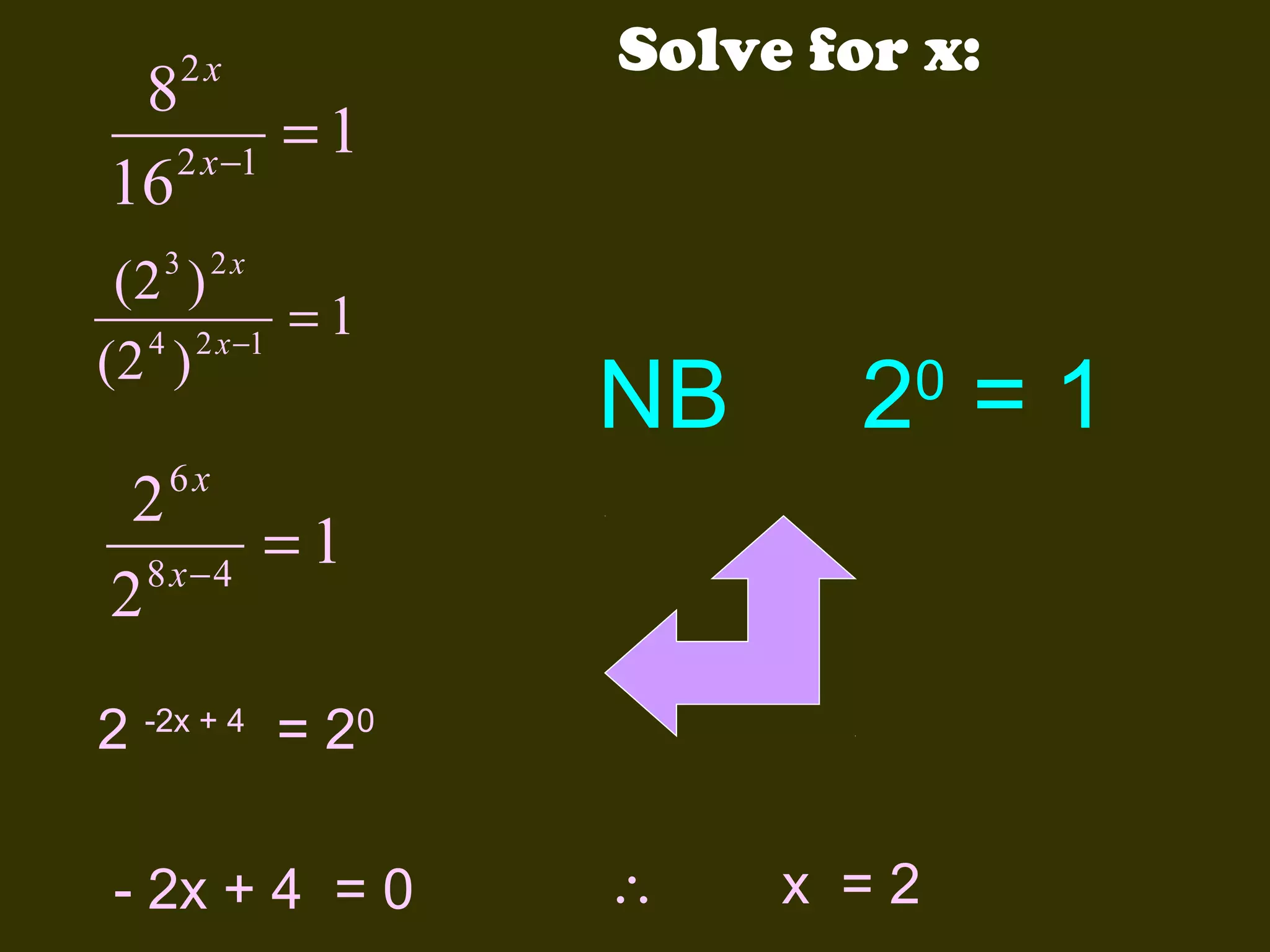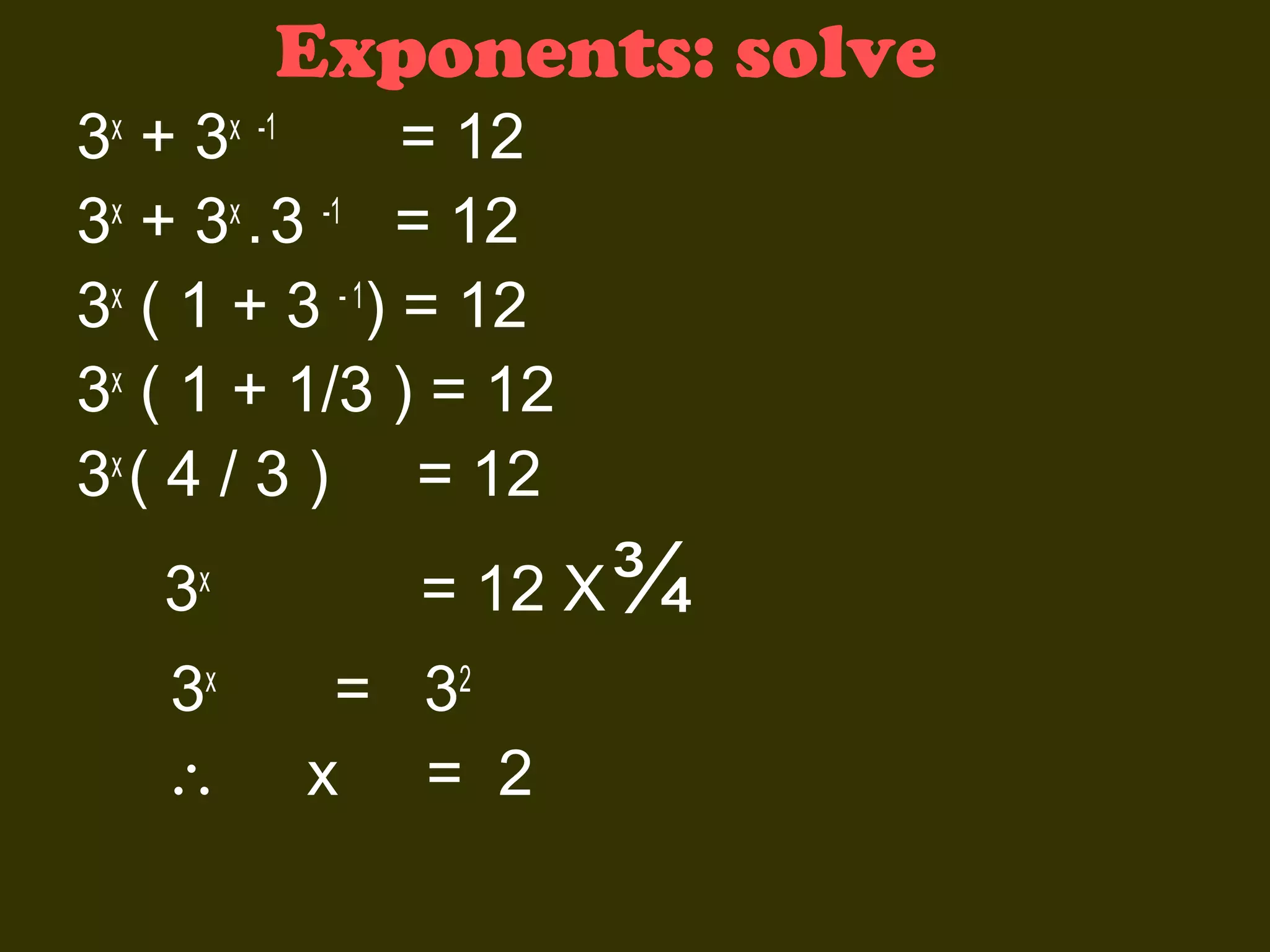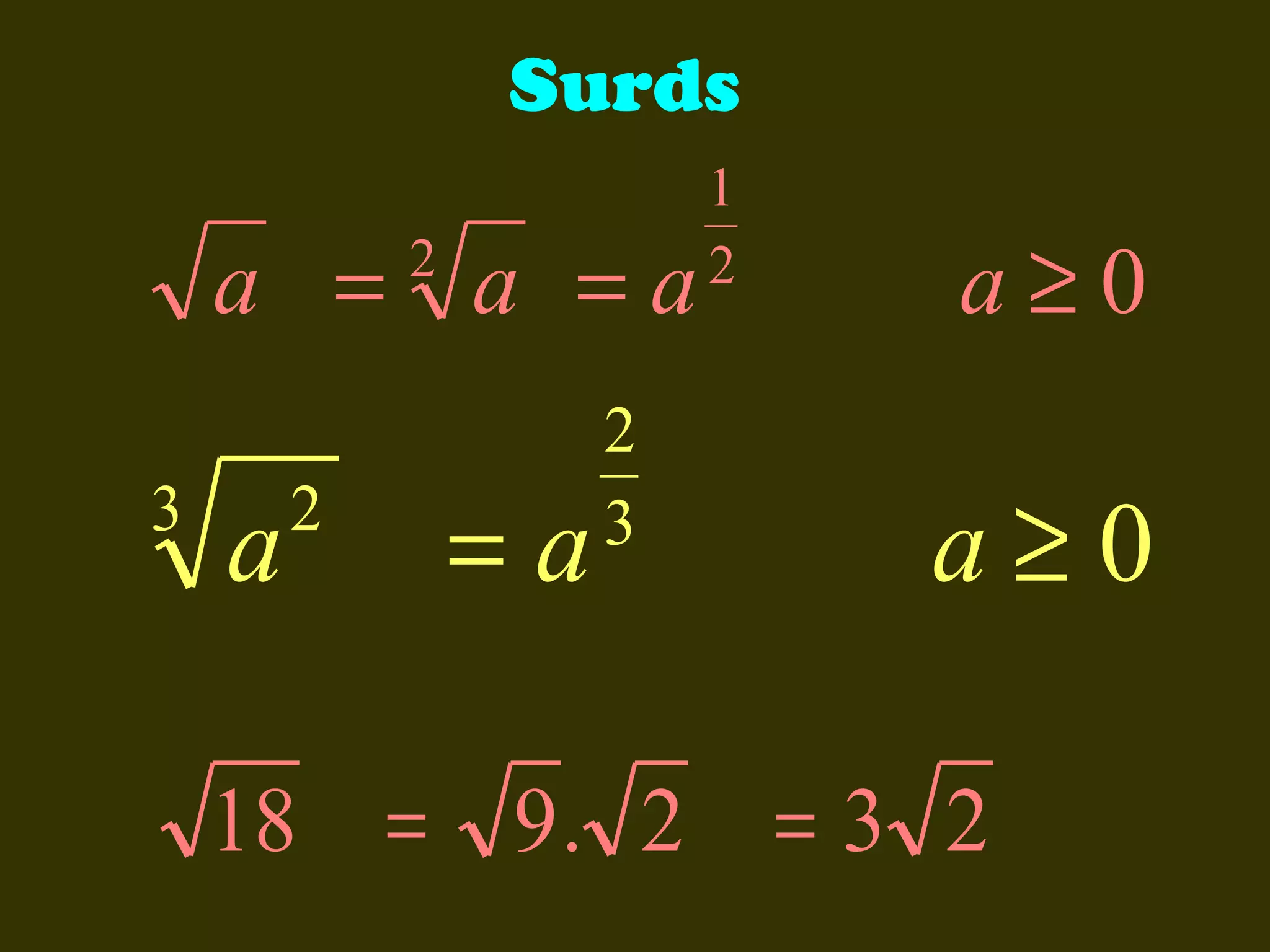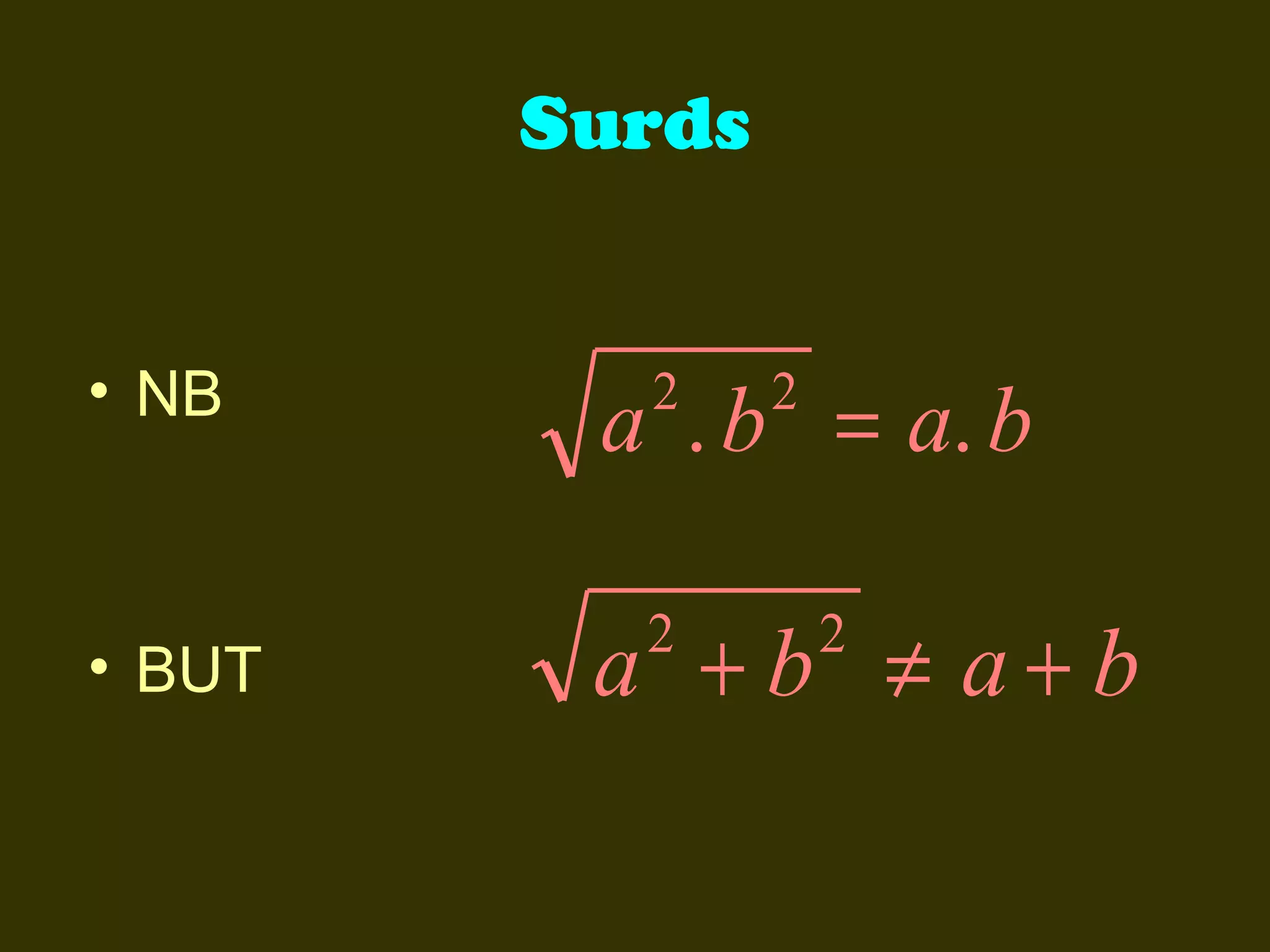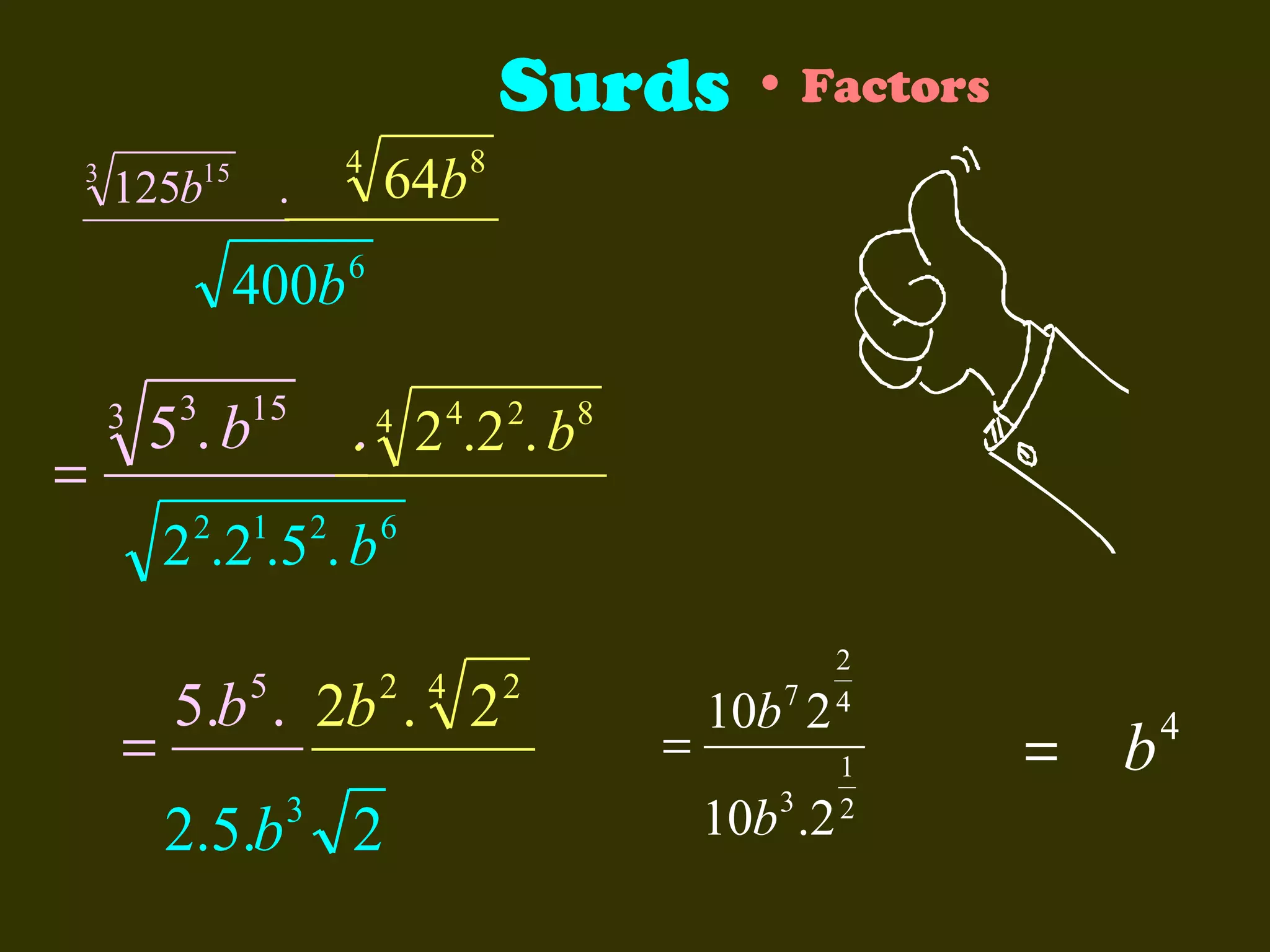This document discusses basic laws and properties of exponents and surds. It begins by defining exponential notation and discussing general cases and special cases of exponents. It then lists several basic laws of exponents, such as am+n = am × an, am/an = am-n, and an-n = a0 = 1. Similar laws are provided for operations involving surds. Examples are provided to illustrate each law. The document also covers simplifying expressions using exponents and surds through factorizing, splitting, and combining like terms. Acknowledgments are provided citing several sources the content was compiled from.